Sunday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P2057 - Safety and Efficacy of Camrelizumab Combined With Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Faryal Altaf, MD (she/her/hers)
BronxCare Health System
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmed Raza, 1, Faiza Fatima, MBBS1, Zain Sadiq, MBBS2, Fnu Kalpina, MBBS3, Muhammad Saffi Ullah, MBBS2, Mudasar Nisar, 1, Muhammad Ansab, 1, Mahnoor Fatima, MBBS4, Faryal Altaf, MD5, Zaheer Qureshi, MD6
1Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 6The Frank H. Netter M.D. School of Medicine at Quinnipiac University, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Gastric cancer (GC), with 1.1 million new cases and 769,000 deaths annually, is a significant global health burden. Camrelizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, combined with apatinib, a VEGFR-2 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor activity. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of this combination in advanced GC.
Methods: A literature search was conducted across PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, Scopus, and clinicaltrials.gov from inception till February 2025. 14 studies evaluating the safety and efficacy of camrelizumab plus apatinib for advanced GC were included. The analysis was conducted on RStudio v4.4.5. Pooled estimates were reported as proportions and 95% CI using the random effect model. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using I². Subgroup analysis was conducted based on treatment exposure.
Results: 564 patients from 14 studies were included in the analysis. The pooled 1-year overall survival (OS) from 8 studies was 61% (95% CI: 45–75; I² = 81.4%), with significantly higher OS of 74% (60–86; p = 0.0092; I² = 63.5%) in the treatment-naïve subgroup compared to the pretreated subgroup [45% (29–62; I² = 63.1%). The pooled 1-year progression-free survival was 22% (6–45; I² = 88.3%. 37% (95% CI: 0.26–0.49; I² = 0%) in the treatment-naïve and 14% (0–47; I² = 91.1%) in the previously treated patients, with no statistical difference between the subgroups (p = 0.1717). The objective response rate was 43% (29-57; I² = 86.2), also significantly higher in the treatment-naïve [55% (35–74); p = 0.0450; I² = 85.6%] versus previously treated patients [30% (17–44); I² = 78.4%]. The pooled disease control rate was 87% (75–95; I2 = 89.3%), also notably greater in the treatment-naïve subgroup with 94% (84–100; I² = 80.5%) compared to the previously treated subgroup at 74% (57–88; I² = 85.9%), with a statistically significant subgroup difference (p = 0.0226). Overall, treatment-naïve status was consistently associated with improved clinical outcomes across all efficacy endpoints.
