Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4204 - The Skin That Spoke: Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Heralding Hidden Gastric Lymphoma
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Kiara Ortiz-Camacho, MD
VA Caribbean Healthcare System
San Juan, PR
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho, MD, Orlando Rodriguez-Amador, MD, Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa, MD, Reyshley Ramos-Marquez, MD, Victor Vivas, MD, Andres Rabell-Bernal, , Carla Cruz-Diaz, MD, Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua, MD, MSc
VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder associated with underlying malignancies, particularly lymphoproliferative neoplasms. While the association between PNP and hematologic malignancies such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia is well established, its occurrence in the context of gastric lymphoma is less commonly reported. Here, we present a unique case of a patient who initially presented with PNP as the initial manifestation of high-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma.
Case Description/
Methods: This is a case of a 78-year-old male with a history of schizophrenia and gastric intestinal metaplasia for the last 10 years who was hospitalized in psychiatric ward with suicidal ideas exacerbated by “problem with his tongue”. He was consulted to dermatology services due to inability to eat due to a progressive oral lesion. Evaluation revealed recalcitrant mucositis with vesiculobullous skin eruption. Biopsies were consistent with PNP, demonstrating overlapping features of lichen planus and pemphigus. CT and PET-CT revealed an infiltrative gastric mass with metastatic spread to the liver, bones and lymph nodes. EGD revealed diffuse gastric erythema and stiffness without visible masses. Biopsies showed chronic gastritis, dense lymphoid infiltrates and H. Pylori organism. Endoscopic ultrasound revealed a 4.9 x 3.3 cm hypoechoic gastrohepatic mass and FNA revealed high-grade B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. The patient was treated for H. Pylori and initiated on chemotherapy and prednisone. The patient continued fragile, with severe oral PNP, and poor response to treatment. Therefore, goals of care were discussed and was admitted to hospice care.
Discussion: PNP is a very rare autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin, mucosa, and can also affect other organs. Diagnosis is difficult because it can present with lesions mimicking erythema multiforme, lichen planus, and pemphigus. Recognizing recalcitrant mucositis as a presenting sign of PNP is essential, as is knowing that this diagnosis is associated with a hidden neoplasm. The association of PNP with gastric lymphoma is exceedingly uncommon. This case underscores the importance of considering occult malignancy, in patients presenting with PNP, and illustrates the diagnostic value of integrating dermatologic, endoscopic, and imaging findings in complex presentations. Early recognition of such paraneoplastic syndromes can guide timely oncologic evaluation and management.
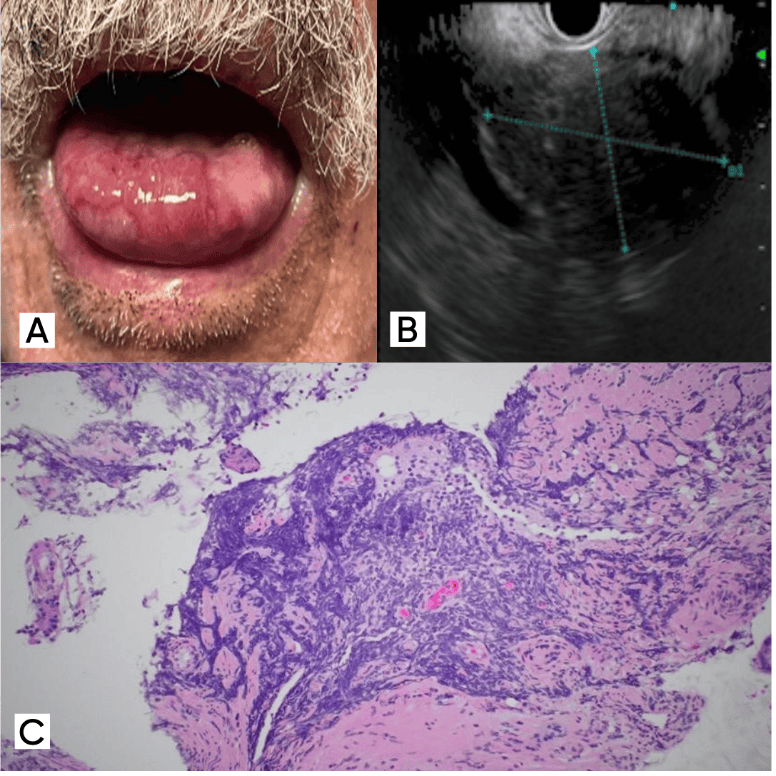
Figure: Figure A. Oral lesion as seen in PNP. B. EUS showing hypoechoic mass in gastrohepatic region. C. Biopsy from gastrohepatic mass demonstrating lymphocyte infiltration as seen in Lymphoma.
