Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4548 - High-Definition Dye Chromoendoscopy Boosts Dysplasia Detection by 75 % Compared With White-Light Surveillance - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
.jpg)
Ashesh Das, MBBS
KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Presenting Author(s)
1KPC Medical College and Hospital , Kolkata, India, Kolkata, West Bengal, India; 2Gayatri Vidya Parishad Institute of Health care and Medical Technology, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3Desert Regional Medical Center, Reseda, CA
Introduction:
High-definition (HD) dye-based chromoendoscopy (CE) is recommended for dysplasia surveillance in colonic IBD, yet many centers have reverted to HD white-light endoscopy (WLE) on the assumption that visual gains have disappeared. We analysed the four most up-to-date Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) comparing HD-CE with HD-WLE—including the multicentre HELIOS 2025 RCT—to provide a data-driven answer.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane Library identified Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) that compares white light versus chromoendoscopy or conventional for colonoscopy through May 2025. Data were analysed using RevMan 4.2.1. Pooled risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using Mantel-Haenszel methods. Random- or fixed-effects models were applied based on heterogeneity (Higgins’ I²). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2.0.
Results:
Dysplasia occurred in 79/512 CE examinations versus 48/542 WLE examinations. Fixed-effect pooling yielded a 43 % relative reduction in miss-rate with WLE (RR 0.57, 95 % CI 0.41–0.80; I² 22 %), equating to ~1 extra dysplasia detected for every 18 patients screened. Advanced neoplasia was rare (9 vs 3 events); the trend favoured CE but did not reach significance (RR 0.55, 95 % CI 0.17–1.82; I² 0 %).
Discussion:
This HD-exclusive meta-analysis confirms that dye augmentation remains clinically meaningful in 2025: CE nearly doubles dysplasia detection across diverse Asian and European cohorts with minimal heterogeneity, firmly validating SCENIC guidance. The low event count for advanced lesions limits power, yet the consistent directionality suggests CE may avert late-stage cancers with larger datasets or AI-assisted optics. Importantly, the benefit was realised without excess heterogeneity, indicating reproducibility in routine practice. These findings argue against abandoning dye spray and instead support streamlined CE or prolonged inspection times to safeguard patients with longstanding colitis. Our work provides the first modern benchmark for technology-enhanced surveillance and sets the stage for future trials integrating virtual chromoendoscopy and computer-aided detection—all with the goal of transforming dysplasia prevention into a reliably achievable standard of care.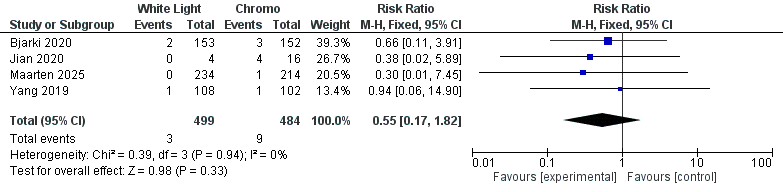
Figure: Forest Plot for Dysplasia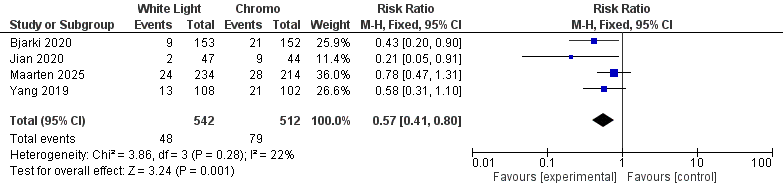
Figure: Forest Plot for Advanced Neooplasia
Disclosures:
Ashesh Das indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haroon Alamy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashesh Das, MBBS1, Venkata Dileep Kumar Veldi, MBBS2, Haroon Alamy, MD3. P4548 - High-Definition Dye Chromoendoscopy Boosts Dysplasia Detection by 75 % Compared With White-Light Surveillance - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
