Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3890 - Successful Use of Rituximab in Refractory Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Case Report
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpeg.jpg)
Khadija Khan, MD
LSU Health Shreveport
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Khadija Khan, MD1, Michael Tran, MD1, Kshitij Arora, MD2, Naba Saeed, MD2
1LSU Health Shreveport, Shreveport, LA; 2LSU Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a rare, chronic inflammatory liver disease that can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if not appropriately managed. First-line therapy typically involves corticosteroids in combination with azathioprine, which induces remission in most patients. However, approximately up to 30% of patients are either refractory to or intolerant of these treatments and require alternative immunosuppressive agents. Rituximab has emerged as a potential rescue therapy in refractory cases, demonstrating promising clinical outcomes. We present a case of AIH refractory to steroids which displayed good response with Rituximab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 52-year-old female with no prior medical history presented with a diffuse maculopapular rash and transaminitis. Laboratory evaluation revealed elevated IgG and positive anti-smooth muscle antibody. Skin and liver biopsies confirmed concurrent Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis and AIH. Liver histology showed plasma cell-rich chronic hepatitis with moderate activity and bridging fibrosis. FibroScan was consistent with F3 fibrosis. The patient was initiated on high dose corticosteroids with an initial favorable response and was started on cyclophosphamide for vasculitis management per Rheumatology recommendations. She declined azathioprine therapy for concern of side effects. Due to persistent transaminitis despite receiving steroids, she was started on rituximab, and cyclophosphamide was subsequently discontinued. She demonstrated significant biochemical improvement, with improvement of liver enzymes and amelioration of clinical symptoms.
