Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P4179 - Efficacy of Mirtazapine in Patients With Functional Dyspepsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Gilmara C. Meine, MD (she/her/hers)
Feevale University
Novo Hamburgo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
Presenting Author(s)
Livia Romariz, MD1, Lucas Delgado, MS2, Julia Juliasse, 3, Gilmara Meine, MD4
1Estácio de Sá University, Niteroi, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; 2Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil; 3Estácio de Sá University, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; 4Feevale University, Novo Hamburgo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
Introduction: Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder, yet current treatment options offer limited relief. Recent studies suggest that mirtazapine may alleviate symptoms in patients with FD. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of mirtazapine for treating patients with FD. Additionally, we conducted subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane LIbrary databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing mirtazapine versus placebo or standard treatment in patients with FD. Random-effects model was used to calculate the pooled mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, with respective 95% confidence intervals (CI). We used R for statistical analyses.
Results: This meta-analysis included three RCTs involving 214 patients aged 18 to 70 years with functional dyspepsia (FD). Of these, 94 patients experienced weight loss following their FD diagnosis. The studies used the Rome III and IV criteria for inclusion. Compared with placebo and standard treatment, mirtazapine significantly decreased Nepean Dyspepsia Index (NDI) (MD -5.21; 95% CI -6.45 to -3.96), Visceral Sensitivity Index (VSI) (MD -7.15; 95% CI -9.49 to -4.80), and Dyspepsia Symptom Severity (DSS) score (MD -2.52; 95% CI -3.92 to -1.11). Mirtazapine also significantly increased body weight (MD 7.81kg; 95% CI 3.34 to 12.28kg). There was no significant difference in the risk of adverse events between the groups (RR 2.53; 95% CI 0.34 to 19.01). The subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss showed consistent results with overall analysis.
Discussion: In patients with FD, mirtazapine was associated with significant reductions in NDI, VSI, and DSS scores, as well as weight gain. These findings suggest mirtazapine is more suitable for FD patients with weight loss.
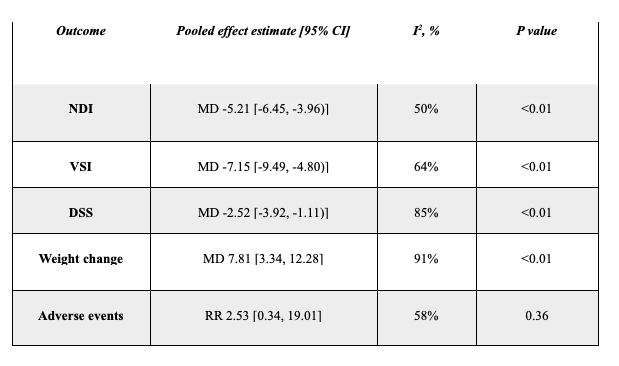
Figure: Primary and secondary outcomes in patients with functional dyspepsia treated with mirtazapine.
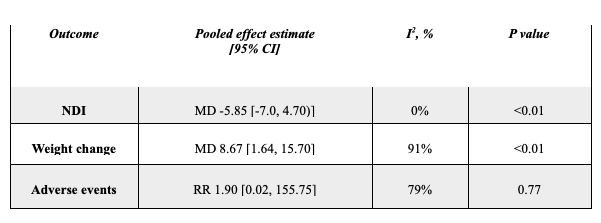
Figure: Subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss.
Disclosures:
Livia Romariz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucas Delgado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julia Juliasse indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gilmara Meine indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Livia Romariz, MD1, Lucas Delgado, MS2, Julia Juliasse, 3, Gilmara Meine, MD4. P4179 - Efficacy of Mirtazapine in Patients With Functional Dyspepsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Estácio de Sá University, Niteroi, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; 2Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil; 3Estácio de Sá University, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; 4Feevale University, Novo Hamburgo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
Introduction: Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder, yet current treatment options offer limited relief. Recent studies suggest that mirtazapine may alleviate symptoms in patients with FD. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of mirtazapine for treating patients with FD. Additionally, we conducted subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane LIbrary databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing mirtazapine versus placebo or standard treatment in patients with FD. Random-effects model was used to calculate the pooled mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, with respective 95% confidence intervals (CI). We used R for statistical analyses.
Results: This meta-analysis included three RCTs involving 214 patients aged 18 to 70 years with functional dyspepsia (FD). Of these, 94 patients experienced weight loss following their FD diagnosis. The studies used the Rome III and IV criteria for inclusion. Compared with placebo and standard treatment, mirtazapine significantly decreased Nepean Dyspepsia Index (NDI) (MD -5.21; 95% CI -6.45 to -3.96), Visceral Sensitivity Index (VSI) (MD -7.15; 95% CI -9.49 to -4.80), and Dyspepsia Symptom Severity (DSS) score (MD -2.52; 95% CI -3.92 to -1.11). Mirtazapine also significantly increased body weight (MD 7.81kg; 95% CI 3.34 to 12.28kg). There was no significant difference in the risk of adverse events between the groups (RR 2.53; 95% CI 0.34 to 19.01). The subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss showed consistent results with overall analysis.
Discussion: In patients with FD, mirtazapine was associated with significant reductions in NDI, VSI, and DSS scores, as well as weight gain. These findings suggest mirtazapine is more suitable for FD patients with weight loss.

Figure: Primary and secondary outcomes in patients with functional dyspepsia treated with mirtazapine.

Figure: Subgroup analysis based on prior history of weight loss.
Disclosures:
Livia Romariz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucas Delgado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julia Juliasse indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gilmara Meine indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Livia Romariz, MD1, Lucas Delgado, MS2, Julia Juliasse, 3, Gilmara Meine, MD4. P4179 - Efficacy of Mirtazapine in Patients With Functional Dyspepsia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
