Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3806 - Alcoholic Liver Disease–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the US: A 25-Year Mortality Analysis (1999–2023)
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Aisha Rehman Siddiqui, MD (she/her/hers)
Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Saad, MBBS1, Eman Alamgir, MBBS2, Muhammad Hamza Sikandari, MD3, Farina Fatima Siddiqui, MBBS4, Fnu Dureshum, MBBS5, Ifrah Hamza, MBBS6, Muhammad Momin. Khan, MBBS7, Iqra Alamgir, MBBS8, Unsa Alamgir, 2, Muhammad Rayan. Syed, MBBS9, Amna Rizwan. Bhatti, MBBS10, Samiullah Shaikh, MD7, Aisha Siddiqui, MD11
1Liaquat University Hospital, Jamshoro, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 2University Medical and Dental College Faisalabad, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science (LUMHS) Jamshoro, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Liaquat Institute of Medical & Health Sciences Jamshoro Thatta, Thatta, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Federal government polyclinic hospital Islamabad, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 7Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 8University Medical & Dental College, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Liaquat university hospital, hyderabad, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 10Federal medical and dental college, Islamabad, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 11Wayne State University, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers in the U.S., and Alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) is emerging as a major driver of hepatocellular carcinoma. In 2022, ALD accounted for 29.8% of all HCC-related deaths, a substantial increase compared to earlier years. Our study aims to assess the temporal trends in ALD-related HCC mortality among US citizens by age, gender, and race.
Methods:
Results: From 1999 to 2023, ALD-related HCC caused a total of 801,200 deaths in the US. The overall AAMR for ALD-related HCC carcinoma in 1999 was 7.7 (95% CI: 7.6 to 7.8) and increased to 16.1 (95% CI: 16 to 16.2) in 2023 with an AAPC of 3.95% (95% CI: 3.64 to 4.48), exhibiting an increasing trend. Men showed a higher AAMR as compared to females from 1999 to 2023 (12.4 vs 3.6) and (23.5 vs 9.4). AAPC was higher among females. According to the racial distribution, American Alaskans showed the highest mortality (AAMR: 31.76), followed by Hispanics or Latinos (16.13), White Americans (11.57), Blacks or African Americans (10.46), and Asians or Pacific Islanders (8.51). Regional analysis also revealed disparities in AAMR, with the West having the highest AAMR of 16.69, followed by the South (10.36), the Midwest (10.15), and the Northeast (8.53). The states with AAMRs were Wyoming, Alaska, Washington, and California. Metropolitan regions demonstrated a higher AAMR 11 (11-11) compared to non-metropolitan regions, with 10.8 (10.8-10.9). Non- metropolitan regions demonstrated an overall increasing trend with an AAPC of 5.09%.
Discussion: Alcoholic liver disease is one of the important causes of HCC-related mortality in the U.S. A constant increase in the overall mortality rate from 1999 to 2023 is very concerning and needs policy changes regarding alcoholism and improved quality care for HCC patients. The disproportionate significantly increased mortality rates among American Indians or Alaska Natives also require further investigations to identify the cause.
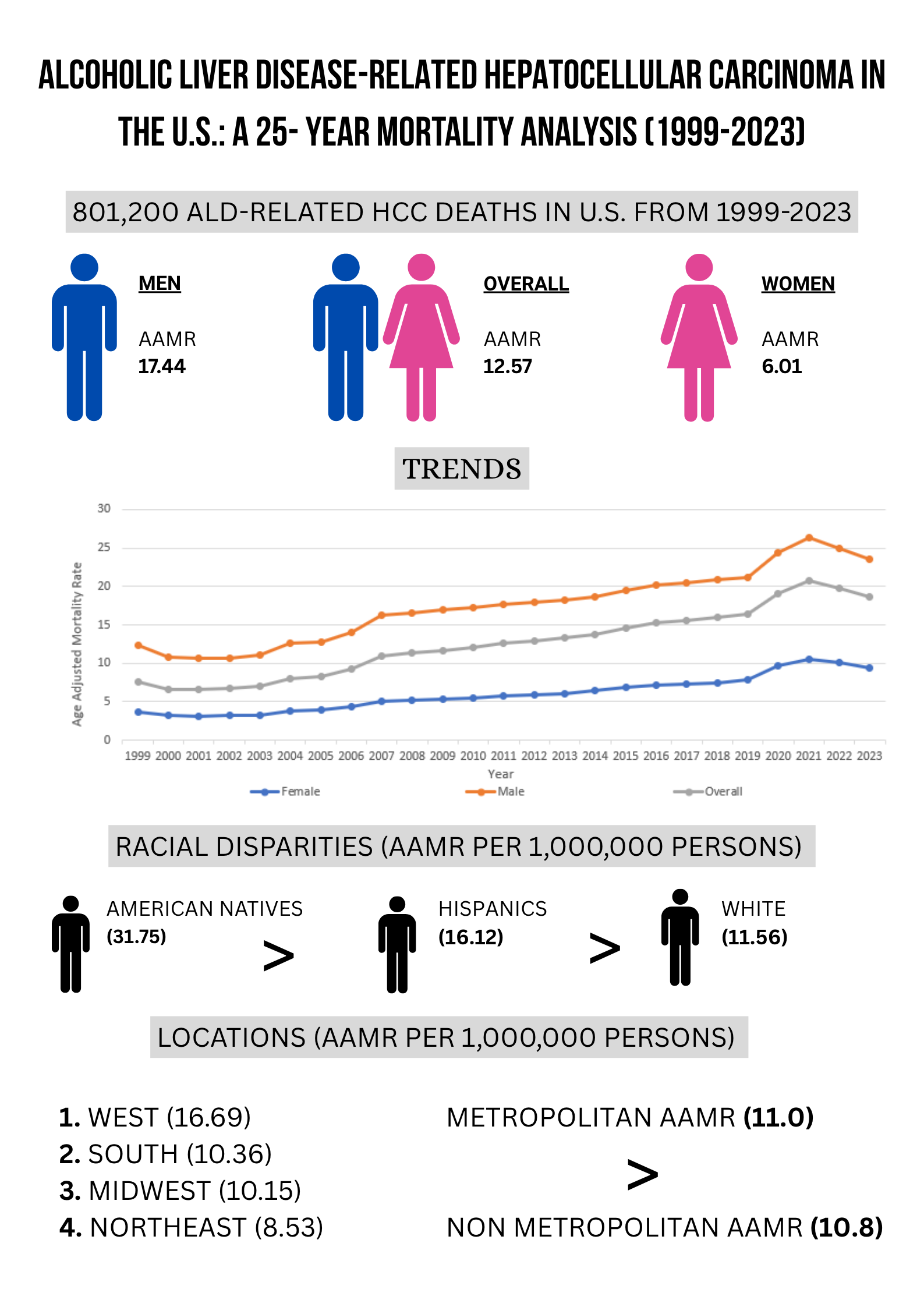
Figure: Alcoholic Liver Disease–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the U.S.: A 25-Year Mortality Analysis (1999–2023)
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eman Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza Sikandari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farina Fatima Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Dureshum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ifrah Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Unsa Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Bhatti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiullah Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aisha Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad, MBBS1, Eman Alamgir, MBBS2, Muhammad Hamza Sikandari, MD3, Farina Fatima Siddiqui, MBBS4, Fnu Dureshum, MBBS5, Ifrah Hamza, MBBS6, Muhammad