Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4180 - Comparative Efficacy of Surgical and Endoscopic Pyloric Interventions in Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MC
Muhammad YN Chaudhary, MBChB
Indiana University Southwest Internal Medicine Residency Program
Evansville, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Ahsan Qayoom, MBBS2, Syed Arsalan Ahmad, MBBS2, Rabee Danish, MBBS2, Muhammad Burhan, MBBS2, Ali Abdullah, MBBS2, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG3
1Indiana University Southwest Internal Medicine Residency Program, Evansville, IN; 2Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3Indiana University School of Medicine, Vincennes, IN
Introduction: Gastroparesis is a chronic gastrointestinal motility disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction. While pharmacological therapy is often the initial approach, refractory cases necessitate procedural intervention. Pyloroplasty, Peroral Pyloromyotomy (POP), and Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) have emerged as key therapeutic options. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare their efficacy using the Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) and 4-hour gastric retention percentages.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library was conducted to identify studies reporting outcomes of pyloroplasty, POP, and G-POEM in adult gastroparesis patients. Extracted data included pre- and post-intervention GCSI scores and 4-hour gastric retention percentages. Pooled estimates were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic.
Results: A total of 23 studies comprising 1,419 participants met inclusion criteria. All interventions showed symptomatic and physiological improvements. Pyloroplasty (2 studies): GCSI score improved from 3.66 (95% CI: 3.045–4.276) to 2.465 (2.370–2.559); gastric retention improved from 9.034% (–3.872–21.940) to 32.991% (27.210–38.772). POP (2 studies): GCSI score reduced from 3.788 (3.397–4.179) to 2.326 (2.051–2.601); retention improved from 10.884% (9.392–12.376) to 33.302% (31.223–35.380).G-POEM (6 studies): GCSI improved from 3.129 (2.426–2.832) to 1.703 (1.125–2.280); retention from 27.778% (17.466–38.090) to 38.664% (29.383–47.904). Heterogeneity ranged from low to high across variables (I²: 0%–99.2%). Figure 1 and Table 1 summarise the results of the study.
Discussion: Pyloroplasty, POP, and G-POEM are effective in improving both symptoms and gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis. G-POEM, supported by the largest number of studies, demonstrated the most robust outcomes. These findings support the expanding role of pyloric-directed therapies in gastroparesis management, but head-to-head trials are needed for definitive guidance.
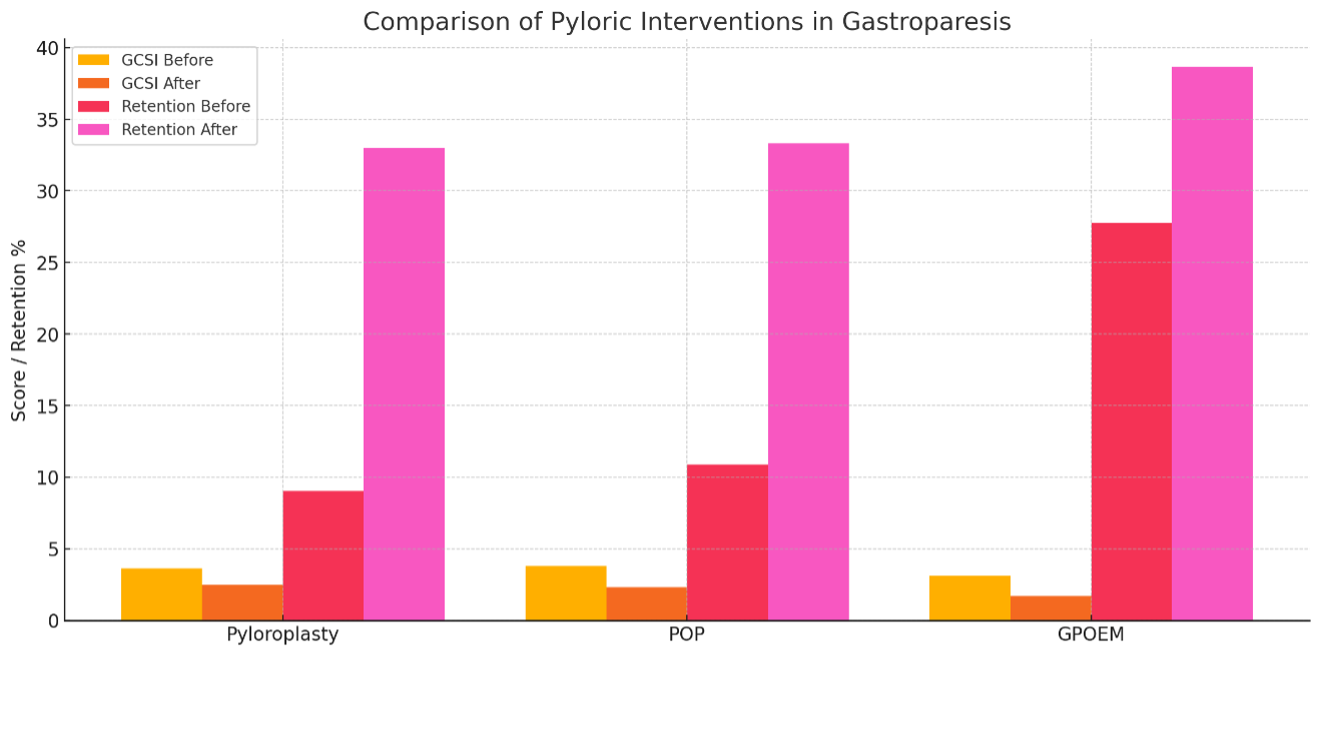
Figure: Figure 1: GCSI: Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index, Lower scores indicate symptom improvement. 4-hour Gastric retention (%): Higher post-intervention values reflect better gastric emptying. G-POEM, greatest overall improvement in both symptom relief and gastric retention. POP and Pyloroplasty also shows significant improvement but fewer studies included.