Discussion: Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes, is an established treatment for several autoimmune diseases. In the context of AIH, Rituximab is emerging as a potential therapeutic option, particularly in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of standard immunosuppressive therapy with corticosteroids and azathioprine. Preliminary studies and case series have demonstrated promising responses with Rituximab in this subset of patients. However, despite these encouraging findings, Rituximab has not yet received FDA approval for the treatment of AIH. Additional studies are necessary to further evaluate its efficacy and safety profile in this patient population and to support its integration into standard treatment protocols.
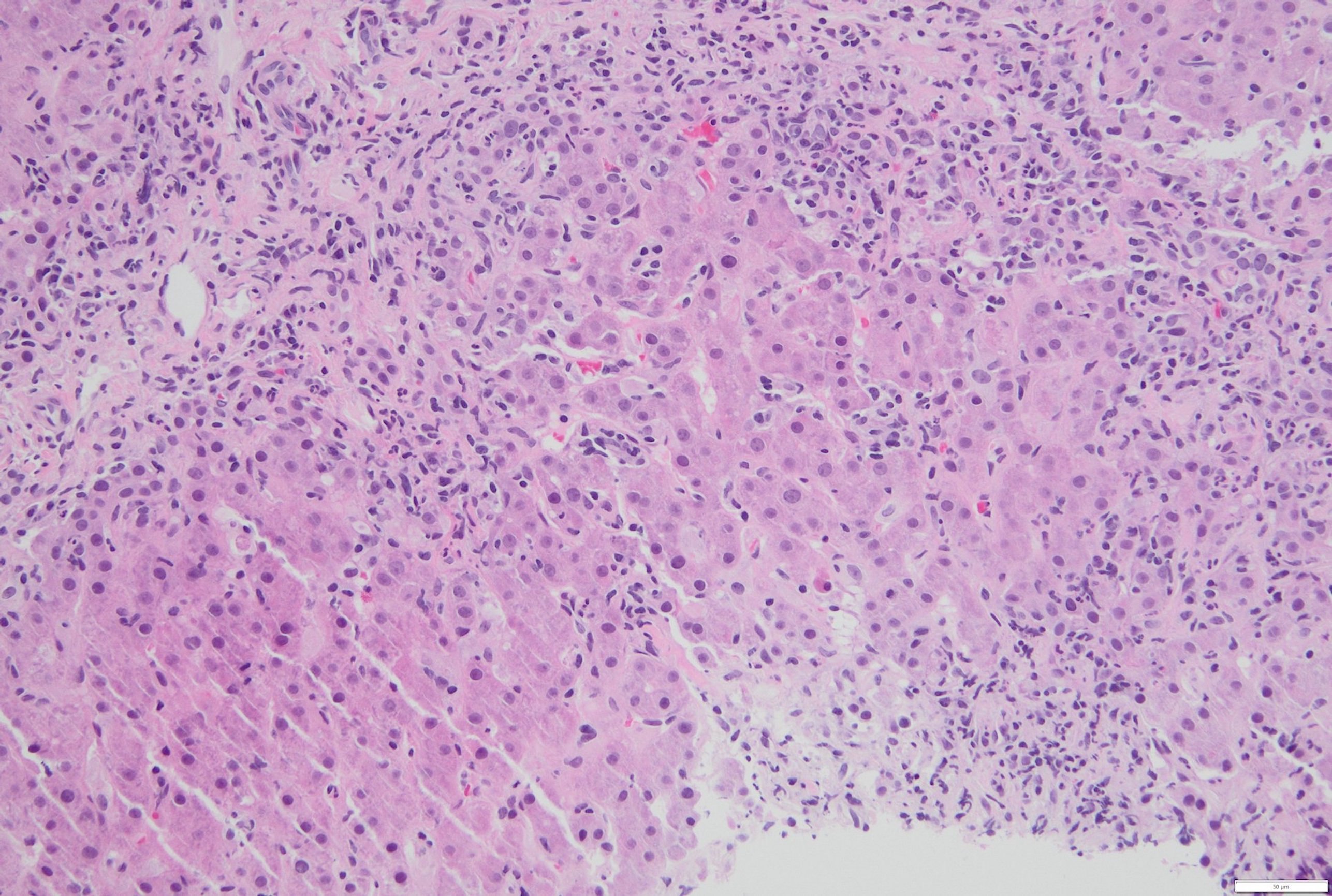
Figure: Liver biopsy: Portal based plasma cell rich moderate chronic inflammation with interface hepatitis, moderate lobular inflammation , acidophil bodies and bridging fibrosis ( H&E stain; 200X magnification)
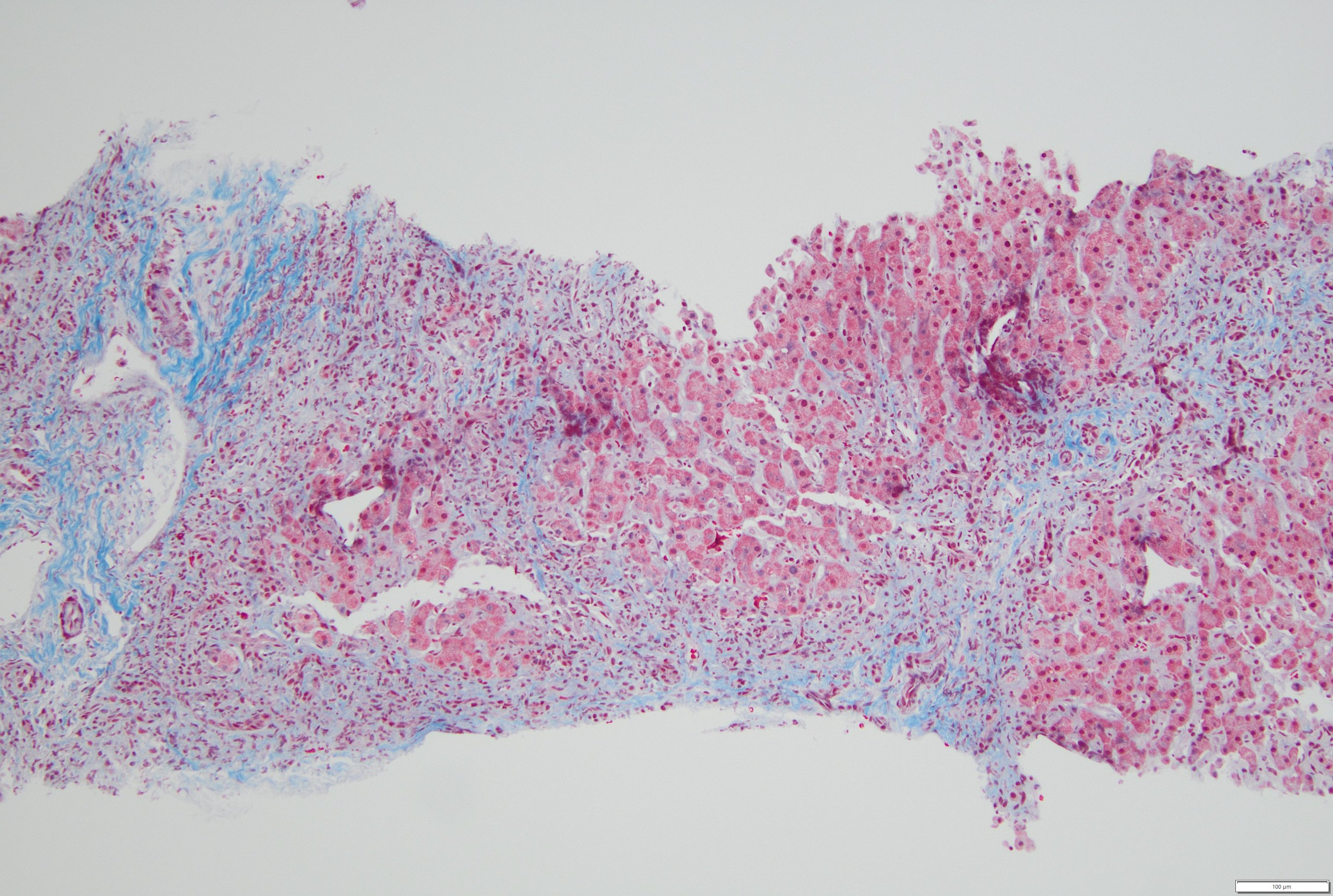
Figure: Liver biopsy displaying fibrosis (Masson trichrome stain, 100X magnification)
Disclosures:
Khadija Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Tran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kshitij Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naba Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Khan, MD1, Michael Tran, MD1, Kshitij Arora, MD2, Naba Saeed, MD2. P3890 - Successful Use of Rituximab in Refractory Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1LSU Health Shreveport, Shreveport, LA; 2LSU Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a rare, chronic inflammatory liver disease that can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if not appropriately managed. First-line therapy typically involves corticosteroids in combination with azathioprine, which induces remission in most patients. However, approximately up to 30% of patients are either refractory to or intolerant of these treatments and require alternative immunosuppressive agents. Rituximab has emerged as a potential rescue therapy in refractory cases, demonstrating promising clinical outcomes. We present a case of AIH refractory to steroids which displayed good response with Rituximab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 52-year-old female with no prior medical history presented with a diffuse maculopapular rash and transaminitis. Laboratory evaluation revealed elevated