Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P4795 - Shifting Public Interest in Colonoscopy During and After COVID-19: A 10-Year Google Trends Study of Perioperative Search Terms
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- TA
Tarick Ahmad, BS
Albany Medical Center
Albany, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Tarick Ahmad, BS1, Tejash E. Sikka, BS2, Yehya Maitah, 1, Victor Aisogun, BS2, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD1, Seth Richter, MD, FACG1
1Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY; 2Albany Medical College, Albany, NY
Introduction: Colonoscopy is a fundamental procedure for colorectal cancer screening. However, there is limited data whether public interest in colonoscopy has increased over the past decade. Additionally, the COVID pandemic’s impact on patient interest in colonoscopy requires more insight along with which perioperative topics patients most commonly search online. Google Trends provides the relative search volume (RSV) for Google search terms. This study utilizes Google Trends to determine whether public interest in colonoscopy has changed between 2015 and 2025, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, and to identify which colonoscopy-related search terms reflect the highest patient interest.
Methods: A retrospective study on public interest in colonoscopy was performed from January 2015 to June 2025 in the United States using Google Trends. Additionally, 50 perioperative search terms related to colonoscopy were identified through ChatGPT. The mean RSV was calculated for each term. RSV ranges from 0–100 and represents interest in a search term at a specific point during the time frame; 0 is minimal interest and 100 is peak interest. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) compared mean RSVs across terms, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results: Public interest in colonoscopy declined significantly during the early COVID-19 pandemic (mean RSV: 44.0) compared to the pre-pandemic period (mean RSV: 49.8; p = 0.003), followed by a substantial rebound post-COVID (mean RSV: 82.2; p < 0.001 vs both earlier periods). Among the 50 search terms analyzed, several showed significant increases in public interest following COVID. For example, mean RSVs for “how much does a colonoscopy cost” (pre-COVID: 10.1 vs post-COVID: 58.4) and “colonoscopy prep not working” (pre-COVID: 6.6 vs post-COVID: 53.5) increased markedly (both p < 0.001), reflecting possible shifts in patient concerns and preparation challenges. A comprehensive list of notable perioperative terms with sufficient data and their changes across time periods is provided in Figure 1.
Discussion: Patient interest in colonoscopy significantly declined during the early COVID-19 pandemic but has since rebounded to peak levels. Patients are particularly interested in concerns related to bleeding, dietary restrictions, bowel preparation, cost, and procedural necessity. These findings can inform the development of more targeted, patient-centered educational materials that address the most frequently searched concerns regarding colonoscopy.
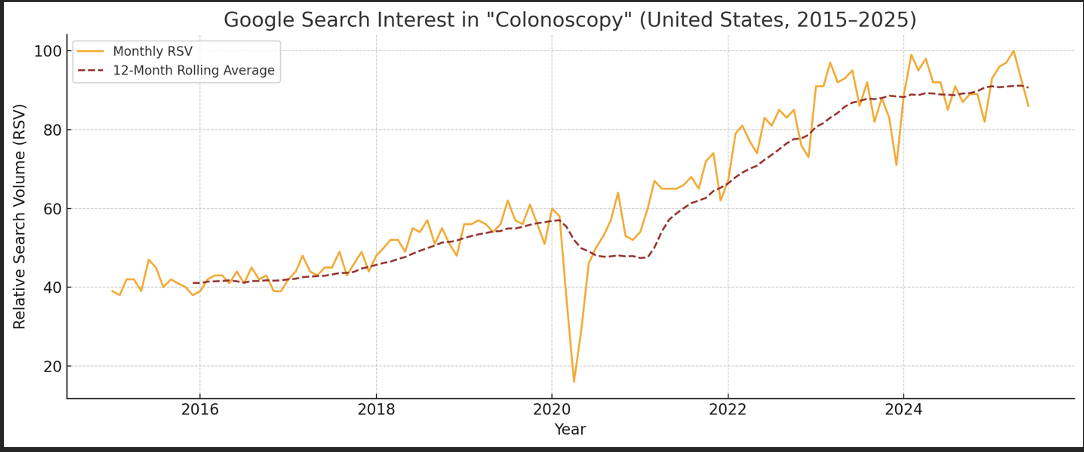
Figure: Change in Public Interest for Common Colonoscopy-Related Search Terms Pre- and Post-COVID-19
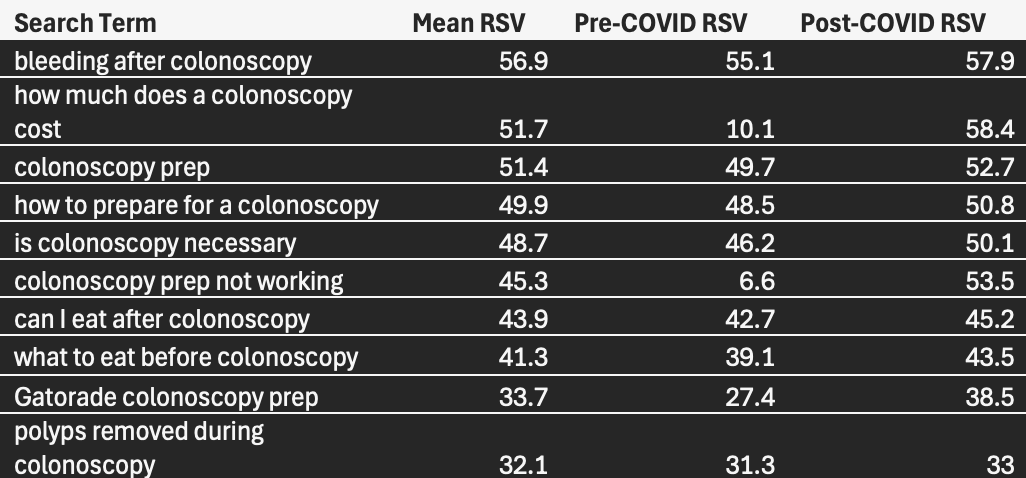
Figure: Monthly and 12-month rolling average RSV for “colonoscopy” (2015–2025), showing a sharp COVID-related dip in 2020 followed by sustained growth in public interest.
