Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P2625 - Role of Cell-Free DNA in Colorectal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpeg.jpg)
Ashiya Loomba, MBBS (she/her/hers)
Maharaja Agrasen Medical College
Karnal, Haryana, India
Presenting Author(s)
Ashiya Loomba, MBBS1, Jasmin Hundal, MD, DipABLM, MS, MPH2, Devendra Patel, MD3
1Maharaja Agrasen Medical College, Karnal, Haryana, India; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Saint Vincent Hospital, Erie, PA
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is globally the third most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related deaths. In 2025, it is estimated to cause 7.6% of all new cancer cases and 8.6% of all cancer deaths in the US. While colonoscopy remains the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening, its invasive nature makes compliance poor. Recently, circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) has gained attention as a less invasive modality for early detection of colorectal cancer.
Methods: This systematic review was conducted to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA from blood samples for early detection of CRC. Literature search was carried out on PUBMED and Cochrane Library for studies published between January 2020 and May 2025. After screening 29 studies for eligibility, 9 studies involving a total of 118639 participants were included. PRISMA guidelines were followed for screening and data extraction.
Results: Among 9 studies included, 6 focused on cfDNA and 3 addressed circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Five studied the methylation profiles including one focusing on HAND1 and SEPT9 gene, whereas three evaluated cfDNA fragmentation. Significant findings include 83% sensitivity and 90% specificity of cfDNA for diagnosing CRC. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) was an important biomarker with 72-91% area under curve (AUC) for detecting CRC, and hazard ratio of 3.3 on Kaplan-meier analysis. cfDNA fragmentation analysis revealed >90% sensitivity and upto 98% specificity for CRC detection. Studies focusing on ctDNA showed significantly higher median ctDNA concentration (p< 0.001) and higher methylation scores with more positive loci in CRC patients compared to the healthy population. 5hmC as a biomarker had 84% sensitivity and 92% specificity. HAND1 gene methylation was more promising with 93% sensitivity and 80% specificity, contrast to SEPT9 gene with 67% sensitivity and 87% specificity.
Discussion: Findings from this review underscore that cfDNA, along with epigenetic methylation and fragmentation analysis, is a promising non-invasive assay for early detection of CRC. While this could be an accurate test for CRC screening in future, extensive studies comparing it to existing modalities are needed. Fact that this non-invasive test can be beneficial for CRC screening in the underserved population, where cancer screening is still a question, needs further attention. (AI was used for grammar check).
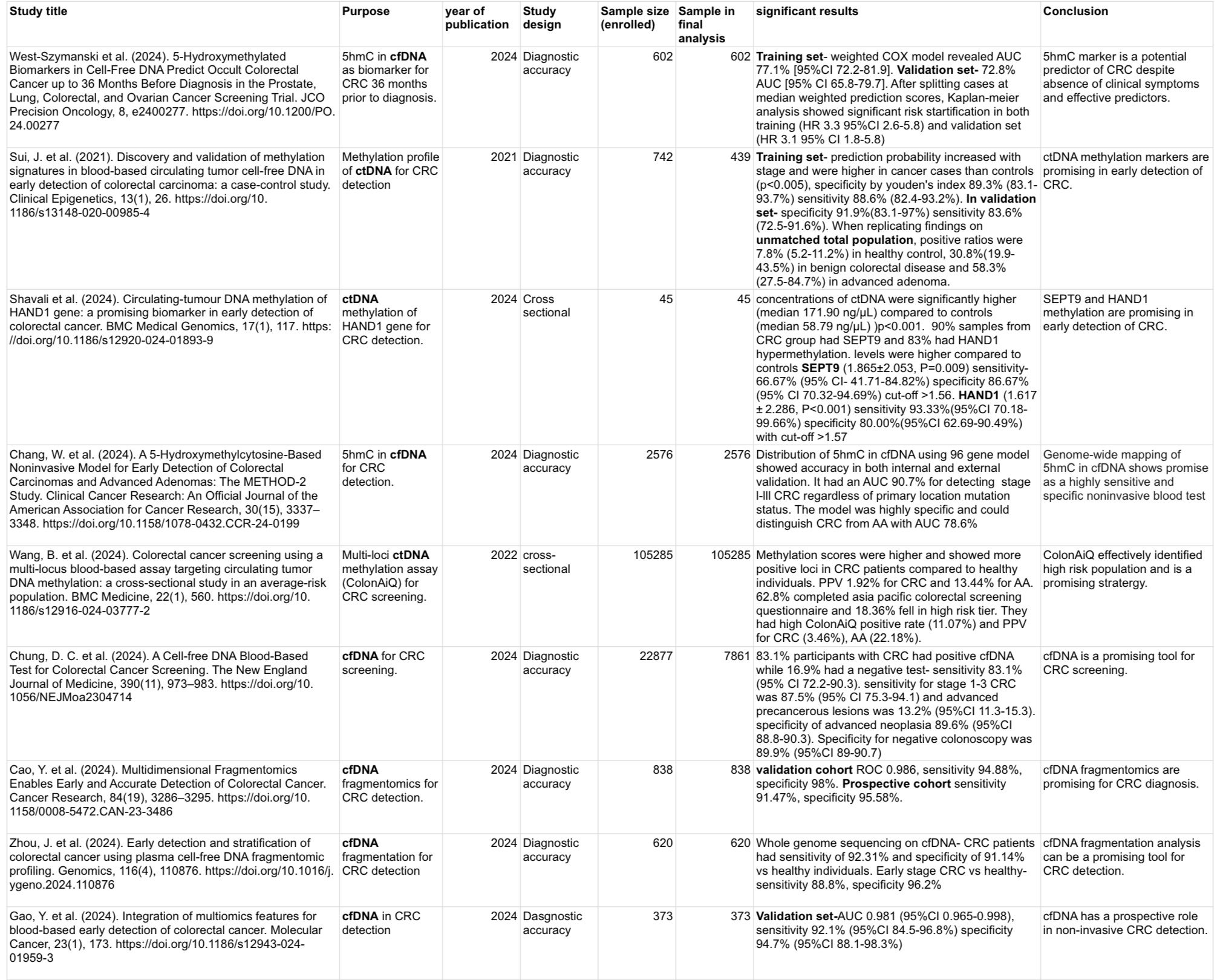
Figure: Diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA in colorectal cancer detection: data extracted from 9 studies.
Disclosures:
