Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3546 - Comparing Different Endoscopic Treatments in the Management of Small Colorectal Polyps: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ammad Javaid Chaudhary, MD
Henry Ford Health
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Hafsa Shahid, MBBS7, Muhammad Shahzil, MBBS8, Usman Bin Hameed, MD9, Samreen Zafar, MD10, Mazen Elatrache, MD1, Sumit Singla, MD1, Tobias Zuchelli, 11
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 7Brigham and Women's Hospital, Detroit, MI; 8Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Detroit, MI; 9Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI; 10Lake Huron Medical Center, Port Huron, MI; 11Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Small colorectal polyps are commonly detected during routine screening and may pose a risk for colorectal cancer if left untreated. Various endoscopic treatments are available for their management, but these approaches' relative efficacy and safety remain unclear. This network meta-analysis aims to compare the effectiveness of different endoscopic treatments for small colorectal polyps, providing comprehensive insights to guide clinical decision-making.
Methods: PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect were comprehensively searched from inception until January 2025 for studies comparing endoscopic interventions for small colorectal polyps (< 10mm). This review followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. A frequentist network meta-analysis was performed using R version 4.2.1 and employing the “netmeta” package. Risk Ratios (RR) and 95% Confidence interval (CI) were pooled using the random effects model for dichotomous outcomes. The relative ranking of the interventions for various outcomes was estimated using the p-scores. The studies were evaluated for quality with the Cochrane Rob 2 tool, while publication bias was assessed through funnel plots and Egger’s regression test.
