Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P2458 - Drug Exposure and Microscopic Colitis: Analysis of a Large Multi-Institutional Research Network
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Muhammad Ahmad Bashir, MD, MBBS, BSc
West Virginia University
Morgantown, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Ahmad Bashir, MD, MBBS, BSc1, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Yousaf B. Hadi, MD1, Muhammad Saud Khalid, MBBS3
1West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 2GI and Hepatology - West Virginia University, West Virginia, VA; 3Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Microscopic colitis (MC) is increasing in incidence worldwide. While its etiology remains unclear, an association with various medications has been suggested, though large-scale data are limited. We aimed to determine the risk of MC in patients exposed to specific drugs within a large, multi-institutional healthcare database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX research network. Patients aged >18 years with no prior history of MC or inflammatory bowel disease undergoing colonoscopy with biopsy were included and divided into cohorts based on exposure to drugs of interest within 3 months prior to procedure. Control cohorts comprised patients with no prior exposure to the studied drug. After crude analysis, unexposed cohorts were propensity score-matched for age, gender, race, smoking status, and alcohol use for a propensity matched analysis. Primary outcome was diagnosis of MC following procedure.
Results: A total of 1,234,310 patients undergoing colonoscopy with biopsy were analyzed across the cohorts. Among major drug classes, SSRIs [RR 1.40(1.31-1.51)] and NSAIDs [RR 1.05 (1.01-1.11)] were noted to be significantly associated with increased risk of MC diagnosis. Highest risk among SSRIs was noted with Sertraline [RR 1.58 (1.39-1.79)] while Diclofenac was noted to have the highest risk among NSAIDs [RR 1.61 (1.41-1.84)]. Table 1.
As a class, PPIs were associated with a lower risk of MC diagnosis [RR 0.86 (0.80-0.91)] however Dexlansoprazole showed an independent increase in risk: RR 2.62 (1.38-4.95). H2 blocker use was noted to have no increased risk of MC diagnosis.
Statins were noted to be associated with a decreased risk of MC diagnosis: [RR 0.88 (0.84-0.93)]. Among Parkinson’s disease drugs, the combination agent Stalevo was noted to be associated with significant increase in risk. Table 1
Discussion: In this large cohort, we identified important associations between medication use and MC. SSRIs, particularly sertraline, and certain NSAIDs (diclofenac, celecoxib) were associated with highest increase in risk. Interestingly, overall use of statins, H2RAs, and PPIs showed no increase in risk, though specific drugs within these classes (e.g., dexlansoprazole) demonstrated an association. These findings add important data for identifying potential culprit agents in patients with MC and can help identify alternative medications from the same drug class if continued use is needed.
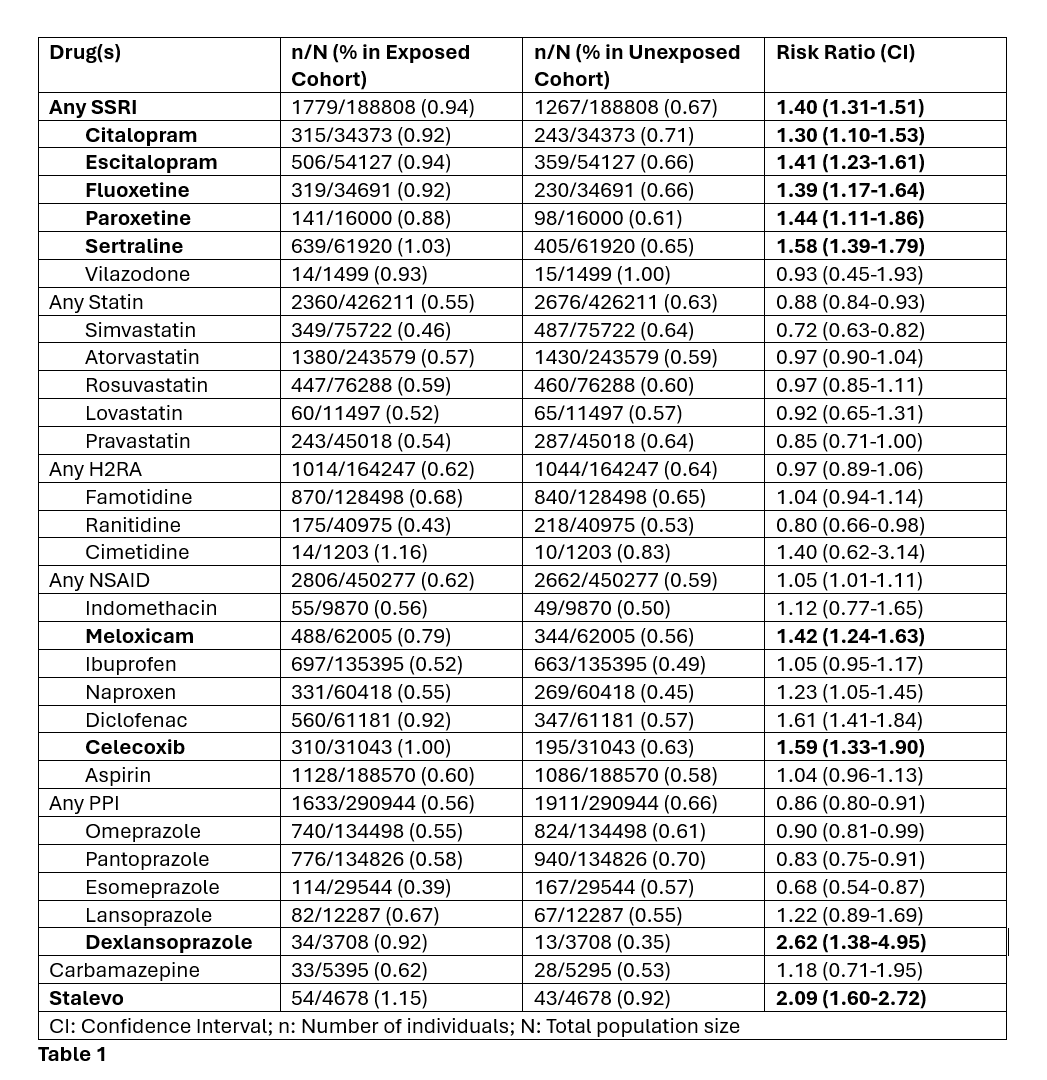
Figure: Table 1. Risk of MC with Drug Exposure: Propensity Score Matched Analysis
Disclosures:
