Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3735 - A Review of Reports of Hepatic Failure and Hepatitis to the FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) From Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Pharmacotherapy
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- NA
Nick Adimi, MD, MS, BS
Advocate Lutheran General
Park Ridge, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Nick Adimi, MD, MS, BS, Ethan Anderson, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG
Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Pharmacotherapy of IBD consists of a multitude of medication classifications. This study aims to identify hepatic injury across all treatment modalities of CD and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) utilizing reports to FAERS.
Methods: The FAERS database consists of voluntarily reported post-marketing adverse drug reactions (ADRs). 30,668,520 total reports from Jan 1968 to March 2025 were collected. Reports of ADRs of all FDA approved IBD therapies including azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, tacrolimus, balsalazide, mesalamine, osalazine, sulfasalazine, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, infliximab, natalizumab, vedolizumab, guselkumab, mirikixumab, risankizumab, ustekinumab, tofacitinib, upadacitinib, etrasimod, and ozanimod were reviewed. Reports of cases of hepatitis and hepatic failure in the treatment of CD or UC were collected. Using the OpenVigil program, signals for these ADRs were determined using reporter odds ratios (RORs) calculated with the following formula:
ROR = (a/c)/(b/d)
a: =drug with ADR, b: =all drugs with ADR, c=all ADRs for the drug, d=other drugs with other ADRs. A ROR >1 indicates an ADR frequency is not occurring by chance alone, suggesting a significant post-marketing signal.
Results: Tables 1 and 2 below show a truncated list of the reviewed medications, portraying significant ROR in ADR related to hepatitis or hepatic failure.
There were 218 reports of hepatitis, and 135 reports of hepatic failure identified in patients with CD and UC. Azathioprine (ROR 4.26), mercaptopurine (ROR 3.08), and methotrexate (ROR 2.58) showed significant ROR for hepatitis in CD. Mercaptopurine (ROR 3.34), tacrolimus (ROR 21.17), and infliximab (ROR 1.86) showed significant ROR for hepatic failure in CD. Azathioprine (ROR 6.80), mercaptopurine (ROR 9.34), and methotrexate (ROR 4.13) showed significant ROR for hepatitis in UC. Azathioprine (ROR 5.64), tacrolimus (ROR 13.18), and balsalazide (ROR 7.79) showed significant ROR for hepatic failure in UC. Adalimumab demonstrated an apparent protective effect (See Tables 1 and 2).
Discussion: Analysis of reports to FAERS suggests that azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, tacrolimus and infliximab are associated with reports of hepatic injury in patients with CD. Azathioprine, mercaptopurine, tacrolimus, methotrexate, and balsalazide are associated with hepatic injury in patients with UC. Using this method of analysis, adalimumab appears to have a protective effect against hepatic injury in patients with CD and UC.
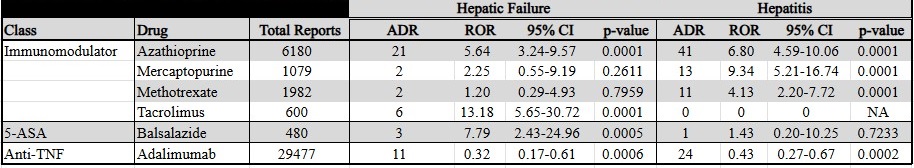
Figure: Table 1: Adverse Drug Reaction in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. All FDA approved pharmacotherapies for UC with total FAERS adverse drug reaction reports and specific analysis of adverse drug reaction of hepatic failure and hepatitis.
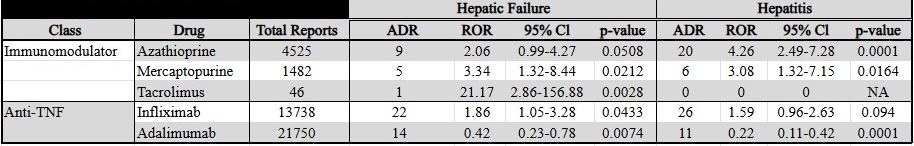
Figure: Table 2: Adverse Drug Reaction in the Treatment of Crohn's Disease. All FDA approved pharmacotherapies for CD with total FAERS adverse drug reaction reports and specific analysis of adverse drug reaction of hepatic failure and hepatitis.