Disclosures:
Tarick Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tejash Sikka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yehya Maitah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victor Aisogun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Alshakhatreh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seth Richter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarick Ahmad, BS1, Tejash E. Sikka, BS2, Yehya Maitah, 1, Victor Aisogun, BS2, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD1, Seth Richter, MD, FACG1. P4795 - Shifting Public Interest in Colonoscopy During and After COVID-19: A 10-Year Google Trends Study of Perioperative Search Terms, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY; 2Albany Medical College, Albany, NY
Introduction: Colonoscopy is a fundamental procedure for colorectal cancer screening. However, there is limited data whether public interest in colonoscopy has increased over the past decade. Additionally, the COVID pandemic’s impact on patient interest in colonoscopy requires more insight along with which perioperative topics patients most commonly search online. Google Trends provides the relative search volume (RSV) for Google search terms. This study utilizes Google Trends to determine whether public interest in colonoscopy has changed between 2015 and 2025, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, and to identify which colonoscopy-related search terms reflect the highest patient interest.
Methods: A retrospective study on public interest in colonoscopy was performed from January 2015 to June 2025 in the United States using Google Trends. Additionally, 50 perioperative search terms related to colonoscopy were identified through ChatGPT. The mean RSV was calculated for each term. RSV ranges from 0–100 and represents interest in a search term at a specific point during the time frame; 0 is minimal interest and 100 is peak interest. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) compared mean RSVs across terms, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results: Public interest in colonoscopy declined significantly during the early COVID-19 pandemic (mean RSV: 44.0) compared to the pre-pandemic period (mean RSV: 49.8; p = 0.003), followed by a substantial rebound post-COVID (mean RSV: 82.2; p < 0.001 vs both earlier periods). Among the 50 search terms analyzed, several showed significant increases in public interest following COVID. For example, mean RSVs for “how much does a colonoscopy cost” (pre-COVID: 10.1 vs post-COVID: 58.4) and “colonoscopy prep not working” (pre-COVID: 6.6 vs post-COVID: 53.5) increased markedly (both p < 0.001), reflecting possible shifts in patient concerns and preparation challenges. A comprehensive list of notable perioperative terms with sufficient data and their changes across time periods is provided in Figure 1.
Discussion: Patient interest in colonoscopy significantly declined during the early COVID-19 pandemic but has since rebounded to peak levels. Patients are particularly interested in concerns related to bleeding, dietary restrictions, bowel preparation, cost, and procedural necessity. These findings can inform the development of more targeted, patient-centered educational materials that address the most frequently searched concerns regarding colonoscopy.

Figure: Change in Public Interest for Common Colonoscopy-Related Search Terms Pre- and Post-COVID-19

Figure: Monthly and 12-month rolling average RSV for “colonoscopy” (2015–2025), showing a sharp COVID-related dip in 2020 followed by sustained growth in public interest.
Disclosures:
Tarick Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tejash Sikka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yehya Maitah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victor Aisogun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Alshakhatreh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seth Richter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarick Ahmad, BS1, Tejash E. Sikka, BS2, Yehya Maitah, 1, Victor Aisogun, BS2, Osama Alshakhatreh, MD1, Seth Richter, MD, FACG1. P4795 - Shifting Public Interest in Colonoscopy During and After COVID-19: A 10-Year Google Trends Study of Perioperative Search Terms, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
