Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4658 - A Case Report and Literature Review of a Rectal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Cv
Claire van Ekdom, BS
Georgetown University School of Medicine
Washington, DC
Presenting Author(s)
1Georgetown University School of Medicine, Washington, DC; 2MedStar Health, Washington, D.C., DC; 3MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction:
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are mesenchymal neoplasms originating from the interstitial cells of Cajal. While a majority of GISTs are found in the stomach, rectal GISTs are rare and make up less than 5% of all GISTs and 0.1% of rectal neoplasms.
Case Description/
Methods:
An 80-year old female presented with an incidental rectal mass on MRI. The patient reported failure to pass stool for 2-3 weeks. No mass was palpated on digital rectal exam (DRE). Flexible sigmoidoscopy identified a 20mm submucosal rectal nodule, but corresponding mucosal biopsies were nondiagnostic. Pelvic MRI revealed a 3 cm lobular mass. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) identified a 3.1 cm multilobulated lesion arising from the muscularis propria (Figure 1). Results from a fine needle biopsy returned positive for spindle cells and CD117, ultimately confirming diagnosis of a rectal GIST. The patient was referred for surgical evaluation.
Discussion:
This case highlights the diagnostic challenges of rectal GISTs.These tumors are often identified incidentally or patients present with nonspecific symptoms. Initial biopsies obtained through flexible sigmoidoscopy are often nondiagnostic due to the submucosal location of rectal GISTs. Ultimately, EUS and biopsy are required for diagnosis. This highlights the diagnostic challenges of GIST and the importance of multidisciplinary coordination to combine expertise and optimize patient care.
Standard treatment for rectal GIST is surgical resection with negative margins (R0) due to the high risk of invasion and local metastasis. In some cases imatinib is used, but due to the rare occurrence of GISTs, there remains a lack of consensus about perioperative treatment. A brief literature review was conducted to summarize tumor size, imatinib use, and outcomes. A search using Ovid MEDLINE for all rectal GIST case reports published in English over the past five years yielded 18 results (Table 1). These findings reinforce the need for further research to establish standardized treatment therapy for rectal GISTs. 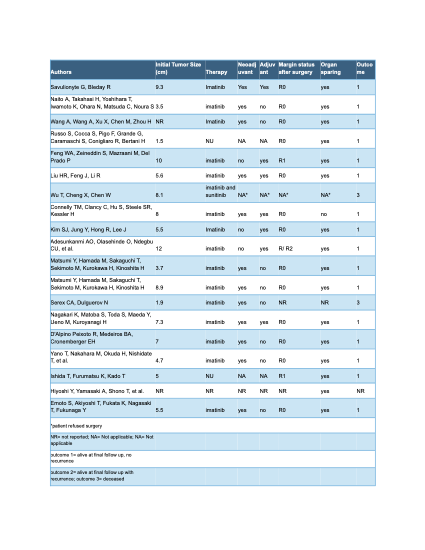
Figure: Table 1: Summary of Published Case Reports on Rectal GISTs (past 5 years). Data adapted from:
1.Savulionyte G, et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2025; 18:e264118.
2. Naito A, et al. Asian Journal of Endoscopic Surg. 2025;18(1):e70025.
3. Wang A, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024;31(12):7796–7797.
4. Russo S, et al. Endoscopy. 2024;56(S 01):E437–E438.
5. Feng WA, et al. Am Surg. 2023;89(7):3289–3291.
6. Liu HR, et al. J Dig Dis. 2022;23(12):720–723.
7. Wu T, Cheng X, Chen W. Medicine. 2022;101(32):e29411.
8. Connelly TM, et al. BMJ Case Reports. 2022;15(3).
9. Kim SJ, et al. Korean J of Gastroenterology. 2021;78(4):235–239.
10. Adesunkanmi AO, et al. The Pan African Medical J. 2021;39:234.
11. Matsumi Y, et al. Colorectal Disease. 2021;23(6):1579–1583.
12. Serex C, et al. BMJ Case Reports. 2021;14(1).
13. Nagakari K, et al. Asian J of Endoscopic Surgery. 2021;14(1):102–105.
14. D'Alpino Peixoto R, et al. J of Gastrointestinal Cancer. 2021;52(1):316–319.
15. Yano T, et al. Asian J of Endoscopic Surg. 2020;13(4):574–577.
16. Ishida T, et al. Dig Endoscopy. 2020;32(3):e49–e51.
17. Hiyoshi Y, et al. Dis of the Colon & Rectum. 2020;63(1):116.
18. Emoto S, et al. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63(11):e542.
Disclosures:
Claire van Ekdom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usman Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srikar Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Al-Dwairy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdalla Khouqeer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walid Chalhoub indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Claire van Ekdom, BS1, Usman Afzal, MD2, Srikar Reddy, MD3, Ahmad Al-Dwairy, MBBS3, Abdalla Khouqeer, MD3, Walid Chalhoub, MD3. P4658 - A Case Report and Literature Review of a Rectal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