Results: Thirty-three RCTS were included in this systematic review and network meta-analysis. Compared to CSP, both underwater Cold snare polypectomy (U-CSP) (RR=1.44,95% CI: [1.16, 1.77]) and hot snare endoscopic mucosal resection (HS-EMR) (RR=1.15, 95% CI: [1.01,1.32]) significantly increased the rate of complete histological resection and U-CSP showed the highest rate (p-score=0.99). Regarding immediate bleeding, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was ranked as the best treatment (0.94), and jumbo forceps polypectomy (JFP) as the worst (p-score=0.22). The risk of delayed bleeding was lowest in the underwater EMR (U-EMR) group (p-score=0.83) and highest in the hot snare polypectomy (HSP) group (p-score=0.08).
Discussion: U-CSP demonstrated the highest rate of complete histological resection, while U-EMR had the lowest risk of delayed bleeding, making them the most effective and safest interventions, respectively. These findings provide evidence-based guidance for selecting optimal endoscopic treatments for small colorectal polyps.
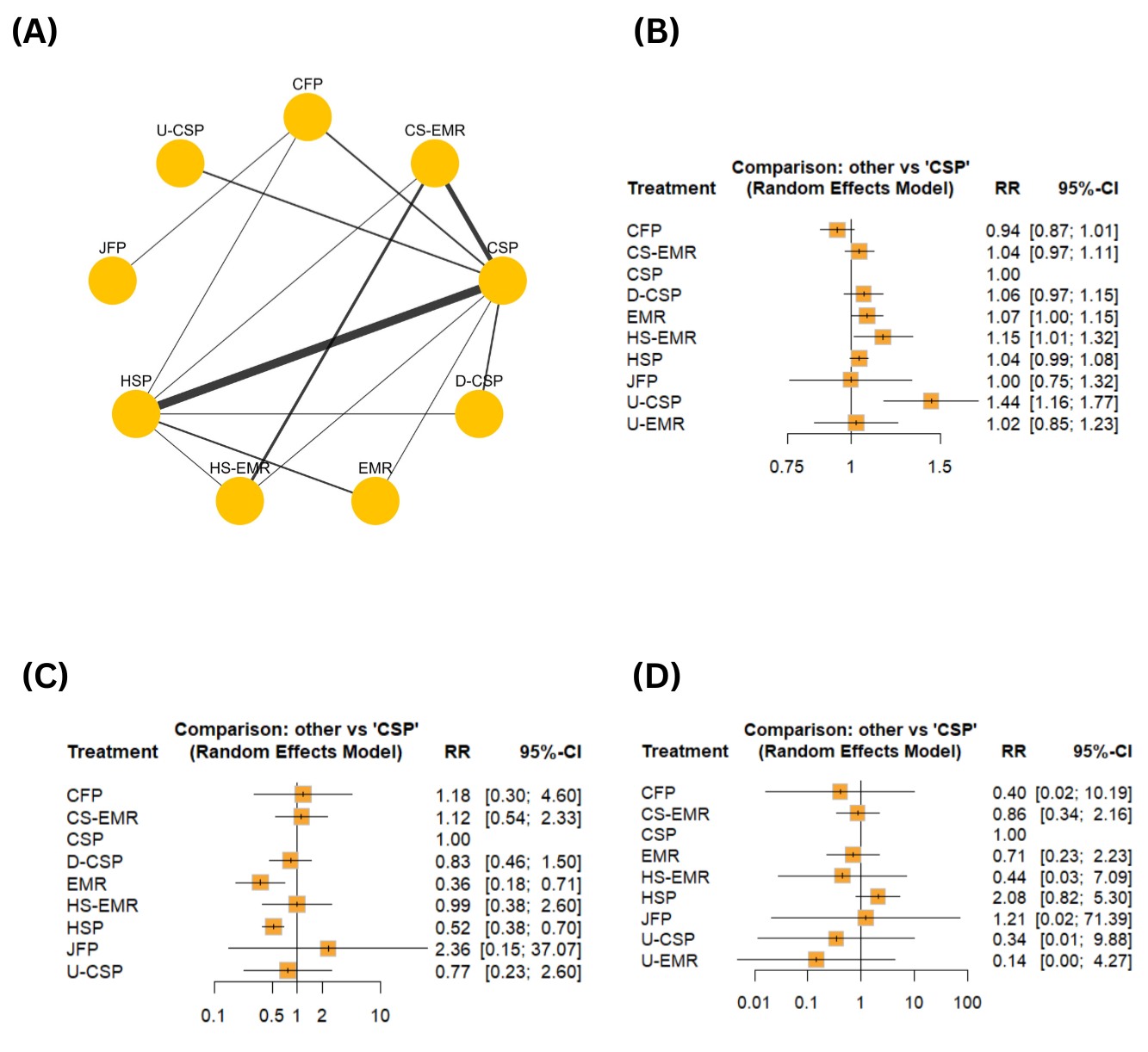
Figure: Figure 1: (A)Network Graph for Complete Histologic Resection (B)Forest Plot for Complete Histologic Resection (C)Forest Plot for Immediate Bleeding (D)Forest Plot Delayed Bleeding
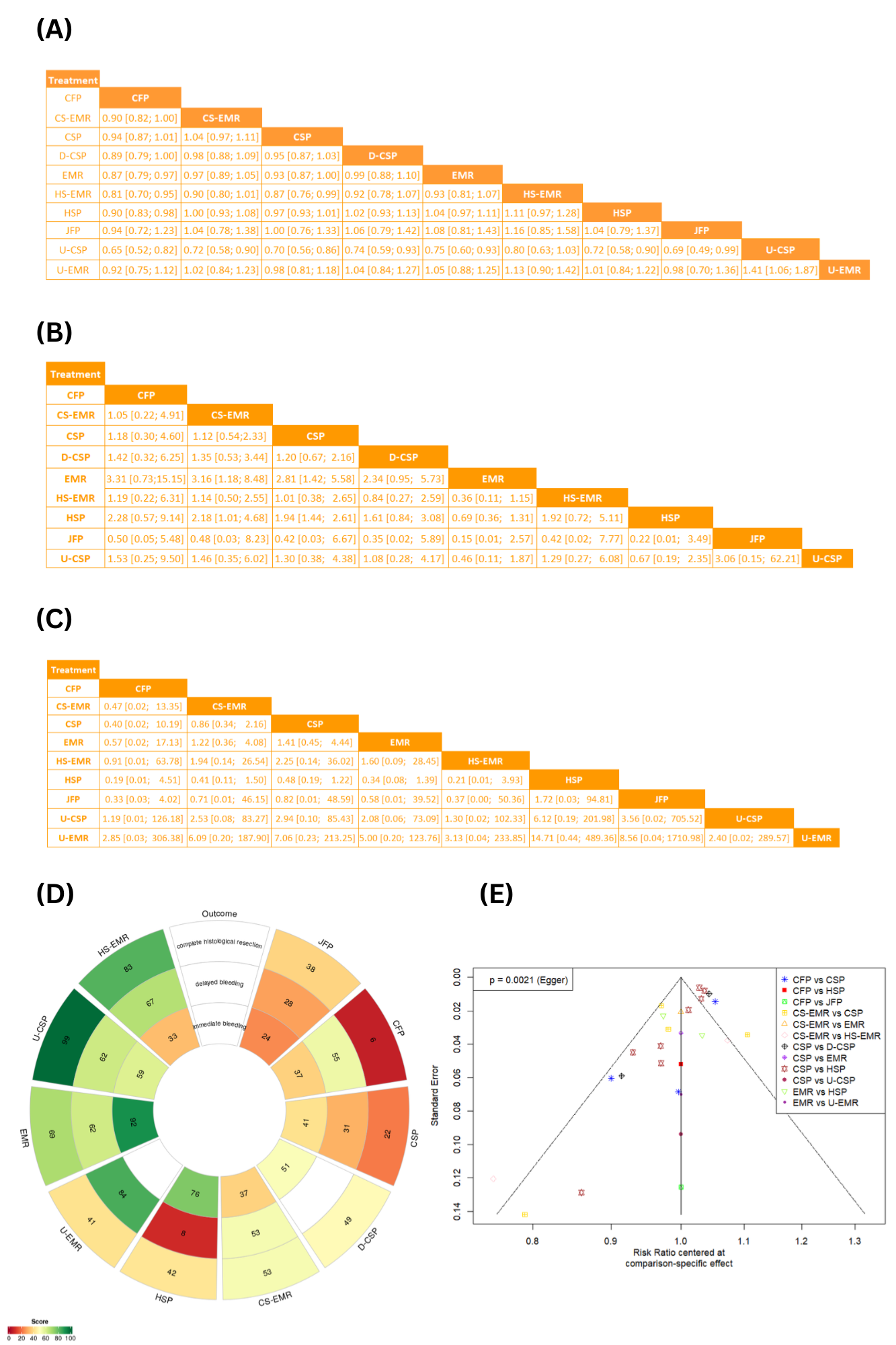
Figure: Figure 2: (A)League Table for Complete Histologic Resection (B)League Table for Immediate Bleeding (C)League Table for Delayed Bleeding (D)Rank-Heat Plot for Treatment Ranking According to P-scores (E)Funnel Plot for Complete Histologic Resection
Disclosures:
Ammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafsa Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shahzil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usman Bin Hameed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazen Elatrache indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumit Singla: Boston Scientific. – Consultant.