IgG and positive anti-smooth muscle antibody. Skin and liver biopsies confirmed concurrent Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis and AIH. Liver histology showed plasma cell-rich chronic hepatitis with moderate activity and bridging fibrosis. FibroScan was consistent with F3 fibrosis. The patient was initiated on high dose corticosteroids with an initial favorable response and was started on cyclophosphamide for vasculitis management per Rheumatology recommendations. She declined azathioprine therapy for concern of side effects. Due to persistent transaminitis despite receiving steroids, she was started on rituximab, and cyclophosphamide was subsequently discontinued. She demonstrated significant biochemical improvement, with improvement of liver enzymes and amelioration of clinical symptoms.
Discussion: Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen on B lymphocytes, is an established treatment for several autoimmune diseases. In the context of AIH, Rituximab is emerging as a potential therapeutic option, particularly in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of standard immunosuppressive therapy with corticosteroids and azathioprine. Preliminary studies and case series have demonstrated promising responses with Rituximab in this subset of patients. However, despite these encouraging findings, Rituximab has not yet received FDA approval for the treatment of AIH. Additional studies are necessary to further evaluate its efficacy and safety profile in this patient population and to support its integration into standard treatment protocols.

Figure: Liver biopsy: Portal based plasma cell rich moderate chronic inflammation with interface hepatitis, moderate lobular inflammation , acidophil bodies and bridging fibrosis ( H&E stain; 200X magnification)

Figure: Liver biopsy displaying fibrosis (Masson trichrome stain, 100X magnification)
Disclosures:
Khadija Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Tran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kshitij Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naba Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Khan, MD1, Michael Tran, MD1, Kshitij Arora, MD2, Naba Saeed, MD2. P3890 - Successful Use of Rituximab in Refractory Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