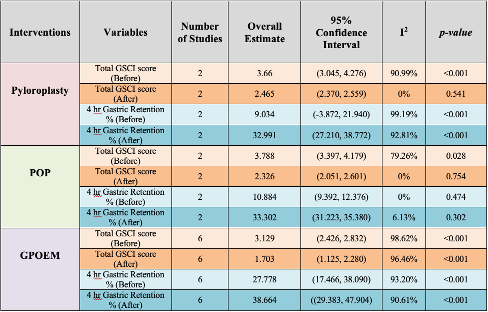
Figure: Table 1: Summary of results.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Jawwad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahsan Qayoom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Arsalan Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabee Danish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Burhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Oluwagbenga Serrano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Ahsan Qayoom, MBBS2, Syed Arsalan Ahmad, MBBS2, Rabee Danish, MBBS2, Muhammad Burhan, MBBS2, Ali Abdullah, MBBS2, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG3. P4180 - Comparative Efficacy of Surgical and Endoscopic Pyloric Interventions in Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University Southwest Internal Medicine Residency Program, Evansville, IN; 2Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3Indiana University School of Medicine, Vincennes, IN
Introduction: Gastroparesis is a chronic gastrointestinal motility disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction. While pharmacological therapy is often the initial approach, refractory cases necessitate procedural intervention. Pyloroplasty, Peroral Pyloromyotomy (POP), and Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) have emerged as key therapeutic options. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare their efficacy using the Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) and 4-hour gastric retention percentages.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library was conducted to identify studies reporting outcomes of pyloroplasty, POP, and G-POEM in adult gastroparesis patients. Extracted data included pre- and post-intervention GCSI scores and 4-hour gastric retention percentages. Pooled estimates were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic.
Results: A total of 23 studies comprising 1,419 participants met inclusion criteria. All interventions showed symptomatic and physiological improvements. Pyloroplasty (2 studies): GCSI score improved from 3.66 (95% CI: 3.045–4.276) to 2.465 (2.370–2.559); gastric retention improved from 9.034% (–3.872–21.940) to 32.991% (27.210–38.772). POP (2 studies): GCSI score reduced from 3.788 (3.397–4.179) to 2.326 (2.051–2.601); retention improved from 10.884% (9.392–12.376) to 33.302% (31.223–35.380).G-POEM (6 studies): GCSI improved from 3.129 (2.426–2.832) to 1.703 (1.125–2.280); retention from 27.778% (17.466–38.090) to 38.664% (29.383–47.904). Heterogeneity ranged from low to high across variables (I²: 0%–99.2%). Figure 1 and Table 1 summarise the results of the study.
Discussion: Pyloroplasty, POP, and G-POEM are effective in improving both symptoms and gastric emptying in patients with gastroparesis. G-POEM, supported by the largest number of studies, demonstrated the most robust outcomes. These findings support the expanding role of pyloric-directed therapies in gastroparesis management, but head-to-head trials are needed for definitive guidance.

Figure: Figure 1: GCSI: Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index, Lower scores indicate symptom improvement. 4-hour Gastric retention (%): Higher post-intervention values reflect better gastric emptying. G-POEM, greatest overall improvement in both symptom relief and gastric retention. POP and Pyloroplasty also shows significant improvement but fewer studies included.

Figure: Table 1: Summary of results.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Jawwad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahsan Qayoom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Arsalan Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabee Danish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Burhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Oluwagbenga Serrano indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB1, Mohammad Jawwad, MBBS2, Ahsan Qayoom, MBBS2, Syed Arsalan Ahmad, MBBS2, Rabee Danish, MBBS2, Muhammad Burhan, MBBS2, Ali Abdullah, MBBS2, Oluwagbenga Serrano, MD, FACG3. P4180 - Comparative Efficacy of Surgical and Endoscopic Pyloric Interventions in Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
