Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2339 - When a Tumor Marker Lies: Liver Abscesses and Choledocholithiasis With Elevated CA 19-9 Imitating Pancreatic Cancer
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Erika Haviland, DO (she/her/hers)
Louisiana State University
New Orleans, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Erika Haviland, DO1, Chloe Spears, MD1, Hunter Hall, MD1, Stephen Landreneau, MD, FACG2
1Louisiana State University, New Orleans, LA; 2LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Liver abscesses are typically more common in males, with in-hospital mortality ranging from 2.5-19%, notably with a higher mortality rate when associated with biliary tract disease1. In one study, roughly 46% of patients had an elevation of Ca 19-9, but only 10% were profoundly elevated >10002. Very few cases have been documented of choledocholithiasis more than ten years post-cholecystectomy, and those are often associated with migrated clips.
Case Description/
Methods: We present a 61-year-old female with history of cholecystectomy 20 years prior who presented with right-sided abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting for two days with acute dysarthria and confusion. She was tachycardic and hypotensive, significant labs were a leukocytosis of 35,000 cells/uL, transaminitis with alanine transaminase (ALT) 215 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 175 U/L, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 125 U/L, and a total bilirubin 5.8 mg/dL. Notably, her CA 19-9 was 9,260. Computed tomography (CT) abdomen showed diffuse intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation without discrete downstream mass or obstructing stone and multiple ill-defined hypoattenuating lesions throughout the liver concerning for metastatic disease. However, Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showed a 1.3 cm filling defect in the distal common bile duct with upstream intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed frank pus from a biliary fistula near the major papilla, choledocholithiasis, and sludge that was swept from the duct. One 10 french x 7 cm plastic stent was placed. Blood cultures were positive for Klebsiella species. She was placed on broad-spectrum antibiotics, which continued for six weeks outpatient. Her confusion resolved quickly after antibiotics were started, and she remained at baseline. She had a successful repeat ERCP and biliary stent removal with resolution of CA 19-9 elevation.
Discussion: While initially concerning for metastases, our patient was found to have choledocholithiasis with resultant liver microabscesses successfully treated with ERCP and antibiotics. We highlight the importance of keeping choledocholithiasis on the differential in the setting of highly elevated tumor markers, hypoattenuating lesions on the liver, and even cases with cholecystectomies twenty years prior.
References:
Akhondi, H., & Sabih, D. E. (2023, July 3). Liver abscess. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538230/
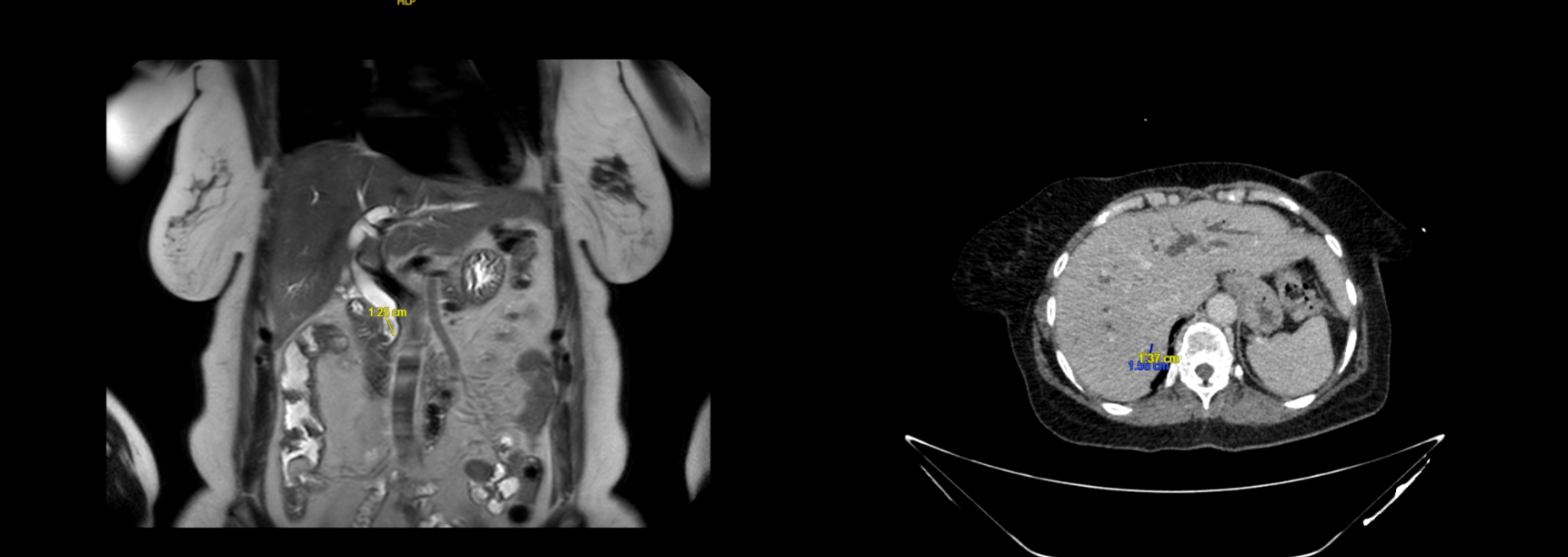
Figure: (left) MRI MRCP with 1.3cm filling defect within the distal common bile duct with upstream intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation. (right) Multiple hypo-attenuating lesions throughout the liver.
