Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5815 - A Meta-Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatments for MASLD
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Xavier Zonna, DO
University at Buffalo
Buffalo, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Xavier Zonna, DO1, Conor Banta, MD2, Lan Nguyen, DO1
1University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 2Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Providence, RI
Introduction: MASLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat and inflammation in the liver. It is rapidly increasing in frequency along with obesity and metabolic dysfunction and is becoming a common etiology of cirrhosis and liver transplantation. Patients with T2DM are at elevated risk for development of MASLD and liver fibrosis. T2DM treatments are thought to improve MASLD by reducing insulin sensitivity and promoting weight loss and reduced adipose tissue thereby reducing hepatic fat. This meta-analysis examines SGLT-2 and GLP-1 treatments for fibrosis reduction in patients with MASLD.
Methods: A literature search using PubMed was performed for randomized control trials involving adult T2DM treatments using SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists for the treatment of MASLD from 2015-2024. Studies were included if they examined improvement in liver fibrosis staging by biopsy or advanced imaging. Studies measuring fibrosis by laboratory indices were excluded. Odds ratio calculations and 95% confidence intervals were used to assess fibrosis reduction in each study. In addition to I2 calculation, fixed and random effects models were applied to evaluate data heterogeneity.
Results: Heterogeneity of fibrosis data was low with I2 of 0% and significant fixed and random effects models (p < 0.001). Out of the seven trials only Takahashi et al. (ipragliflozin) and Loomba et al. (tirzepatide) displayed significant fibrosis reduction (p < 0.05) (Table 1). There was significant variability as evidenced by the size of the confidence intervals in several trials (Figure 1).
Discussion: Only 2 of 7 trials found significant reductions in liver fibrosis for patients. Variation in these results may be due to factors including limited populations in biopsy-proven MASLD trials in addition to dosage differences in the medications used. Population differences are also possible but likely non-contributory in the setting of low data heterogeneity. Despite only 2 significant trials, fixed and random effects models demonstrate these medications significantly reduce fibrosis on average. The data suggests that tirzepatide is superior to other GLP-1 medications which may be the result of its unique action as a dual GLP and GIP agonist leading to increased weight loss. In addition, ipragliflozin may have greater effects on adipose reduction than tofogliflozin as suggested by the trial outcomes. Although further large-scale studies are needed, these results are encouraging for the future of T2DM medications as MASLD treatments.
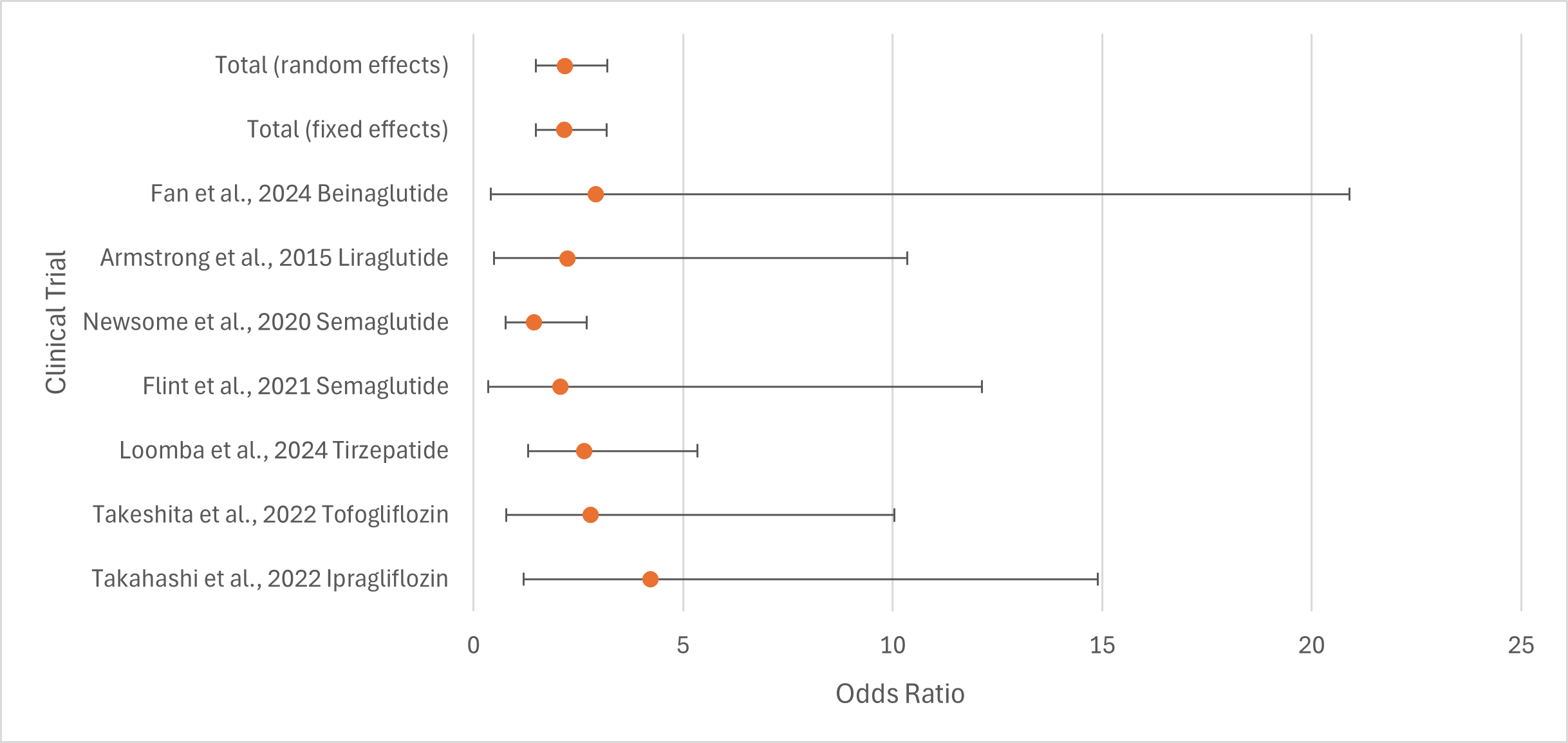
Figure: Table 1: Meta analysis of liver fibrosis reduction for T2DM treatments

