Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4221 - Gastric Rust: A Rare Case of Erosive Gastritis From Oral Iron Therapy
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Lefika Bathobakae, MD, MPH
St. Joseph's University Medical Center
Paterson, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Lefika Bathobakae, MD, MPH1, Maikel Tawadrous, MD2, Atang Koodirile, MD3, Jorge Cuello Lopez, MD1, Reshma John, MD, MPH1, Irhoboudu Atogwe, MD4, Kamal Amer, MD5, Walid Baddoura, MD1
1St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 2St. George's University School of Medicine, Paterson, NJ; 3American University of Antigua College of Medicine, Paterson, NJ; 4Albert Einstein Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 5St. Joseph’s University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ
Introduction: Iron pill-induced gastritis is an underrecognized cause of gastrointestinal (GI) distress in patients receiving oral iron therapy.1–3 This condition is relatively rare but has significant clinical implications.1,2 Its pathophysiology involves the direct toxic effect of iron on the gastric mucosa, leading to necrosis, ulceration, and ischemia.3 Herein, we present a case of iron pill-induced gastritis as a unique complication of oral iron supplementation.
Case Description/
Methods: An 85-year-old woman with a medical history of type 2 DM, HTN, and IDA on iron supplementation was brought to the ED for altered mental status. Although the patient denied any acute complaints, she was only oriented to self and refusing to eat. No facial asymmetry, pathological drooling, pronator drift, or dysarthria was observed on examination. Triage labs: troponin, 343 pg/mL (reference range, 3-17) and blood glucose, 69 mg/dL (reference range, 70-110). The rest of the hemogram results were normal. Given the absence of an acute ischemic pattern on EKG, the troponin level was attributed to demand ischemia and trended down with subsequent labs.
The patient was admitted for hypoactive delirium due to an acute urinary tract infection and was treated with antibiotics. Overnight, the patient had two melenic stools, and hemoglobin level dropped from 12.4 g/dL to 9.8 g/dL. The patient was resuscitated with IV fluids and high-dose PPIs. Although iron supplements are known to cause black or dark stools, an acute drop in hemoglobin level prompted further workup. EGD revealed erythematous mucosa in the gastric fundus and a few angioectasias with bleeding in the gastric fundus that were treated with APC (Figure 1). Histological sections from the gastric fundus showed gastric mucosa with a yellowish-brown crystalline material embedded in the superficial epithelium, consistent with iron pill-induced gastritis (Figure 2). Iron supplementation was discontinued, and the patient continued on PPIs for symptomatic relief.
Discussion: There is a paucity of data on iron pill-induced gastritis in patients receiving therapeutic doses of iron, and the current evidence is limited to case reports and abstracts. Given the increasing prevalence of iron supplementation in diverse patient populations, clinicians should be aware of this rare but serious complication.
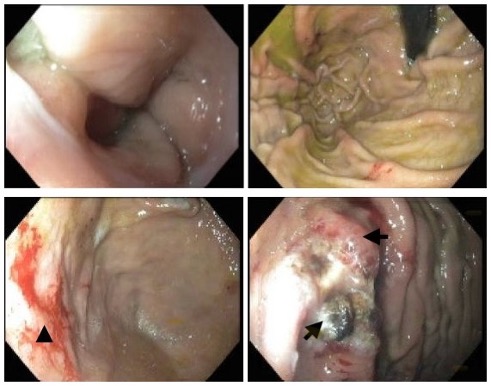
Figure: Figure 1. Endoscopic images showing a mild Schatzki ring in the distal esophagus, erythematous mucosa in the gastric fundus, and a few angioectasias with bleeding in the gastric fundus (black arrows). These were treated with argon plasma coagulation. The duodenal bulb and a second portion of the duodenum were normal.
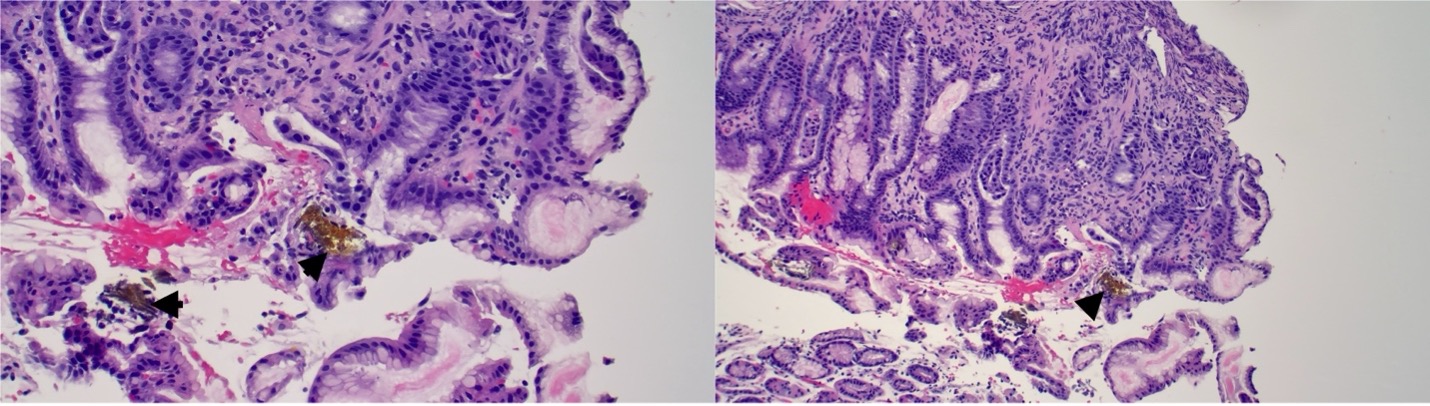
Figure: Figure 2. Histologic sections from the gastric fundus showing gastric mucosa with yellowish-brown crystalline material embedded in a superficial epithelium. These findings were consistent with iron pill-induced gastritis. Gastric biopsies were negative for intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia.
