Sunday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P2058 - Hospital Outcomes in Patients With Coexisting Dieulafoy’s Lesion and Gastric Cancer: A Population-Based Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Wendy T. Garzon-Siatoya, MD
SBH Health System
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Wendy T. Garzon-Siatoya, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD2, Salomon Chamay, MD1, Khalid Aloum, MD1, Lisnaldy Ramirez, MD1, Ali Wakil, MD2, Camelia Ciobanu, MD2, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop Forlemu, MD3, Hamsika Moparty, MD4, Denzil Etienne, MD3, Nithan Narendra, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD3
1SBH Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Dieulafoy’s lesion (DL) is a life-threatening vascular anomaly characterized by an unusually large and tortuous artery, typically located along the lesser curvature of the proximal stomach. The coexistence of Dieulafoy’s lesion with gastric cancer (GC) is rare, with only a few cases documented in the literature. To date, no population-based studies have explored hospital outcomes in patients with both conditions. Using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database, we analyzed the characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized with this dual diagnosis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using the NIS database from 2016 to 2020. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10) codes were used to identify individuals aged 18 years and older with GC (including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, MALT lymphoma, carcinoid tumors, and stromal tumors) with and without DL. Demographic information, baseline characteristics, and outcomes—including mortality, hospital length of stay, total hospital charges, complications, and risk factors—were collected and analyzed. Statistical analysis was performed using the survey procedures function in STATA v.17. Categorical variables were compared using chi-square test, and continuous variables were compared using t-test. Significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results: Of 296,990 patients with GC, 125 had a concomitant diagnosis of DL. The prevalence of DL among patients diagnosed with GC was 0.04%. The mean age was 71.3 ± 2.7 years, with a predominance of males (52.0%) and White patients (48.0%). Inpatient mortality was 12.5%. Common comorbidities among DL patients included cardiac arrhythmias (40%), valvular disease (20%), peripheral vascular disease (20%), renal failure (28%), coagulopathy (36%), gastrointestinal bleeding (32%), and the need for blood transfusion (36%). Patients with GC and DL experienced a significant impact on hospital length of stay and costs, with an average length of stay of 11.4 days and a mean hospital cost of $143,398 (Table 1).
Discussion: The precise mechanism underlying the potential association between GC and DL remains uncertain. One proposed explanation suggests that vascular abnormalities associated with DL may lead to recurrent mucosal damage, such as erosions and ulcers, in the stomach lining. This repeated injury could trigger cycles of active regeneration and dysplasia, potentially accelerating the progression toward carcinogenesis.
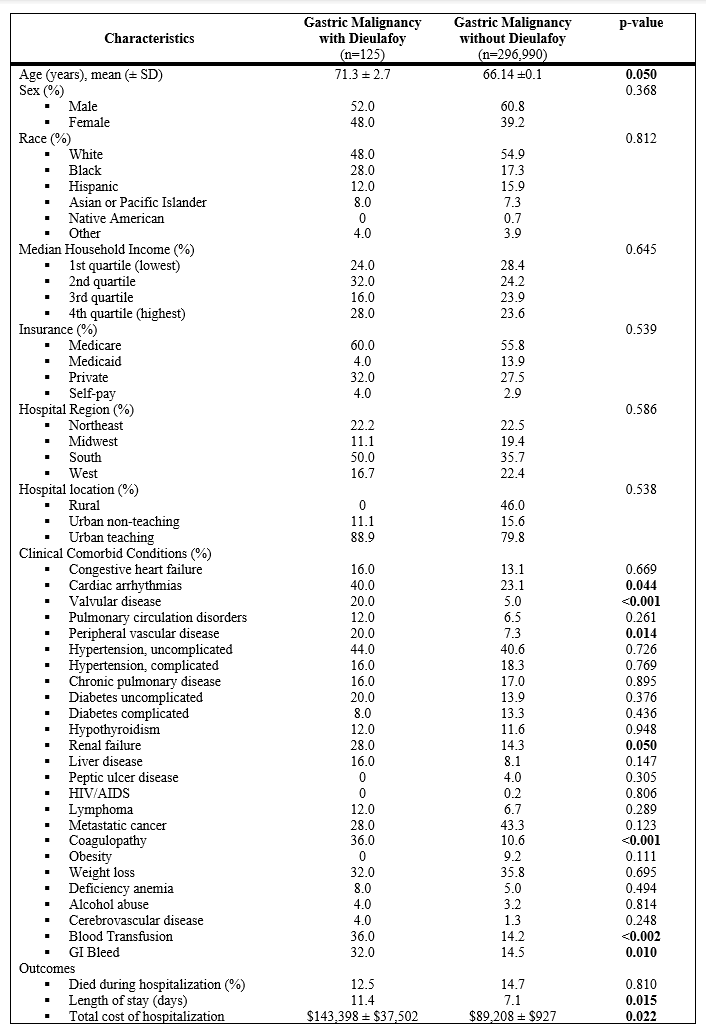
Figure: Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Sample
Disclosures:
Wendy Garzon-Siatoya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arnold Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salomon Chamay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Aloum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisnaldy Ramirez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Wakil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Camelia Ciobanu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamsika Moparty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denzil Etienne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nithan Narendra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhavi Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wendy T. Garzon-Siatoya, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD2, Salomon Chamay, MD1, Khalid Aloum, MD1, Lisnaldy Ramirez, MD1, Ali