Ashiya Loomba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasmin Hundal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Devendra Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashiya Loomba, MBBS1, Jasmin Hundal, MD, DipABLM, MS, MPH2, Devendra Patel, MD3. P2625 - Role of Cell-Free DNA in Colorectal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Maharaja Agrasen Medical College, Karnal, Haryana, India; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Saint Vincent Hospital, Erie, PA
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is globally the third most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related deaths. In 2025, it is estimated to cause 7.6% of all new cancer cases and 8.6% of all cancer deaths in the US. While colonoscopy remains the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening, its invasive nature makes compliance poor. Recently, circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) has gained attention as a less invasive modality for early detection of colorectal cancer.
Methods: This systematic review was conducted to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA from blood samples for early detection of CRC. Literature search was carried out on PUBMED and Cochrane Library for studies published between January 2020 and May 2025. After screening 29 studies for eligibility, 9 studies involving a total of 118639 participants were included. PRISMA guidelines were followed for screening and data extraction.
Results: Among 9 studies included, 6 focused on cfDNA and 3 addressed circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Five studied the methylation profiles including one focusing on HAND1 and SEPT9 gene, whereas three evaluated cfDNA fragmentation. Significant findings include 83% sensitivity and 90% specificity of cfDNA for diagnosing CRC. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) was an important biomarker with 72-91% area under curve (AUC) for detecting CRC, and hazard ratio of 3.3 on Kaplan-meier analysis. cfDNA fragmentation analysis revealed >90% sensitivity and upto 98% specificity for CRC detection. Studies focusing on ctDNA showed significantly higher median ctDNA concentration (p< 0.001) and higher methylation scores with more positive loci in CRC patients compared to the healthy population. 5hmC as a biomarker had 84% sensitivity and 92% specificity. HAND1 gene methylation was more promising with 93% sensitivity and 80% specificity, contrast to SEPT9 gene with 67% sensitivity and 87% specificity.
Discussion: Findings from this review underscore that cfDNA, along with epigenetic methylation and fragmentation analysis, is a promising non-invasive assay for early detection of CRC. While this could be an accurate test for CRC screening in future, extensive studies comparing it to existing modalities are needed. Fact that this non-invasive test can be beneficial for CRC screening in the underserved population, where cancer screening is still a question, needs further attention. (AI was used for grammar check).

Figure: Diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA in colorectal cancer detection: data extracted from 9 studies.
Disclosures:
Ashiya Loomba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasmin Hundal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Devendra Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashiya Loomba, MBBS1, Jasmin Hundal, MD, DipABLM, MS, MPH2, Devendra Patel, MD3. P2625 - Role of Cell-Free DNA in Colorectal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