Muhammad Ahmad Bashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swapna Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yousaf Hadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saud Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahmad Bashir, MD, MBBS, BSc1, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Yousaf B. Hadi, MD1, Muhammad Saud Khalid, MBBS3. P2458 - Drug Exposure and Microscopic Colitis: Analysis of a Large Multi-Institutional Research Network, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 2GI and Hepatology - West Virginia University, West Virginia, VA; 3Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Microscopic colitis (MC) is increasing in incidence worldwide. While its etiology remains unclear, an association with various medications has been suggested, though large-scale data are limited. We aimed to determine the risk of MC in patients exposed to specific drugs within a large, multi-institutional healthcare database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX research network. Patients aged >18 years with no prior history of MC or inflammatory bowel disease undergoing colonoscopy with biopsy were included and divided into cohorts based on exposure to drugs of interest within 3 months prior to procedure. Control cohorts comprised patients with no prior exposure to the studied drug. After crude analysis, unexposed cohorts were propensity score-matched for age, gender, race, smoking status, and alcohol use for a propensity matched analysis. Primary outcome was diagnosis of MC following procedure.
Results: A total of 1,234,310 patients undergoing colonoscopy with biopsy were analyzed across the cohorts. Among major drug classes, SSRIs [RR 1.40(1.31-1.51)] and NSAIDs [RR 1.05 (1.01-1.11)] were noted to be significantly associated with increased risk of MC diagnosis. Highest risk among SSRIs was noted with Sertraline [RR 1.58 (1.39-1.79)] while Diclofenac was noted to have the highest risk among NSAIDs [RR 1.61 (1.41-1.84)]. Table 1.
As a class, PPIs were associated with a lower risk of MC diagnosis [RR 0.86 (0.80-0.91)] however Dexlansoprazole showed an independent increase in risk: RR 2.62 (1.38-4.95). H2 blocker use was noted to have no increased risk of MC diagnosis.
Statins were noted to be associated with a decreased risk of MC diagnosis: [RR 0.88 (0.84-0.93)]. Among Parkinson’s disease drugs, the combination agent Stalevo was noted to be associated with significant increase in risk. Table 1
Discussion: In this large cohort, we identified important associations between medication use and MC. SSRIs, particularly sertraline, and certain NSAIDs (diclofenac, celecoxib) were associated with highest increase in risk. Interestingly, overall use of statins, H2RAs, and PPIs showed no increase in risk, though specific drugs within these classes (e.g., dexlansoprazole) demonstrated an association. These findings add important data for identifying potential culprit agents in patients with MC and can help identify alternative medications from the same drug class if continued use is needed.

Figure: Table 1. Risk of MC with Drug Exposure: Propensity Score Matched Analysis
Disclosures:
Muhammad Ahmad Bashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swapna Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yousaf Hadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saud Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahmad Bashir, MD, MBBS, BSc1, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Yousaf B. Hadi, MD1, Muhammad Saud Khalid, MBBS3. P2458 - Drug Exposure and Microscopic Colitis: Analysis of a Large Multi-Institutional Research Network, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
