Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4416 - Presentation of Rare Pancreatic Oncocytic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm in a 73-year-Old Female
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AA
Ahmad Afzal, MD
Houston Methodist Hospital
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Nandini Ray, MD1, Dayoung Jeon, MD1, Joshua Wong, MD1, Ashish Saharia, MD1, Sudha Kodali, MD1
1Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 2Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Pancreatic oncocytic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IOPN) is a very rare subtype of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), representing about 5% of all intraductal pancreatic neoplasms. Clinically, it often poses diagnostic challenges due to non-specific abdominal symptoms. They usually present as large cystic lesions in the head of the pancreas that are discovered incidentally.
Case Description/
Methods: We present the case of a 73-year-old female with past medical history of adenomatous colon polyps and lung nodules who underwent a CT chest with contrast for routing monitoring of lung nodules. The imaging showed some concerning lesions in her pancreas which prompted a referral to gastroenterology. CT abdomen with contrast showed a hyper enhancing mass in the tail of the pancreas. The patient denied any obvious symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss or jaundice. CEA, CA19-9 and HBA1C levels were checked and were within normal range. She then underwent MRI of the abdomen with contrast which confirmed a complex, mixed solid and cystic mass in the pancreatic tail measuring 25 mm x 24 mm. The mass was also communicating with the main pancreatic duct. Atrophy of the pancreas and dilation of the main pancreatic duct distal to this mass was also noted. Radiological evaluation was nonspecific but favored the mass as a cystic degeneration of a neuroendocrine tumor. The patient was then referred to General Surgery and underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy. Pathology results from the surgical specimen showed IOPN involving the main pancreatic duct, 12 benign lymph nodes and a normal spleen. There was no evidence of invasion. She did well post operatively and received appropriate post-splenectomy vaccines as well, eventually being discharged on post op day 5. At her 6 month follow up, she is asymptomatic without imaging evidence of recurrence on MRI abdomen.
Discussion: Pancreatic IOPN is a pancreatic tumor that is more frequently discovered in males around the seventh decade of life. The recommended treatment is surgical resection due to the risk of invasive carcinoma, which is present in nearly 50% of IOPN cases. Our patient did not have invasive neoplasm but underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy to ensure complete resection, especially due to the close proximity to the splenic vessels. Post operative outcomes for IOPN are generally favorable, with low rates of recurrence when complete resection is achieved.
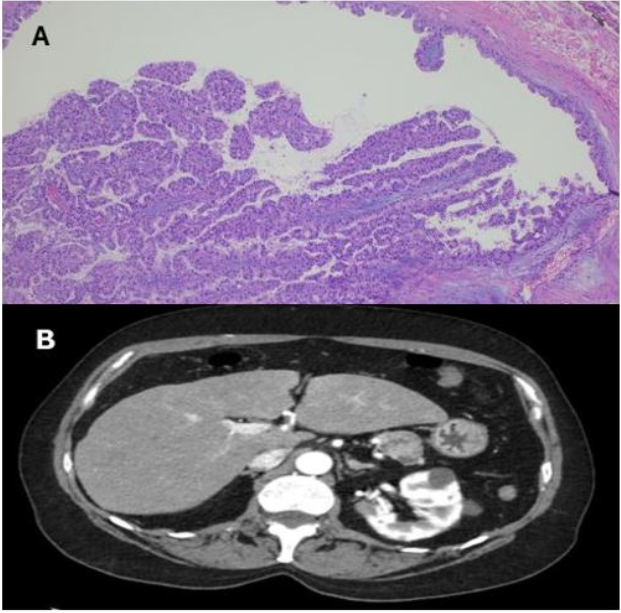
Figure: Figure A: Photomicrograph of the pancreatic oncocytic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Figure B: Axial CT abdomen view of the pancreatic neoplasm measuring 2.9 x 2.4 cm.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apaar Dadlani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nandini Ray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dayoung Jeon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Wong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashish Saharia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudha Kodali: ASTRAZENECA – Advisory Committee/Board Member. GILEAD – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. SIRTEX – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Nandini Ray, MD1, Dayoung Jeon, MD1, Joshua Wong, MD1, Ashish Saharia, MD1, Sudha Kodali, MD1. P4416 - Presentation of Rare Pancreatic Oncocytic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm in a 73-year-Old Female, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 2Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Pancreatic oncocytic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IOPN) is a very rare subtype of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), representing about 5% of all intraductal pancreatic neoplasms. Clinically, it often poses diagnostic challenges due to non-specific abdominal symptoms. They usually present as large cystic lesions in the head of the pancreas that are discovered incidentally.
Case Description/
Methods: We present the case of a 73-year-old female with past medical history of adenomatous colon polyps and lung nodules who underwent a CT chest with contrast for routing monitoring of lung nodules. The imaging showed some concerning lesions in her pancreas which prompted a referral to gastroenterology. CT abdomen with contrast showed a hyper enhancing mass in the tail of the pancreas. The patient denied any obvious symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss or jaundice. CEA, CA19-9 and HBA1C levels were checked and were within normal range. She then underwent MRI of the abdomen with contrast which confirmed a complex, mixed solid and cystic mass in the pancreatic tail measuring 25 mm x 24 mm. The mass was also communicating with the main pancreatic duct. Atrophy of the pancreas and dilation of the main pancreatic duct distal to this mass was also noted. Radiological evaluation was nonspecific but favored the mass as a cystic degeneration of a neuroendocrine tumor. The patient was then referred to General Surgery and underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy. Pathology results from the surgical specimen showed IOPN involving the main pancreatic duct, 12 benign lymph nodes and a normal spleen. There was no evidence of invasion. She did well post operatively and received appropriate post-splenectomy vaccines as well, eventually being discharged on post op day 5. At her 6 month follow up, she is asymptomatic without imaging evidence of recurrence on MRI abdomen.
Discussion: Pancreatic IOPN is a pancreatic tumor that is more frequently discovered in males around the seventh decade of life. The recommended treatment is surgical resection due to the risk of invasive carcinoma, which is present in nearly 50% of IOPN cases. Our patient did not have invasive neoplasm but underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy to ensure complete resection, especially due to the close proximity to the splenic vessels. Post operative outcomes for IOPN are generally favorable, with low rates of recurrence when complete resection is achieved.

Figure: Figure A: Photomicrograph of the pancreatic oncocytic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Figure B: Axial CT abdomen view of the pancreatic neoplasm measuring 2.9 x 2.4 cm.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apaar Dadlani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nandini Ray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dayoung Jeon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Wong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashish Saharia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudha Kodali: ASTRAZENECA – Advisory Committee/Board Member. GILEAD – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. SIRTEX – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Nandini Ray, MD1, Dayoung Jeon, MD1, Joshua Wong, MD1, Ashish Saharia, MD1, Sudha Kodali, MD1. P4416 - Presentation of Rare Pancreatic Oncocytic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm in a 73-year-Old Female, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