Leukopenia (47%, 38–56), neutropenia (38%, 23–54), thrombocytopenia (35%, 24–48), AST elevation (32%, 19–47), ALT elevation (26%, 17–37), hand-foot syndrome (25%, 18–36), and hemangioma (25%, 18–36) were the most frequent adverse events.
Discussion: The combination of camrelizumab and apatinib demonstrates promising efficacy and manageable safety in advanced GC, particularly in treatment-naïve patients, offering a potential new treatment option for patients with limited therapeutic choices.
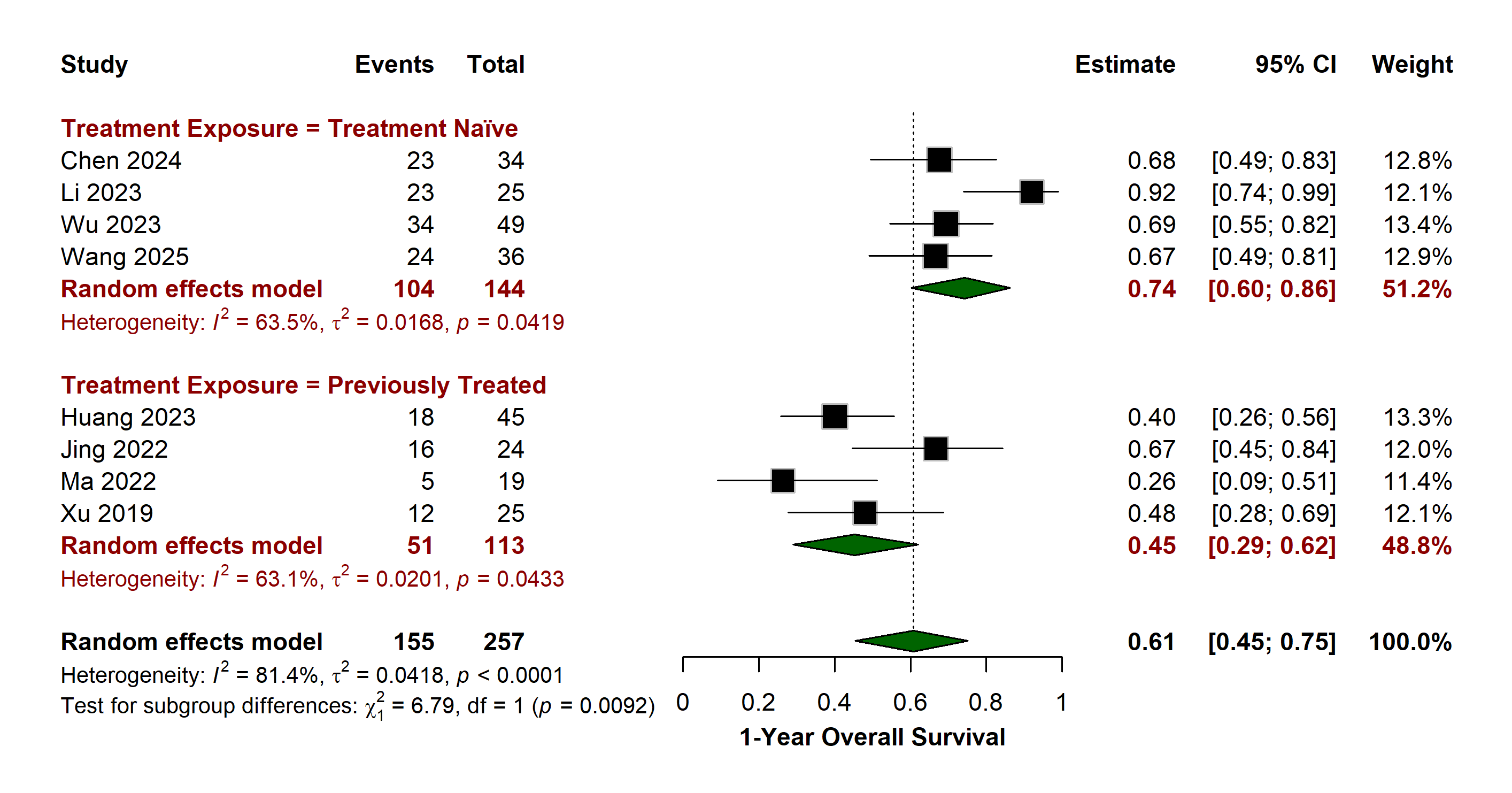
Figure: Forest Plot for 1-Year Overall Survival in Patients Receiving Camrelizumab plus Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer
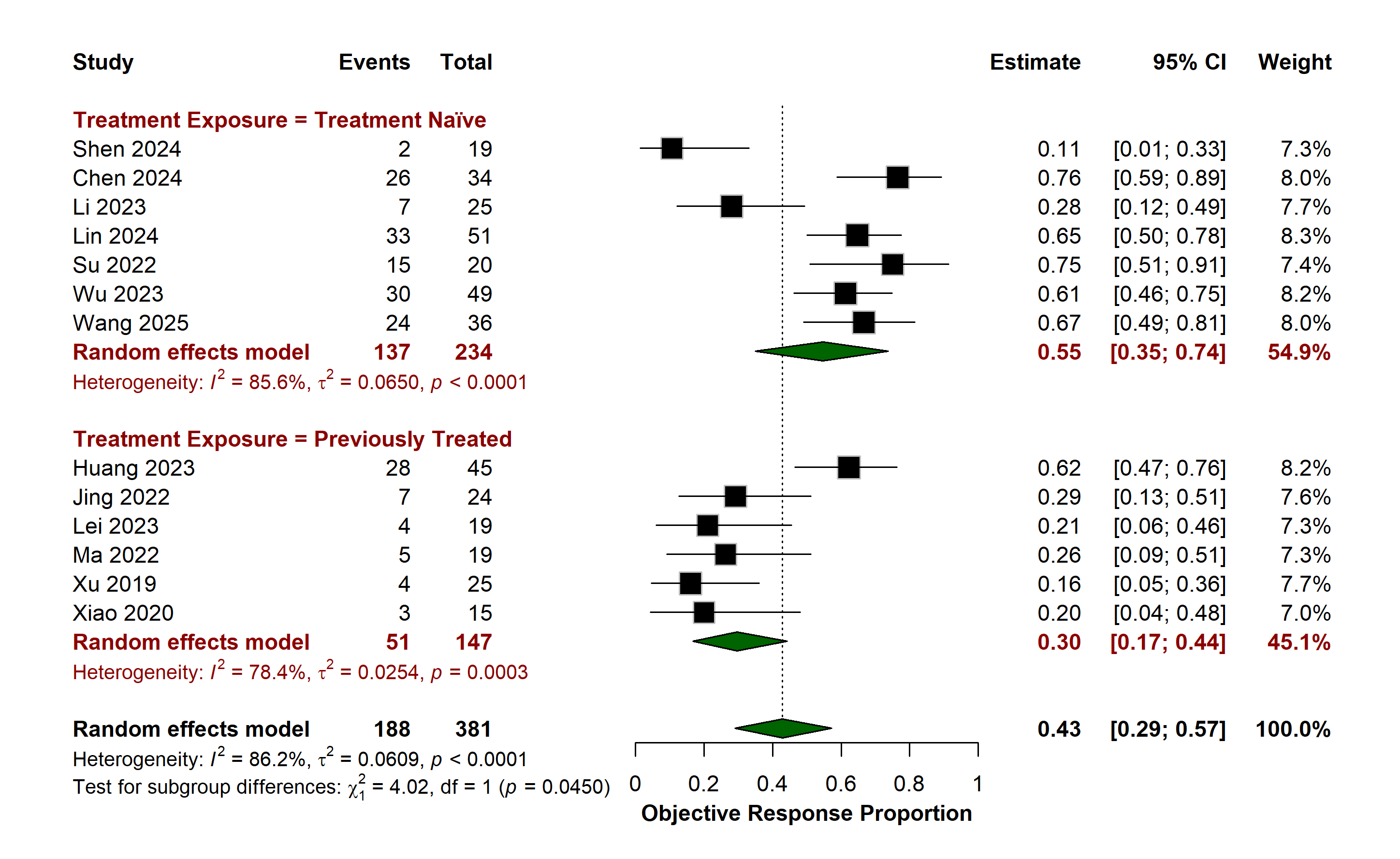
Figure: Forest Plot for Objective Response Rate in Patients Receiving Camrelizumab plus Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer
Disclosures:
Ahmed Raza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faiza Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Sadiq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Kalpina indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saffi Ullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mudasar Nisar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ansab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahnoor Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faryal Altaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zaheer Qureshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Raza, 1, Faiza Fatima, MBBS1, Zain Sadiq, MBBS2, Fnu Kalpina, MBBS3, Muhammad Saffi Ullah, MBBS2, Mudasar Nisar, 1, Muhammad Ansab, 1, Mahnoor Fatima, MBBS4, Faryal Altaf, MD5, Zaheer Qureshi, MD6. P2057 - Safety and Efficacy of Camrelizumab Combined With Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 6The Frank H. Netter M.D. School of Medicine at Quinnipiac University, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Gastric cancer (GC), with 1.1 million new cases and 769,000 deaths annually, is a significant global health burden. Camrelizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, combined with apatinib, a VEGFR-2 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor activity. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of this combination in advanced GC.
Methods: A literature search was conducted across PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, Scopus, and clinicaltrials.gov from inception till February 2025. 14 studies evaluating the safety and efficacy of camrelizumab plus apatinib for advanced GC were included. The analysis was conducted on RStudio v4.4.5. Pooled estimates were reported as proportions and 95% CI using the random effect model. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using I². Subgroup analysis was conducted based on treatment exposure.
