Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3551 - Efficacy and Safety of LAMS for Benign Duodenal Strictures: A Retrospective Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Sufiyan Kamal, MD
University of Texas Health East Texas Physicians
Tyler, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Sufiyan Kamal, MD1, Layth H. Alzubaidy, MD2, Omer Chowdhury, DO1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1
1University of Texas Health East Texas Physicians, Tyler, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center at Tyler, Tyler, TX
Introduction: Duodenal strictures, resulting from both benign and malignant etiologies, can negatively affect patients' quality of life and cause morbidity. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) are increasingly utilized in the management of GI strictures as traditional management options were associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. However, real-world data regarding symptom resolution, clinical efficacy, technical adjuncts such as fluoroscopy, balloon dilatation, safety, and stent migration rates remain limited.
Methods: A retrospective review was performed at a single center involving 9 patients who underwent LAMS placement for the treatment of benign duodenal strictures. The successful placement of the LAMS across the duodenal stricture without any immediate procedural issues was considered a technical success. Symptom resolution after stent implantation was considered a clinical success. Demographic factors, indication, platelet count, use of fluoroscopy, balloon dilatation, symptom resolution, immediate complications, stent migration within 30 days, stent fixation, and anticoagulation use were studied.
Results: This retrospective study included 9 patients with a mean age of 63.2 ± 16.8 years. All patients were managed for benign duodenal sweep strictures (100%). AXIOS stents were used in all cases (100%), with the majority (8 out of 9, or 88.9%) receiving 20mm x 10mm stents and 15mm x 10mm stents in 11.1% (1/9) of patients. In about a third of the cases (3 patients), additional stent fixation was performed. A history of prior stricture dilation was documented in 44.4% (4/9) of patients. Technical success was achieved in 100% (9/9) of patients with successful stent placement. Clinical success was seen in 7 patients (77.8%). No immediate complications were reported (100%). Within 30 days, 2 patients (22.2%) were readmitted, but there were no reports of stent migration.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that LAMS placement for duodenal strictures achieves excellent technical success with a favorable safety profile and a 77.8% symptom resolution rate. The absence of immediate complications and stent migration within 30 days supports the safety of this approach. Our study shows that fluoroscopy and balloon dilation may improve procedural outcomes, and stent fixation may reduce stent migration risk. Further larger sample size prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings.
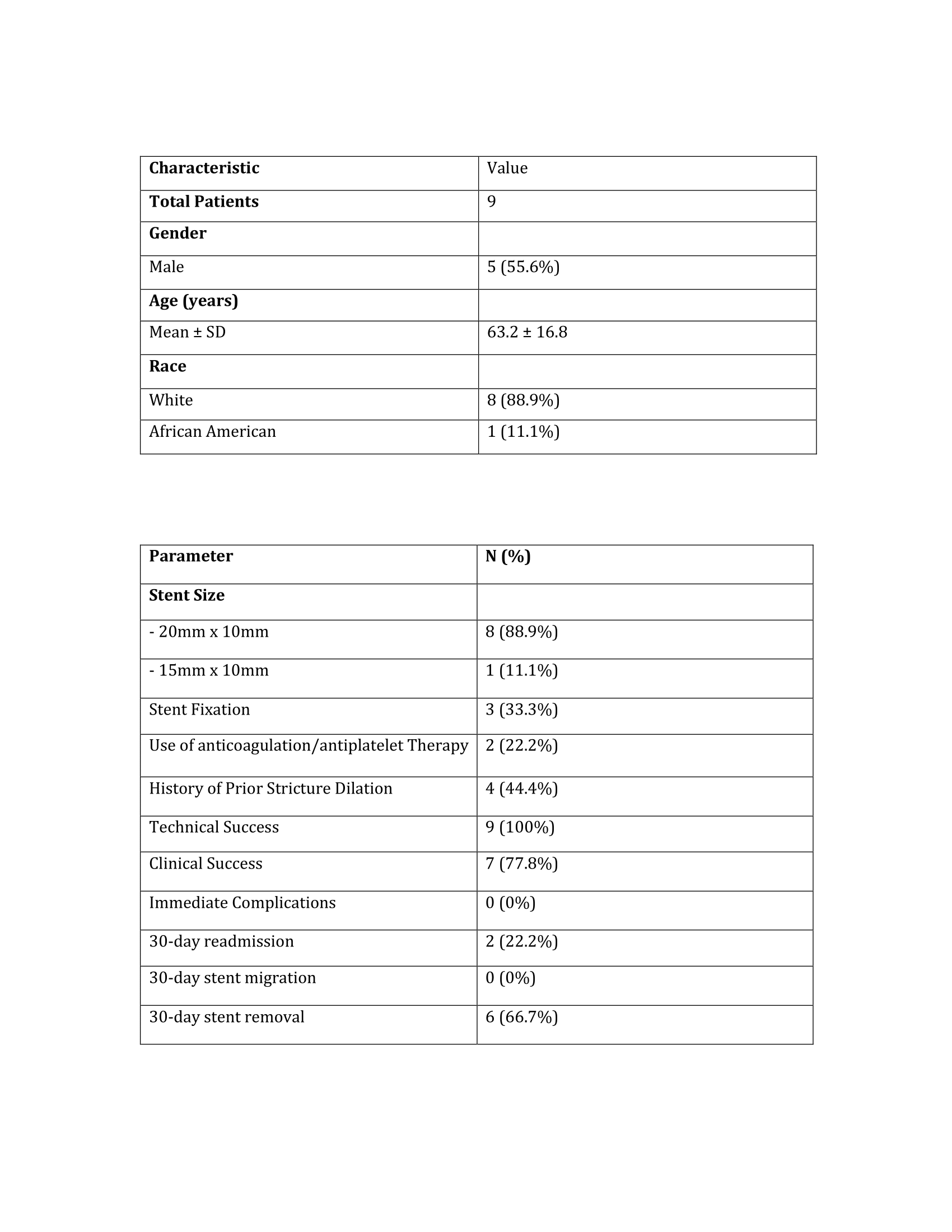
Figure: Table 1: Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics.
Table 2: Procedural Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes
Disclosures:
Sufiyan Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Layth Alzubaidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Chowdhury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Majeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sufiyan Kamal, MD1, Layth H. Alzubaidy, MD2, Omer Chowdhury, DO1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1. P3551 - Efficacy and Safety of LAMS for Benign Duodenal Strictures: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health East Texas Physicians, Tyler, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center at Tyler, Tyler, TX
Introduction: Duodenal strictures, resulting from both benign and malignant etiologies, can negatively affect patients' quality of life and cause morbidity. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) are increasingly utilized in the management of GI strictures as traditional management options were associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. However, real-world data regarding symptom resolution, clinical efficacy, technical adjuncts such as fluoroscopy, balloon dilatation, safety, and stent migration rates remain limited.
Methods: A retrospective review was performed at a single center involving 9 patients who underwent LAMS placement for the treatment of benign duodenal strictures. The successful placement of the LAMS across the duodenal stricture without any immediate procedural issues was considered a technical success. Symptom resolution after stent implantation was considered a clinical success. Demographic factors, indication, platelet count, use of fluoroscopy, balloon dilatation, symptom resolution, immediate complications, stent migration within 30 days, stent fixation, and anticoagulation use were studied.
Results: This retrospective study included 9 patients with a mean age of 63.2 ± 16.8 years. All patients were managed for benign duodenal sweep strictures (100%). AXIOS stents were used in all cases (100%), with the majority (8 out of 9, or 88.9%) receiving 20mm x 10mm stents and 15mm x 10mm stents in 11.1% (1/9) of patients. In about a third of the cases (3 patients), additional stent fixation was performed. A history of prior stricture dilation was documented in 44.4% (4/9) of patients. Technical success was achieved in 100% (9/9) of patients with successful stent placement. Clinical success was seen in 7 patients (77.8%). No immediate complications were reported (100%). Within 30 days, 2 patients (22.2%) were readmitted, but there were no reports of stent migration.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that LAMS placement for duodenal strictures achieves excellent technical success with a favorable safety profile and a 77.8% symptom resolution rate. The absence of immediate complications and stent migration within 30 days supports the safety of this approach. Our study shows that fluoroscopy and balloon dilation may improve procedural outcomes, and stent fixation may reduce stent migration risk. Further larger sample size prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings.

Figure: Table 1: Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics.
Table 2: Procedural Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes
Disclosures:
Sufiyan Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Layth Alzubaidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Chowdhury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Majeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sufiyan Kamal, MD1, Layth H. Alzubaidy, MD2, Omer Chowdhury, DO1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1. P3551 - Efficacy and Safety of LAMS for Benign Duodenal Strictures: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