Wakil, MD2, Camelia Ciobanu, MD2, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop Forlemu, MD3, Hamsika Moparty, MD4, Denzil Etienne, MD3, Nithan Narendra, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD3. P2058 - Hospital Outcomes in Patients With Coexisting Dieulafoy’s Lesion and Gastric Cancer: A Population-Based Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1SBH Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Dieulafoy’s lesion (DL) is a life-threatening vascular anomaly characterized by an unusually large and tortuous artery, typically located along the lesser curvature of the proximal stomach. The coexistence of Dieulafoy’s lesion with gastric cancer (GC) is rare, with only a few cases documented in the literature. To date, no population-based studies have explored hospital outcomes in patients with both conditions. Using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database, we analyzed the characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized with this dual diagnosis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using the NIS database from 2016 to 2020. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10) codes were used to identify individuals aged 18 years and older with GC (including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, MALT lymphoma, carcinoid tumors, and stromal tumors) with and without DL. Demographic information, baseline characteristics, and outcomes—including mortality, hospital length of stay, total hospital charges, complications, and risk factors—were collected and analyzed. Statistical analysis was performed using the survey procedures function in STATA v.17. Categorical variables were compared using chi-square test, and continuous variables were compared using t-test. Significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results: Of 296,990 patients with GC, 125 had a concomitant diagnosis of DL. The prevalence of DL among patients diagnosed with GC was 0.04%. The mean age was 71.3 ± 2.7 years, with a predominance of males (52.0%) and White patients (48.0%). Inpatient mortality was 12.5%. Common comorbidities among DL patients included cardiac arrhythmias (40%), valvular disease (20%), peripheral vascular disease (20%), renal failure (28%), coagulopathy (36%), gastrointestinal bleeding (32%), and the need for blood transfusion (36%). Patients with GC and DL experienced a significant impact on hospital length of stay and costs, with an average length of stay of 11.4 days and a mean hospital cost of $143,398 (Table 1).
Discussion: The precise mechanism underlying the potential association between GC and DL remains uncertain. One proposed explanation suggests that vascular abnormalities associated with DL may lead to recurrent mucosal damage, such as erosions and ulcers, in the stomach lining. This repeated injury could trigger cycles of active regeneration and dysplasia, potentially accelerating the progression toward carcinogenesis.

Figure: Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Sample
Disclosures:
Wendy Garzon-Siatoya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arnold Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salomon Chamay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Aloum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisnaldy Ramirez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Wakil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Camelia Ciobanu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop Forlemu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamsika Moparty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denzil Etienne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nithan Narendra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhavi Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wendy T. Garzon-Siatoya, MD1, Arnold Forlemu, MD2, Salomon Chamay, MD1, Khalid Aloum, MD1, Lisnaldy Ramirez, MD1, Ali Wakil, MD2, Camelia Ciobanu, MD2, Raissa Nana Sede Mbakop Forlemu, MD3, Hamsika Moparty, MD4, Denzil Etienne, MD3, Nithan Narendra, MD1, Madhavi Reddy, MD3. P2058 - Hospital Outcomes in Patients With Coexisting Dieulafoy’s Lesion and Gastric Cancer: A Population-Based Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