Disclosures:
Lefika Bathobakae indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maikel Tawadrous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atang Koodirile indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jorge Cuello Lopez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reshma John indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irhoboudu Atogwe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamal Amer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walid Baddoura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lefika Bathobakae, MD, MPH1, Maikel Tawadrous, MD2, Atang Koodirile, MD3, Jorge Cuello Lopez, MD1, Reshma John, MD, MPH1, Irhoboudu Atogwe, MD4, Kamal Amer, MD5, Walid Baddoura, MD1. P4221 - Gastric Rust: A Rare Case of Erosive Gastritis From Oral Iron Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 2St. George's University School of Medicine, Paterson, NJ; 3American University of Antigua College of Medicine, Paterson, NJ; 4Albert Einstein Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 5St. Joseph’s University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ
Introduction: Iron pill-induced gastritis is an underrecognized cause of gastrointestinal (GI) distress in patients receiving oral iron therapy.1–3 This condition is relatively rare but has significant clinical implications.1,2 Its pathophysiology involves the direct toxic effect of iron on the gastric mucosa, leading to necrosis, ulceration, and ischemia.3 Herein, we present a case of iron pill-induced gastritis as a unique complication of oral iron supplementation.
Case Description/
Methods: An 85-year-old woman with a medical history of type 2 DM, HTN, and IDA on iron supplementation was brought to the ED for altered mental status. Although the patient denied any acute complaints, she was only oriented to self and refusing to eat. No facial asymmetry, pathological drooling, pronator drift, or dysarthria was observed on examination. Triage labs: troponin, 343 pg/mL (reference range, 3-17) and blood glucose, 69 mg/dL (reference range, 70-110). The rest of the hemogram results were normal. Given the absence of an acute ischemic pattern on EKG, the troponin level was attributed to demand ischemia and trended down with subsequent labs.
The patient was admitted for hypoactive delirium due to an acute urinary tract infection and was treated with antibiotics. Overnight, the patient had two melenic stools, and hemoglobin level dropped from 12.4 g/dL to 9.8 g/dL. The patient was resuscitated with IV fluids and high-dose PPIs. Although iron supplements are known to cause black or dark stools, an acute drop in hemoglobin level prompted further workup. EGD revealed erythematous mucosa in the gastric fundus and a few angioectasias with bleeding in the gastric fundus that were treated with APC (Figure 1). Histological sections from the gastric fundus showed gastric mucosa with a yellowish-brown crystalline material embedded in the superficial epithelium, consistent with iron pill-induced gastritis (Figure 2). Iron supplementation was discontinued, and the patient continued on PPIs for symptomatic relief.
Discussion: There is a paucity of data on iron pill-induced gastritis in patients receiving therapeutic doses of iron, and the current evidence is limited to case reports and abstracts. Given the increasing prevalence of iron supplementation in diverse patient populations, clinicians should be aware of this rare but serious complication.

Figure: Figure 1. Endoscopic images showing a mild Schatzki ring in the distal esophagus, erythematous mucosa in the gastric fundus, and a few angioectasias with bleeding in the gastric fundus (black arrows). These were treated with argon plasma coagulation. The duodenal bulb and a second portion of the duodenum were normal.

Figure: Figure 2. Histologic sections from the gastric fundus showing gastric mucosa with yellowish-brown crystalline material embedded in a superficial epithelium. These findings were consistent with iron pill-induced gastritis. Gastric biopsies were negative for intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia.
Disclosures:
Lefika Bathobakae indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maikel Tawadrous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atang Koodirile indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jorge Cuello Lopez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reshma John indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irhoboudu Atogwe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamal Amer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walid Baddoura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lefika Bathobakae, MD, MPH1, Maikel Tawadrous, MD2, Atang Koodirile, MD3, Jorge Cuello Lopez, MD1, Reshma John, MD, MPH1, Irhoboudu Atogwe, MD4, Kamal Amer, MD5, Walid Baddoura, MD1. P4221 - Gastric Rust: A Rare Case of Erosive Gastritis From Oral Iron Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