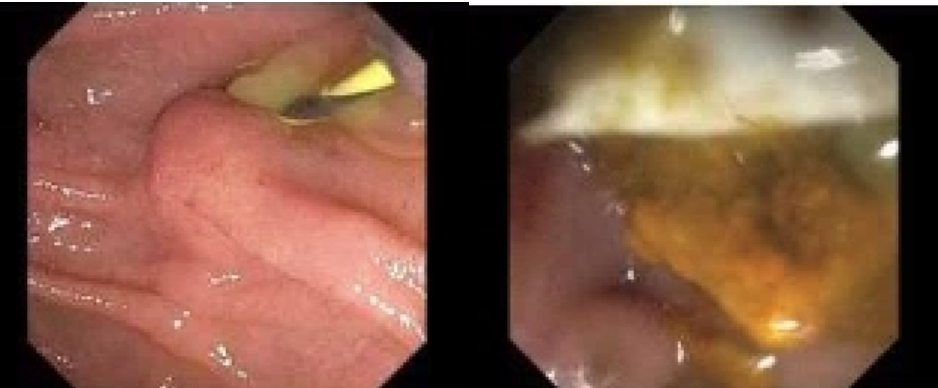
Figure: Large amount of purulence coming from the major duodenal papilla on ERCP (left) with bile duct stone and sludge (right).
Disclosures:
Erika Haviland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chloe Spears indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hunter Hall indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Landreneau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erika Haviland, DO1, Chloe Spears, MD1, Hunter Hall, MD1, Stephen Landreneau, MD, FACG2. P2339 - When a Tumor Marker Lies: Liver Abscesses and Choledocholithiasis With Elevated CA 19-9 Imitating Pancreatic Cancer, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Louisiana State University, New Orleans, LA; 2LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Liver abscesses are typically more common in males, with in-hospital mortality ranging from 2.5-19%, notably with a higher mortality rate when associated with biliary tract disease1. In one study, roughly 46% of patients had an elevation of Ca 19-9, but only 10% were profoundly elevated >10002. Very few cases have been documented of choledocholithiasis more than ten years post-cholecystectomy, and those are often associated with migrated clips.
Case Description/
Methods: We present a 61-year-old female with history of cholecystectomy 20 years prior who presented with right-sided abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting for two days with acute dysarthria and confusion. She was tachycardic and hypotensive, significant labs were a leukocytosis of 35,000 cells/uL, transaminitis with alanine transaminase (ALT) 215 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 175 U/L, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 125 U/L, and a total bilirubin 5.8 mg/dL. Notably, her CA 19-9 was 9,260. Computed tomography (CT) abdomen showed diffuse intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation without discrete downstream mass or obstructing stone and multiple ill-defined hypoattenuating lesions throughout the liver concerning for metastatic disease. However, Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showed a 1.3 cm filling defect in the distal common bile duct with upstream intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) revealed frank pus from a biliary fistula near the major papilla, choledocholithiasis, and sludge that was swept from the duct. One 10 french x 7 cm plastic stent was placed. Blood cultures were positive for Klebsiella species. She was placed on broad-spectrum antibiotics, which continued for six weeks outpatient. Her confusion resolved quickly after antibiotics were started, and she remained at baseline. She had a successful repeat ERCP and biliary stent removal with resolution of CA 19-9 elevation.
Discussion: While initially concerning for metastases, our patient was found to have choledocholithiasis with resultant liver microabscesses successfully treated with ERCP and antibiotics. We highlight the importance of keeping choledocholithiasis on the differential in the setting of highly elevated tumor markers, hypoattenuating lesions on the liver, and even cases with cholecystectomies twenty years prior.
References:
Akhondi, H., & Sabih, D. E. (2023, July 3). Liver abscess. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538230/

Figure: (left) MRI MRCP with 1.3cm filling defect within the distal common bile duct with upstream intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilatation. (right) Multiple hypo-attenuating lesions throughout the liver.

Figure: Large amount of purulence coming from the major duodenal papilla on ERCP (left) with bile duct stone and sludge (right).
Disclosures:
Erika Haviland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chloe Spears indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hunter Hall indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Landreneau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erika Haviland, DO1, Chloe Spears, MD1, Hunter Hall, MD1, Stephen Landreneau, MD, FACG2. P2339 - When a Tumor Marker Lies: Liver Abscesses and Choledocholithiasis With Elevated CA 19-9 Imitating Pancreatic Cancer, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
