Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4596 - Tofacitinib vs Vedolizumab: A 36-Month Journey in Ulcerative Proctitis Management With Insights on Efficacy and Safety: Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis Using TriNetX Database

Amine Rakab, MD (he/him/his)
Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine
Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar
Presenting Author(s)
1University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 2The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 3University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 4Department of Internal Medicine, TriHealth Inc., Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH; 5University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 6Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 7Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 8Saint Agnes Medical Center, Fresno CA, Fresno, CA; 9Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 10Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Washington, DC; 11University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction:
Tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and vedolizumab, an integrin antagonist, are therapeutic options for ulcerative colitis, including ulcerative proctitis (UP). This study aims to compare the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib versus vedolizumab in patients with UP over 36 months.
Methods:
Utilizing TriNetX Network Database, a retrospective cohort study was conducted comparing patients with UP treated with tofacitinib (n=567) versus vedolizumab (n=567). Propensity score matching was employed to balance baseline characteristics and minimize confounding. Outcomes included oral and intravenous corticosteroid use, hospitalization, proctectomy rates, venous thromboembolism (VTE), major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and opportunistic infections at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
Results:
At 6 months, the use of IV corticosteroids was significantly lower in the Tofacitinib group compared to the Vedolizumab group (OR = 0.47, 95% CI: 0.337–0.648). Similarly, the use of IV or oral corticosteroids was reduced in the Tofacitinib group (OR = 0.766, 95% CI: 0.597–0.983). However, hospitalization rates were higher in the Tofacitinib group (OR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.088–1.932). At 12 months, IV corticosteroid use remained lower in the Tofacitinib group (OR = 0.506, 95% CI: 0.374–0.684), but hospitalization rates were again higher (OR = 1.328, 95% CI: 1.018–1.733). At 24 months, the Tofacitinib group showed significantly reduced use of IV corticosteroids (OR = 0.488, 95% CI: 0.367–0.648) and IV or oral corticosteroids (OR = 0.727, 95% CI: 0.573–0.921). Additionally, the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) was lower in the Tofacitinib group (OR = 0.445, 95% CI: 0.209–0.948). By 36 months, the trend continued, with reduced use of IV corticosteroids (OR = 0.508, 95% CI: 0.386–0.669) and IV or oral corticosteroids (OR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.585–0.936) in the Tofacitinib group, alongside a lower risk of VTE (OR = 0.469, 95% CI: 0.233–0.942). Other outcomes, including proctectomy rates, MACE, and opportunistic infections, showed no significant differences between groups across all time points.
Discussion:
In patients with UP, tofacitinib may reduce corticosteroid dependence compared to vedolizumab over 36 months. However, it may be associated with higher hospitalization rates in the early treatment phase. Further studies are needed to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of both treatments.
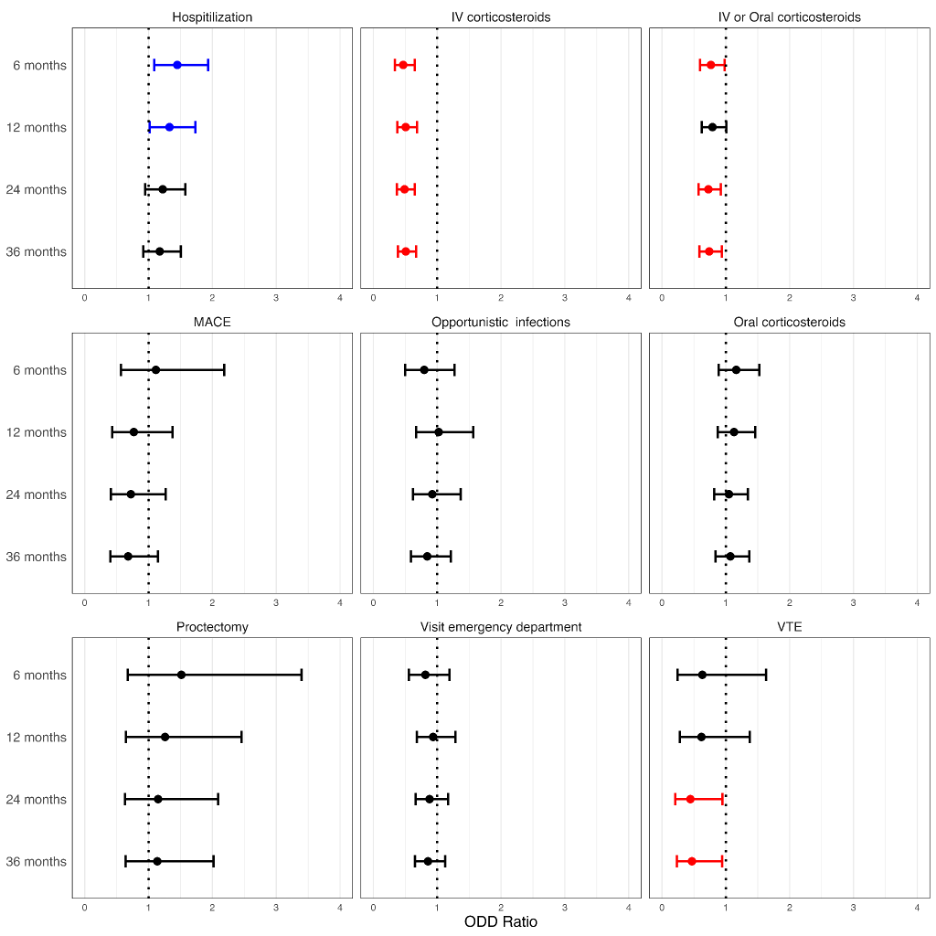
Figure: Comparison of clinical outcomes between tofacitinib and vedolizumab in ulcerative proctitis patients over 36 months
Disclosures:
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maram Albandak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umberto Battistin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hayder Alamily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mhd Kutaiba Albuni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamad Oum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aline Charabaty: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Celltrion – Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. guardant health – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant. scrubs & heels foundation – co-founder. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf, MD1, Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD2, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD2, Sana Rabeeah, MD2, Maram Albandak, MD2, Umberto Battistin, MD2, Hayder Alamily, MD3, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD4, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD5, Shahem Abbarh, MD6, Mulham Alom, MD7, Muhamad Oum, MD8, Amine Rakab, MD9, Aline Charabaty, MD, FACG10, Yaseen Alastal, MD11. P4596 - Tofacitinib vs Vedolizumab: A 36-Month Journey in Ulcerative Proctitis Management With Insights on Efficacy and Safety: Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis Using TriNetX Database, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