Momin. Khan, MBBS7, Iqra Alamgir, MBBS8, Unsa Alamgir, 2, Muhammad Rayan. Syed, MBBS9, Amna Rizwan. Bhatti, MBBS10, Samiullah Shaikh, MD7, Aisha Siddiqui, MD11. P3806 - Alcoholic Liver Disease–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the US: A 25-Year Mortality Analysis (1999–2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Liaquat University Hospital, Jamshoro, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 2University Medical and Dental College Faisalabad, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science (LUMHS) Jamshoro, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Liaquat Institute of Medical & Health Sciences Jamshoro Thatta, Thatta, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Federal government polyclinic hospital Islamabad, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 7Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 8University Medical & Dental College, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 9Liaquat university hospital, hyderabad, Hyderabad, Sindh, Pakistan; 10Federal medical and dental college, Islamabad, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 11Wayne State University, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers in the U.S., and Alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) is emerging as a major driver of hepatocellular carcinoma. In 2022, ALD accounted for 29.8% of all HCC-related deaths, a substantial increase compared to earlier years. Our study aims to assess the temporal trends in ALD-related HCC mortality among US citizens by age, gender, and race.
Methods:
Results: From 1999 to 2023, ALD-related HCC caused a total of 801,200 deaths in the US. The overall AAMR for ALD-related HCC carcinoma in 1999 was 7.7 (95% CI: 7.6 to 7.8) and increased to 16.1 (95% CI: 16 to 16.2) in 2023 with an AAPC of 3.95% (95% CI: 3.64 to 4.48), exhibiting an increasing trend. Men showed a higher AAMR as compared to females from 1999 to 2023 (12.4 vs 3.6) and (23.5 vs 9.4). AAPC was higher among females. According to the racial distribution, American Alaskans showed the highest mortality (AAMR: 31.76), followed by Hispanics or Latinos (16.13), White Americans (11.57), Blacks or African Americans (10.46), and Asians or Pacific Islanders (8.51). Regional analysis also revealed disparities in AAMR, with the West having the highest AAMR of 16.69, followed by the South (10.36), the Midwest (10.15), and the Northeast (8.53). The states with AAMRs were Wyoming, Alaska, Washington, and California. Metropolitan regions demonstrated a higher AAMR 11 (11-11) compared to non-metropolitan regions, with 10.8 (10.8-10.9). Non- metropolitan regions demonstrated an overall increasing trend with an AAPC of 5.09%.
Discussion: Alcoholic liver disease is one of the important causes of HCC-related mortality in the U.S. A constant increase in the overall mortality rate from 1999 to 2023 is very concerning and needs policy changes regarding alcoholism and improved quality care for HCC patients. The disproportionate significantly increased mortality rates among American Indians or Alaska Natives also require further investigations to identify the cause.

Figure: Alcoholic Liver Disease–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the U.S.: A 25-Year Mortality Analysis (1999–2023)
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eman Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza Sikandari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farina Fatima Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Dureshum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ifrah Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Unsa Alamgir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Bhatti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiullah Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aisha Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad, MBBS1, Eman Alamgir, MBBS2, Muhammad Hamza Sikandari, MD3, Farina Fatima Siddiqui, MBBS4, Fnu Dureshum, MBBS5, Ifrah Hamza, MBBS6, Muhammad Momin. Khan, MBBS7, Iqra Alamgir, MBBS8, Unsa Alamgir, 2, Muhammad Rayan. Syed, MBBS9, Amna Rizwan. Bhatti, MBBS10, Samiullah Shaikh, MD7, Aisha Siddiqui, MD11. P3806 - Alcoholic Liver Disease–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the US: A 25-Year Mortality Analysis (1999–2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