Disclosures:
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Orlando Rodriguez-Amador indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reyshley Ramos-Marquez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victor Vivas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Rabell-Bernal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Cruz-Diaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho, MD, Orlando Rodriguez-Amador, MD, Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa, MD, Reyshley Ramos-Marquez, MD, Victor Vivas, MD, Andres Rabell-Bernal, , Carla Cruz-Diaz, MD, Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua, MD, MSc. P4204 - The Skin That Spoke: Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Heralding Hidden Gastric Lymphoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho, MD, Orlando Rodriguez-Amador, MD, Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa, MD, Reyshley Ramos-Marquez, MD, Victor Vivas, MD, Andres Rabell-Bernal, , Carla Cruz-Diaz, MD, Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua, MD, MSc
VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder associated with underlying malignancies, particularly lymphoproliferative neoplasms. While the association between PNP and hematologic malignancies such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia is well established, its occurrence in the context of gastric lymphoma is less commonly reported. Here, we present a unique case of a patient who initially presented with PNP as the initial manifestation of high-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma.
Case Description/
Methods: This is a case of a 78-year-old male with a history of schizophrenia and gastric intestinal metaplasia for the last 10 years who was hospitalized in psychiatric ward with suicidal ideas exacerbated by “problem with his tongue”. He was consulted to dermatology services due to inability to eat due to a progressive oral lesion. Evaluation revealed recalcitrant mucositis with vesiculobullous skin eruption. Biopsies were consistent with PNP, demonstrating overlapping features of lichen planus and pemphigus. CT and PET-CT revealed an infiltrative gastric mass with metastatic spread to the liver, bones and lymph nodes. EGD revealed diffuse gastric erythema and stiffness without visible masses. Biopsies showed chronic gastritis, dense lymphoid infiltrates and H. Pylori organism. Endoscopic ultrasound revealed a 4.9 x 3.3 cm hypoechoic gastrohepatic mass and FNA revealed high-grade B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. The patient was treated for H. Pylori and initiated on chemotherapy and prednisone. The patient continued fragile, with severe oral PNP, and poor response to treatment. Therefore, goals of care were discussed and was admitted to hospice care.
Discussion: PNP is a very rare autoimmune blistering disease that affects the skin, mucosa, and can also affect other organs. Diagnosis is difficult because it can present with lesions mimicking erythema multiforme, lichen planus, and pemphigus. Recognizing recalcitrant mucositis as a presenting sign of PNP is essential, as is knowing that this diagnosis is associated with a hidden neoplasm. The association of PNP with gastric lymphoma is exceedingly uncommon. This case underscores the importance of considering occult malignancy, in patients presenting with PNP, and illustrates the diagnostic value of integrating dermatologic, endoscopic, and imaging findings in complex presentations. Early recognition of such paraneoplastic syndromes can guide timely oncologic evaluation and management.

Figure: Figure A. Oral lesion as seen in PNP. B. EUS showing hypoechoic mass in gastrohepatic region. C. Biopsy from gastrohepatic mass demonstrating lymphocyte infiltration as seen in Lymphoma.
Disclosures:
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Orlando Rodriguez-Amador indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reyshley Ramos-Marquez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victor Vivas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Rabell-Bernal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Cruz-Diaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kiara Ortiz-Camacho, MD, Orlando Rodriguez-Amador, MD, Juan G. Feliciano-Figueroa, MD, Reyshley Ramos-Marquez, MD, Victor Vivas, MD, Andres Rabell-Bernal, , Carla Cruz-Diaz, MD, Priscilla Magno-Pagatzaurtundua, MD, MSc. P4204 - The Skin That Spoke: Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Heralding Hidden Gastric Lymphoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

