Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P2534 - Incidental Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia on Routine Screening Colonoscopy
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Dimitri Melki, MD (he/him/his)
University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health
Windsor, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3
1University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Windsor, CT; 2University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, East Windsor, CT; 3University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Springfield, MA
Introduction: High-grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN 3) is a precancerous lesion most commonly diagnosed through anal cytology and anoscopy in high-risk populations with HPV or HIV. Its incidental detection during a routine colorectal cancer screening colonoscopy is rare and can have important clinical implications.
Case Description/
Methods: A 54-year-old woman with no significant past medical history underwent average-risk screening colonoscopy performed by a colorectal surgeon. Colonoscopy revealed two large, flat polyps in the ascending colon. Complete removal was not achieved. Pathology revealed both to be sessile serrated polyps (SSPs), so patient was referred to gastroenterology (GI) for re-attempt at removal.
On repeat colonoscopy by GI, two large polyps were removed, in addition to two smaller polyps. Near the end of the exam, when the colonoscope was retroflexed in the rectum to check for hemorrhoids, a 7 mm polyp was seen at the anal canal. The polyp was removed by hot snare following submucosal injection with Eleview. On pathology, high-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN 3) was noted. Patient was then referred back to colorectal surgery for management.
To note, patient had no known risk factors for AIN, such as history of HPV, immunosuppression, or high-risk sexual behavior.
Discussion: This case highlights the importance of careful rectal examination during colonoscopy, even in average-risk patients. AIN is often asymptomatic and can go unrecognized, particularly when lesions mimic benign polyps. While no standard guidelines exist for managing incidentally found AIN 3 in average-risk individuals, expert referral and close surveillance are recommended.
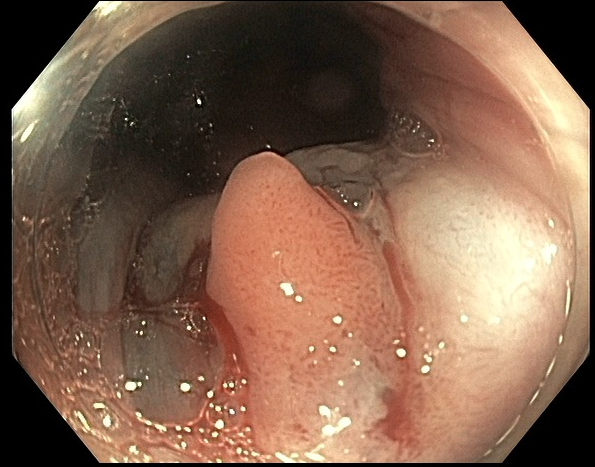
Figure: Polyp at anal canal
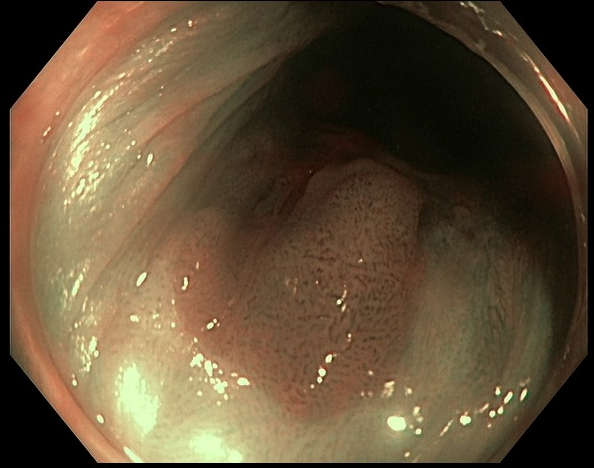
Figure: narrow band imaging of polyp at anal canal
Disclosures:
Dimitri Melki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Groudan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nha Duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3. P2534 - Incidental Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia on Routine Screening Colonoscopy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Windsor, CT; 2University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, East Windsor, CT; 3University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Springfield, MA
Introduction: High-grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN 3) is a precancerous lesion most commonly diagnosed through anal cytology and anoscopy in high-risk populations with HPV or HIV. Its incidental detection during a routine colorectal cancer screening colonoscopy is rare and can have important clinical implications.
Case Description/
Methods: A 54-year-old woman with no significant past medical history underwent average-risk screening colonoscopy performed by a colorectal surgeon. Colonoscopy revealed two large, flat polyps in the ascending colon. Complete removal was not achieved. Pathology revealed both to be sessile serrated polyps (SSPs), so patient was referred to gastroenterology (GI) for re-attempt at removal.
On repeat colonoscopy by GI, two large polyps were removed, in addition to two smaller polyps. Near the end of the exam, when the colonoscope was retroflexed in the rectum to check for hemorrhoids, a 7 mm polyp was seen at the anal canal. The polyp was removed by hot snare following submucosal injection with Eleview. On pathology, high-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN 3) was noted. Patient was then referred back to colorectal surgery for management.
To note, patient had no known risk factors for AIN, such as history of HPV, immunosuppression, or high-risk sexual behavior.
Discussion: This case highlights the importance of careful rectal examination during colonoscopy, even in average-risk patients. AIN is often asymptomatic and can go unrecognized, particularly when lesions mimic benign polyps. While no standard guidelines exist for managing incidentally found AIN 3 in average-risk individuals, expert referral and close surveillance are recommended.

Figure: Polyp at anal canal

Figure: narrow band imaging of polyp at anal canal
Disclosures:
Dimitri Melki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Groudan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nha Duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3. P2534 - Incidental Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia on Routine Screening Colonoscopy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