Results: 564 patients from 14 studies were included in the analysis. The pooled 1-year overall survival (OS) from 8 studies was 61% (95% CI: 45–75; I² = 81.4%), with significantly higher OS of 74% (60–86; p = 0.0092; I² = 63.5%) in the treatment-naïve subgroup compared to the pretreated subgroup [45% (29–62; I² = 63.1%). The pooled 1-year progression-free survival was 22% (6–45; I² = 88.3%. 37% (95% CI: 0.26–0.49; I² = 0%) in the treatment-naïve and 14% (0–47; I² = 91.1%) in the previously treated patients, with no statistical difference between the subgroups (p = 0.1717). The objective response rate was 43% (29-57; I² = 86.2), also significantly higher in the treatment-naïve [55% (35–74); p = 0.0450; I² = 85.6%] versus previously treated patients [30% (17–44); I² = 78.4%]. The pooled disease control rate was 87% (75–95; I2 = 89.3%), also notably greater in the treatment-naïve subgroup with 94% (84–100; I² = 80.5%) compared to the previously treated subgroup at 74% (57–88; I² = 85.9%), with a statistically significant subgroup difference (p = 0.0226). Overall, treatment-naïve status was consistently associated with improved clinical outcomes across all efficacy endpoints.
Leukopenia (47%, 38–56), neutropenia (38%, 23–54), thrombocytopenia (35%, 24–48), AST elevation (32%, 19–47), ALT elevation (26%, 17–37), hand-foot syndrome (25%, 18–36), and hemangioma (25%, 18–36) were the most frequent adverse events.
Discussion: The combination of camrelizumab and apatinib demonstrates promising efficacy and manageable safety in advanced GC, particularly in treatment-naïve patients, offering a potential new treatment option for patients with limited therapeutic choices.

Figure: Forest Plot for 1-Year Overall Survival in Patients Receiving Camrelizumab plus Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer

Figure: Forest Plot for Objective Response Rate in Patients Receiving Camrelizumab plus Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer
Disclosures:
Ahmed Raza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faiza Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Sadiq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Kalpina indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saffi Ullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mudasar Nisar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ansab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahnoor Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faryal Altaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zaheer Qureshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Raza, 1, Faiza Fatima, MBBS1, Zain Sadiq, MBBS2, Fnu Kalpina, MBBS3, Muhammad Saffi Ullah, MBBS2, Mudasar Nisar, 1, Muhammad Ansab, 1, Mahnoor Fatima, MBBS4, Faryal Altaf, MD5, Zaheer Qureshi, MD6. P2057 - Safety and Efficacy of Camrelizumab Combined With Apatinib for Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
