Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3646 - Real-World Comparative Outcomes of Nivolumab + Ipilimumab versus Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A TriNetx Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Sameh Gomaa, MD
Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health
Phoenixville, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2
1Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health, Phoenixville, PA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Needham, MA
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer related death. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab (ATZ+BEV) has transformed the treatment landscape for advanced HCC and now a first-line option following the IMbrave150 trial. The Checkmate 040 randomized controlled trial has shown Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) has improved long-term survival benefit. This study aims to compare outcomes of both treatment modalities for advanced HCC.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX database. Criteria included adult patients >18 years of age with Advanced HCC recently initiating (ATZ+BEV) or (NIVO+IPI). Outcomes include overall survival, most recent AFP, AST, ALT, Bilirubin, INR, and Platelet count levels. Time to AFP to reach 0-40 ng/ml. Risk of developing hepatic encephalopathy or coma, hospitalization, and adverse events. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed for demographics, lab results, MELD and ECOG scores, and confounding comorbidities. Results were expressed as risk difference (RD) with 95% CI. Time to event endpoints using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models reported as hazard ratio (HR) and log-rank P values.
Results: After matching, the cohort included 1979 patients in (ATZ+BEV) group and 1973 patients in (NIVO+IPI) group. (ATZ+BEV) showed significantly increased median survival 997 vs 504 days (HR 0.67, 95 % CI 0.61–0.74 log-rank p < 0.0001). However mean AFP differed statistically (ATZ+BEV) 7,746 vs (NIVO+IPI) 17,495 p = 0.006. Time to normalization of AFP to below 40 was not significant, p=0.196. (ATZ+BEV) recipients experienced high risk of inpatient visits (RD 2.08%, 95% CI -3.089,7.257, P=0.43). The risk of developing predefined adverse events was similar between regimens with a nonsignificant RD.
Discussion: In this real-world matched cohort, (ATZ+BEV) conferred superior overall survival but was associated and greater healthcare utilization, while adverse event rates were comparable between treatments.
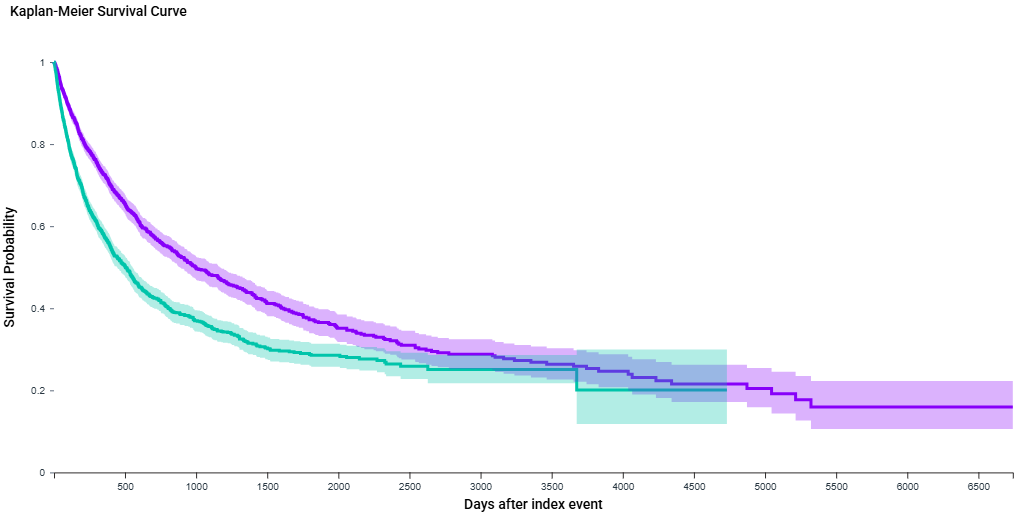
Figure: KM curve overall survival ATZ+BEV (purple) vs NIVO+IPI (blue)
Disclosures:
Sameh Gomaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hatem Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Alabdul Razzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eyad Abdulrazzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2. P3646 - Real-World Comparative Outcomes of Nivolumab + Ipilimumab versus Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A TriNetx Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health, Phoenixville, PA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Needham, MA
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer related death. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab (ATZ+BEV) has transformed the treatment landscape for advanced HCC and now a first-line option following the IMbrave150 trial. The Checkmate 040 randomized controlled trial has shown Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) has improved long-term survival benefit. This study aims to compare outcomes of both treatment modalities for advanced HCC.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX database. Criteria included adult patients >18 years of age with Advanced HCC recently initiating (ATZ+BEV) or (NIVO+IPI). Outcomes include overall survival, most recent AFP, AST, ALT, Bilirubin, INR, and Platelet count levels. Time to AFP to reach 0-40 ng/ml. Risk of developing hepatic encephalopathy or coma, hospitalization, and adverse events. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed for demographics, lab results, MELD and ECOG scores, and confounding comorbidities. Results were expressed as risk difference (RD) with 95% CI. Time to event endpoints using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models reported as hazard ratio (HR) and log-rank P values.
Results: After matching, the cohort included 1979 patients in (ATZ+BEV) group and 1973 patients in (NIVO+IPI) group. (ATZ+BEV) showed significantly increased median survival 997 vs 504 days (HR 0.67, 95 % CI 0.61–0.74 log-rank p < 0.0001). However mean AFP differed statistically (ATZ+BEV) 7,746 vs (NIVO+IPI) 17,495 p = 0.006. Time to normalization of AFP to below 40 was not significant, p=0.196. (ATZ+BEV) recipients experienced high risk of inpatient visits (RD 2.08%, 95% CI -3.089,7.257, P=0.43). The risk of developing predefined adverse events was similar between regimens with a nonsignificant RD.
Discussion: In this real-world matched cohort, (ATZ+BEV) conferred superior overall survival but was associated and greater healthcare utilization, while adverse event rates were comparable between treatments.

Figure: KM curve overall survival ATZ+BEV (purple) vs NIVO+IPI (blue)
Disclosures:
Sameh Gomaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hatem Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Alabdul Razzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eyad Abdulrazzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2. P3646 - Real-World Comparative Outcomes of Nivolumab + Ipilimumab versus Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A TriNetx Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