Tobias Zuchelli: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Hafsa Shahid, MBBS7, Muhammad Shahzil, MBBS8, Usman Bin Hameed, MD9, Samreen Zafar, MD10, Mazen Elatrache, MD1, Sumit Singla, MD1, Tobias Zuchelli, 11. P3546 - Comparing Different Endoscopic Treatments in the Management of Small Colorectal Polyps: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 7Brigham and Women's Hospital, Detroit, MI; 8Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Detroit, MI; 9Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI; 10Lake Huron Medical Center, Port Huron, MI; 11Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Small colorectal polyps are commonly detected during routine screening and may pose a risk for colorectal cancer if left untreated. Various endoscopic treatments are available for their management, but these approaches' relative efficacy and safety remain unclear. This network meta-analysis aims to compare the effectiveness of different endoscopic treatments for small colorectal polyps, providing comprehensive insights to guide clinical decision-making.
Methods: PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect were comprehensively searched from inception until January 2025 for studies comparing endoscopic interventions for small colorectal polyps (< 10mm). This review followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. A frequentist network meta-analysis was performed using R version 4.2.1 and employing the “netmeta” package. Risk Ratios (RR) and 95% Confidence interval (CI) were pooled using the random effects model for dichotomous outcomes. The relative ranking of the interventions for various outcomes was estimated using the p-scores. The studies were evaluated for quality with the Cochrane Rob 2 tool, while publication bias was assessed through funnel plots and Egger’s regression test.
Results: Thirty-three RCTS were included in this systematic review and network meta-analysis. Compared to CSP, both underwater Cold snare polypectomy (U-CSP) (RR=1.44,95% CI: [1.16, 1.77]) and hot snare endoscopic mucosal resection (HS-EMR) (RR=1.15, 95% CI: [1.01,1.32]) significantly increased the rate of complete histological resection and U-CSP showed the highest rate (p-score=0.99). Regarding immediate bleeding, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was ranked as the best treatment (0.94), and jumbo forceps polypectomy (JFP) as the worst (p-score=0.22). The risk of delayed bleeding was lowest in the underwater EMR (U-EMR) group (p-score=0.83) and highest in the hot snare polypectomy (HSP) group (p-score=0.08).
Discussion: U-CSP demonstrated the highest rate of complete histological resection, while U-EMR had the lowest risk of delayed bleeding, making them the most effective and safest interventions, respectively. These findings provide evidence-based guidance for selecting optimal endoscopic treatments for small colorectal polyps.

Figure: Figure 1: (A)Network Graph for Complete Histologic Resection (B)Forest Plot for Complete Histologic Resection (C)Forest Plot for Immediate Bleeding (D)Forest Plot Delayed Bleeding

Figure: Figure 2: (A)League Table for Complete Histologic Resection (B)League Table for Immediate Bleeding (C)League Table for Delayed Bleeding (D)Rank-Heat Plot for Treatment Ranking According to P-scores (E)Funnel Plot for Complete Histologic Resection
Disclosures:
Ammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafsa Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shahzil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usman Bin Hameed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazen Elatrache indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumit Singla: Boston Scientific. – Consultant.
Tobias Zuchelli: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Hafsa Shahid, MBBS7, Muhammad Shahzil, MBBS8, Usman Bin Hameed, MD9, Samreen Zafar, MD10, Mazen Elatrache, MD1, Sumit Singla, MD1, Tobias Zuchelli, 11. P3546 - Comparing Different Endoscopic Treatments in the Management of Small Colorectal Polyps: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
