Monday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P3026 - What Lies Among the Duodenal Folds: A Lymphangioma
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Nisar Amin, MD
Charleston Area Medical Center
Charleston, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Harleen Chela, MBBS, MD1, Nisar Amin, MD2, Ebubekir Daglilar, MD2
1West Virginia University Charleston Area Medical Center, South Charleston, WV; 2Charleston Area Medical Center, Charleston, WV
Introduction: Lymphangiomas are benign lesions that occur due to a malformation involving the lymphatic system and are not commonly encountered and are even more infrequent within the digestive tract. Within the gastrointestinal tract, the duodenum is an uncommon location for lymphangiomas and they are also rarely found in adults. We present a case of a duodenal lymphangioma found incidentally during upper endoscopy.
Case Description/
Methods: 67 year old male with past medical history of COPD on chronic oxygen at home, Atrial fibrillation, aortic bioprosthetic valve on warfarin, and hypertension was admitted with dyspnea, weakness and melena. Labs were remarkable for Hgb of 4.9 g/dl along with supratherapeutic INR of 6.75. Gastroenterology team was consulted and upper endoscopy was performed and unfortunately did not yield an explanation for the melena and showed only mild gastritis. In the second portion of the duodenum, a submucosal polypoid lesion about 2cm in size was seen with a yellowish overlying hue with whitish colored spots and positive pillow sign (Figures 1, 2 & 3). Biopsies were obtained and whitish exudate was seen exuding from it when biopsied. On histopathology, the biopsies revealed small bowel mucosa with focally dilated lacteals in lamina propria suggestive of a lymphangioma (Figure 4). Plan was for colonoscopy for evaluation of melena which was declined by patient at the time.
Discussion: Lymphangiomas are generally benign tumors that are most commonly encountered in locations such as the neck and the axilla. An obstruction of the lymphatic system is thought to be the underlying factor in the pathogenesis of these growths that does not communicate normally with the systemic lymphatics. Macroscopically, they appear as submucosal growths during endoscopy and can have overlying white spots that may suggest underlying chyle. Milky white material may be expressed once it is biopsied. Microscopically, they are characterized by dilated lymphatics in the submucosa and based on pathology, they are of three different types: capillary, cavernous, and cystic lymphangioma. They are often discovered incidentally and are asymptomatic, though they can be complicated by an infection, bleeding or fistula formation. Fortunately, in our patient this was an incidental finding without any consequences. Duodenal lymphangiomas are quite rare with only few cases described in the literature and this unexpected finding with unique features warrants awareness and recognition during endoscopy.
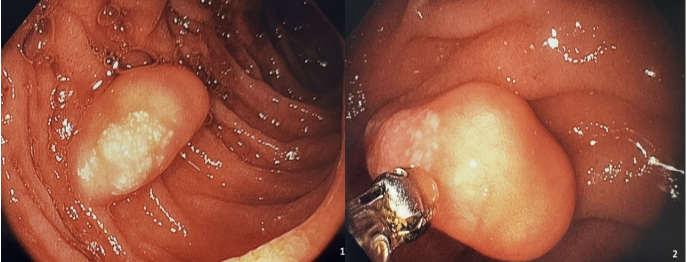
Figure: Figure 1: Second portion of duodenum with polypoid lesion with yellowish hue and overlying whitish colored spots.
Figure 2: Same duodenal lesion just prior to being biopsied.
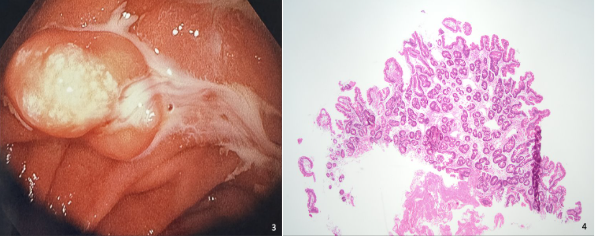
Figure: Figure 3: Whitish exudate merging from duodenal lesion upon being biopsied.
Figure 4: Histopathology image in hematoxylin and eosin stain duodenal mucosa with dilated lacteals (magnification 10x).
Disclosures:
Harleen Chela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nisar Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ebubekir Daglilar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harleen Chela, MBBS, MD1, Nisar Amin, MD2, Ebubekir Daglilar, MD2. P3026 - What Lies Among the Duodenal Folds: A Lymphangioma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1West Virginia University Charleston Area Medical Center, South Charleston, WV; 2Charleston Area Medical Center, Charleston, WV
Introduction: Lymphangiomas are benign lesions that occur due to a malformation involving the lymphatic system and are not commonly encountered and are even more infrequent within the digestive tract. Within the gastrointestinal tract, the duodenum is an uncommon location for lymphangiomas and they are also rarely found in adults. We present a case of a duodenal lymphangioma found incidentally during upper endoscopy.
Case Description/
Methods: 67 year old male with past medical history of COPD on chronic oxygen at home, Atrial fibrillation, aortic bioprosthetic valve on warfarin, and hypertension was admitted with dyspnea, weakness and melena. Labs were remarkable for Hgb of 4.9 g/dl along with supratherapeutic INR of 6.75. Gastroenterology team was consulted and upper endoscopy was performed and unfortunately did not yield an explanation for the melena and showed only mild gastritis. In the second portion of the duodenum, a submucosal polypoid lesion about 2cm in size was seen with a yellowish overlying hue with whitish colored spots and positive pillow sign (Figures 1, 2 & 3). Biopsies were obtained and whitish exudate was seen exuding from it when biopsied. On histopathology, the biopsies revealed small bowel mucosa with focally dilated lacteals in lamina propria suggestive of a lymphangioma (Figure 4). Plan was for colonoscopy for evaluation of melena which was declined by patient at the time.
Discussion: Lymphangiomas are generally benign tumors that are most commonly encountered in locations such as the neck and the axilla. An obstruction of the lymphatic system is thought to be the underlying factor in the pathogenesis of these growths that does not communicate normally with the systemic lymphatics. Macroscopically, they appear as submucosal growths during endoscopy and can have overlying white spots that may suggest underlying chyle. Milky white material may be expressed once it is biopsied. Microscopically, they are characterized by dilated lymphatics in the submucosa and based on pathology, they are of three different types: capillary, cavernous, and cystic lymphangioma. They are often discovered incidentally and are asymptomatic, though they can be complicated by an infection, bleeding or fistula formation. Fortunately, in our patient this was an incidental finding without any consequences. Duodenal lymphangiomas are quite rare with only few cases described in the literature and this unexpected finding with unique features warrants awareness and recognition during endoscopy.

Figure: Figure 1: Second portion of duodenum with polypoid lesion with yellowish hue and overlying whitish colored spots.
Figure 2: Same duodenal lesion just prior to being biopsied.

Figure: Figure 3: Whitish exudate merging from duodenal lesion upon being biopsied.
Figure 4: Histopathology image in hematoxylin and eosin stain duodenal mucosa with dilated lacteals (magnification 10x).
Disclosures:
Harleen Chela indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nisar Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ebubekir Daglilar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harleen Chela, MBBS, MD1, Nisar Amin, MD2, Ebubekir Daglilar, MD2. P3026 - What Lies Among the Duodenal Folds: A Lymphangioma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