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot of meta-analysis of liver fibrosis reduction
Disclosures:
Xavier Zonna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Conor Banta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lan Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xavier Zonna, DO1, Conor Banta, MD2, Lan Nguyen, DO1. P5815 - A Meta-Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatments for MASLD, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 2Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Providence, RI
Introduction: MASLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat and inflammation in the liver. It is rapidly increasing in frequency along with obesity and metabolic dysfunction and is becoming a common etiology of cirrhosis and liver transplantation. Patients with T2DM are at elevated risk for development of MASLD and liver fibrosis. T2DM treatments are thought to improve MASLD by reducing insulin sensitivity and promoting weight loss and reduced adipose tissue thereby reducing hepatic fat. This meta-analysis examines SGLT-2 and GLP-1 treatments for fibrosis reduction in patients with MASLD.
Methods: A literature search using PubMed was performed for randomized control trials involving adult T2DM treatments using SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists for the treatment of MASLD from 2015-2024. Studies were included if they examined improvement in liver fibrosis staging by biopsy or advanced imaging. Studies measuring fibrosis by laboratory indices were excluded. Odds ratio calculations and 95% confidence intervals were used to assess fibrosis reduction in each study. In addition to I2 calculation, fixed and random effects models were applied to evaluate data heterogeneity.
Results: Heterogeneity of fibrosis data was low with I2 of 0% and significant fixed and random effects models (p < 0.001). Out of the seven trials only Takahashi et al. (ipragliflozin) and Loomba et al. (tirzepatide) displayed significant fibrosis reduction (p < 0.05) (Table 1). There was significant variability as evidenced by the size of the confidence intervals in several trials (Figure 1).
Discussion: Only 2 of 7 trials found significant reductions in liver fibrosis for patients. Variation in these results may be due to factors including limited populations in biopsy-proven MASLD trials in addition to dosage differences in the medications used. Population differences are also possible but likely non-contributory in the setting of low data heterogeneity. Despite only 2 significant trials, fixed and random effects models demonstrate these medications significantly reduce fibrosis on average. The data suggests that tirzepatide is superior to other GLP-1 medications which may be the result of its unique action as a dual GLP and GIP agonist leading to increased weight loss. In addition, ipragliflozin may have greater effects on adipose reduction than tofogliflozin as suggested by the trial outcomes. Although further large-scale studies are needed, these results are encouraging for the future of T2DM medications as MASLD treatments.

Figure: Table 1: Meta analysis of liver fibrosis reduction for T2DM treatments

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot of meta-analysis of liver fibrosis reduction
Disclosures:
Xavier Zonna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Conor Banta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lan Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xavier Zonna, DO1, Conor Banta, MD2, Lan Nguyen, DO1. P5815 - A Meta-Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatments for MASLD, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