Disclosures:
Nick Adimi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Anderson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Ehrenpreis: E2Bio Consultants – Intellectual Property/Patents, CEO, Owner/Ownership Interest. E2Bio Life Sciences – CEO, Owner/Ownership Interest.
Nick Adimi, MD, MS, BS, Ethan Anderson, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG. P3735 - A Review of Reports of Hepatic Failure and Hepatitis to the FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) From Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Pharmacotherapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Pharmacotherapy of IBD consists of a multitude of medication classifications. This study aims to identify hepatic injury across all treatment modalities of CD and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) utilizing reports to FAERS.
Methods: The FAERS database consists of voluntarily reported post-marketing adverse drug reactions (ADRs). 30,668,520 total reports from Jan 1968 to March 2025 were collected. Reports of ADRs of all FDA approved IBD therapies including azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, tacrolimus, balsalazide, mesalamine, osalazine, sulfasalazine, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, infliximab, natalizumab, vedolizumab, guselkumab, mirikixumab, risankizumab, ustekinumab, tofacitinib, upadacitinib, etrasimod, and ozanimod were reviewed. Reports of cases of hepatitis and hepatic failure in the treatment of CD or UC were collected. Using the OpenVigil program, signals for these ADRs were determined using reporter odds ratios (RORs) calculated with the following formula:
ROR = (a/c)/(b/d)
a: =drug with ADR, b: =all drugs with ADR, c=all ADRs for the drug, d=other drugs with other ADRs. A ROR >1 indicates an ADR frequency is not occurring by chance alone, suggesting a significant post-marketing signal.
Results: Tables 1 and 2 below show a truncated list of the reviewed medications, portraying significant ROR in ADR related to hepatitis or hepatic failure.
There were 218 reports of hepatitis, and 135 reports of hepatic failure identified in patients with CD and UC. Azathioprine (ROR 4.26), mercaptopurine (ROR 3.08), and methotrexate (ROR 2.58) showed significant ROR for hepatitis in CD. Mercaptopurine (ROR 3.34), tacrolimus (ROR 21.17), and infliximab (ROR 1.86) showed significant ROR for hepatic failure in CD. Azathioprine (ROR 6.80), mercaptopurine (ROR 9.34), and methotrexate (ROR 4.13) showed significant ROR for hepatitis in UC. Azathioprine (ROR 5.64), tacrolimus (ROR 13.18), and balsalazide (ROR 7.79) showed significant ROR for hepatic failure in UC. Adalimumab demonstrated an apparent protective effect (See Tables 1 and 2).
Discussion: Analysis of reports to FAERS suggests that azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, tacrolimus and infliximab are associated with reports of hepatic injury in patients with CD. Azathioprine, mercaptopurine, tacrolimus, methotrexate, and balsalazide are associated with hepatic injury in patients with UC. Using this method of analysis, adalimumab appears to have a protective effect against hepatic injury in patients with CD and UC.

Figure: Table 1: Adverse Drug Reaction in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. All FDA approved pharmacotherapies for UC with total FAERS adverse drug reaction reports and specific analysis of adverse drug reaction of hepatic failure and hepatitis.

Figure: Table 2: Adverse Drug Reaction in the Treatment of Crohn's Disease. All FDA approved pharmacotherapies for CD with total FAERS adverse drug reaction reports and specific analysis of adverse drug reaction of hepatic failure and hepatitis.
Disclosures:
Nick Adimi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Anderson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Ehrenpreis: E2Bio Consultants – Intellectual Property/Patents, CEO, Owner/Ownership Interest. E2Bio Life Sciences – CEO, Owner/Ownership Interest.
Nick Adimi, MD, MS, BS, Ethan Anderson, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG. P3735 - A Review of Reports of Hepatic Failure and Hepatitis to the FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) From Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Pharmacotherapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
