Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5495 - A Young Gut Gone Rogue: Ischemic Colitis in a Healthy 22-Year-Old
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MB
Mohamad Ali Borji, MD
Canyon Vista Medical Center
Sierra Vista, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamad Ali Borji, MD1, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD1, Samuel Cheong, DO2
1Canyon Vista Medical Center, Sierra Vista, AZ; 2Banner - University of Arizona Tucson, Tucson, AZ
Introduction: Ischemic colitis (IC) is the most common form of gastrointestinal (GI) ischemia, resulting from compromised colonic blood flow. Predisposing factors include trauma, thrombosis, systemic hypoperfusion, mechanical obstruction, and certain medications. We present a rare case of IC in an otherwise healthy young adult without identifiable risk factors.
Case Description/
Methods: A 22-year-old male with no significant medical history presented with sudden-onset abdominal pain and hematochezia. He denied significant alcohol use, recreational drugs, NSAID use, or recent antibiotics but reported vaping nicotine for three years and social alcohol consumption. A CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed findings consistent with ischemic colitis of the distal ileum. Emergent exploratory laparotomy showed diffuse inflammation of the transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon, along with dilated and hyperemic small bowel loops, suggesting a global inflammatory process. His hospital course was complicated by shock requiring vasopressors and acute renal failure needing dialysis.
Colonoscopy with biopsies confirmed active colitis with ulceration and ileitis. Infectious, autoimmune (vasculitis), and hypercoagulable workups were unremarkable, and urine toxicology was negative. Fecal calprotectin was significantly elevated at 3710 μg/g. Biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of acute ischemic colitis. The patient improved with supportive care and was discharged with plans for outpatient gastroenterology follow-up and a repeat colonoscopy.
Discussion: Acute ischemic colitis typically occurs in older adults with risk factors such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypercoagulable states. In this young patient, transient hypoperfusion from hemodynamic instability and vasopressor use likely contributed. Ketamine administration may have further affected cardiovascular dynamics. Although comprehensive evaluations were negative, transient mesenteric thrombosis or microvascular injury during systemic inflammation cannot be excluded. Notably, animal studies suggest that chronic vaping induces oxidative stress and colonic inflammation, possibly compromising mucosal integrity and predisposing to ischemic injury. This case underscores the multifactorial nature of ischemic colitis in young adults and highlights vaping as a potential, emerging risk factor.
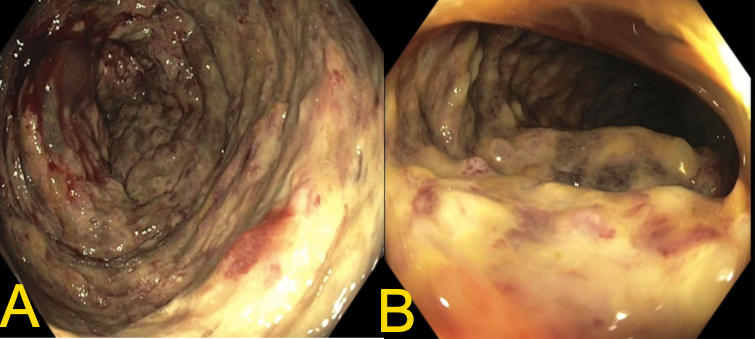
Figure: Image A taken from the transverse colon.
Image B taken from the sigmoid colon.
Both revealing diffuse severe mucosal changes characterized by congestion (edema), erosions, erythema, friability, granularity, loss of vascularity, mucus and deep ulcerations.
Disclosures:
Mohamad Ali Borji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Omar Diab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samuel Cheong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Ali Borji, MD1, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD1, Samuel Cheong, DO2. P5495 - A Young Gut Gone Rogue: Ischemic Colitis in a Healthy 22-Year-Old, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Canyon Vista Medical Center, Sierra Vista, AZ; 2Banner - University of Arizona Tucson, Tucson, AZ
Introduction: Ischemic colitis (IC) is the most common form of gastrointestinal (GI) ischemia, resulting from compromised colonic blood flow. Predisposing factors include trauma, thrombosis, systemic hypoperfusion, mechanical obstruction, and certain medications. We present a rare case of IC in an otherwise healthy young adult without identifiable risk factors.
Case Description/
Methods: A 22-year-old male with no significant medical history presented with sudden-onset abdominal pain and hematochezia. He denied significant alcohol use, recreational drugs, NSAID use, or recent antibiotics but reported vaping nicotine for three years and social alcohol consumption. A CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed findings consistent with ischemic colitis of the distal ileum. Emergent exploratory laparotomy showed diffuse inflammation of the transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon, along with dilated and hyperemic small bowel loops, suggesting a global inflammatory process. His hospital course was complicated by shock requiring vasopressors and acute renal failure needing dialysis.
Colonoscopy with biopsies confirmed active colitis with ulceration and ileitis. Infectious, autoimmune (vasculitis), and hypercoagulable workups were unremarkable, and urine toxicology was negative. Fecal calprotectin was significantly elevated at 3710 μg/g. Biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of acute ischemic colitis. The patient improved with supportive care and was discharged with plans for outpatient gastroenterology follow-up and a repeat colonoscopy.
Discussion: Acute ischemic colitis typically occurs in older adults with risk factors such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypercoagulable states. In this young patient, transient hypoperfusion from hemodynamic instability and vasopressor use likely contributed. Ketamine administration may have further affected cardiovascular dynamics. Although comprehensive evaluations were negative, transient mesenteric thrombosis or microvascular injury during systemic inflammation cannot be excluded. Notably, animal studies suggest that chronic vaping induces oxidative stress and colonic inflammation, possibly compromising mucosal integrity and predisposing to ischemic injury. This case underscores the multifactorial nature of ischemic colitis in young adults and highlights vaping as a potential, emerging risk factor.

Figure: Image A taken from the transverse colon.
Image B taken from the sigmoid colon.
Both revealing diffuse severe mucosal changes characterized by congestion (edema), erosions, erythema, friability, granularity, loss of vascularity, mucus and deep ulcerations.
Disclosures:
Mohamad Ali Borji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Omar Diab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samuel Cheong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Ali Borji, MD1, Mohamad Omar Diab, MD1, Samuel Cheong, DO2. P5495 - A Young Gut Gone Rogue: Ischemic Colitis in a Healthy 22-Year-Old, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
