Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5806 - Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Multicenter Propensity-Matched Longitudinal Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahmed Salem, MD
Maimonides Medical Center
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmed Salem, MD1, Sarah Meribout, MD1, Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD2, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD3, Neha Sharma, MD1, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Islam Mohamed, MD5, Fatima Khan, MD1, Syed Mujtaba Baqir, MD1, Samantha Ehrlich, MD1, Samar Pal S. Sandhu, MBBS1, Rajdeep Singh, MD6, Islam Rajab, MD7, Carla Barberan Parraga, MD1, Avleen Kaur, MD8, Nakul Mahajan, MBBS1, Abdallah Hussein, MD9, Tanuj Chokshi, MD1, Joseph Menand, MD1, MariaLisa Itzoe, DO, MPH1, Bani Roland, MD10, Yuriy Tsirlin, MD1, Gerard Mullin, MD11, Mohammad Alomari, MD12, Mauricio Garcia, MD13, Aaron Z. Tokayer, MD, MHS1
1Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Mount Sinai West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 3Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 5University of Missouri Columbia, Columbia, MO; 6PEACEHEALTH, Longview, WA; 7St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 8SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 9Virtua Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital, Camden, NJ; 10Brooklyn VA Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 11Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 12University of Arkansas, Little Rock, AR; 13University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction:
Background:
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) is increasingly recognized as a systemic metabolic condition. While it has been associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), the long-term real-world magnitude of this risk remains underexplored.
Aim:
To assess the incidence and predictors of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with MASLD compared to matched non-MASLD controls.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective multicenter cohort study using TriNetX, a U.S.-based network of longitudinal electronic health records. Adults (≥18 years) diagnosed with MAFLD (ICD-10: K76.0) from Jan 1, 2010, to Dec 31, 2023, were included. Exclusion criteria: prior MI, stroke, cardiovascular procedures, alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, or cirrhosis at baseline.
Controls were matched 1:1 for age, sex, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, tobacco use, and use of statins or antiplatelets.
The primary outcome was 5-year incidence of MACE: MI, stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), and cardiovascular death. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) were estimated via Cox models controlling for metabolic syndrome, HbA1c, and medications. Kaplan-Meier analysis illustrated cumulative risk.
Results: After matching, 48,552 patients (24,276 per group) were included. Mean age: 57.4 years; 52.8% female. Median follow-up: 5.2 years.
MASLD patients had significantly higher 5-year MACE incidence:
Statin use was protective in both groups (aHR 0.67; 95% CI: 0.56–0.80). Sensitivity analyses confirmed findings across subgroups by diabetes, sex, LDL, and BMI. Kaplan-Meier curves showed divergence by 24 months, with sustained separation over 5 years.
Discussion: MASLD is independently linked to increased long-term risk of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death. These real-world findings support classifying MASLD as a systemic disease and underscore the need for early cardiovascular screening, aggressive risk management, and statin therapy.
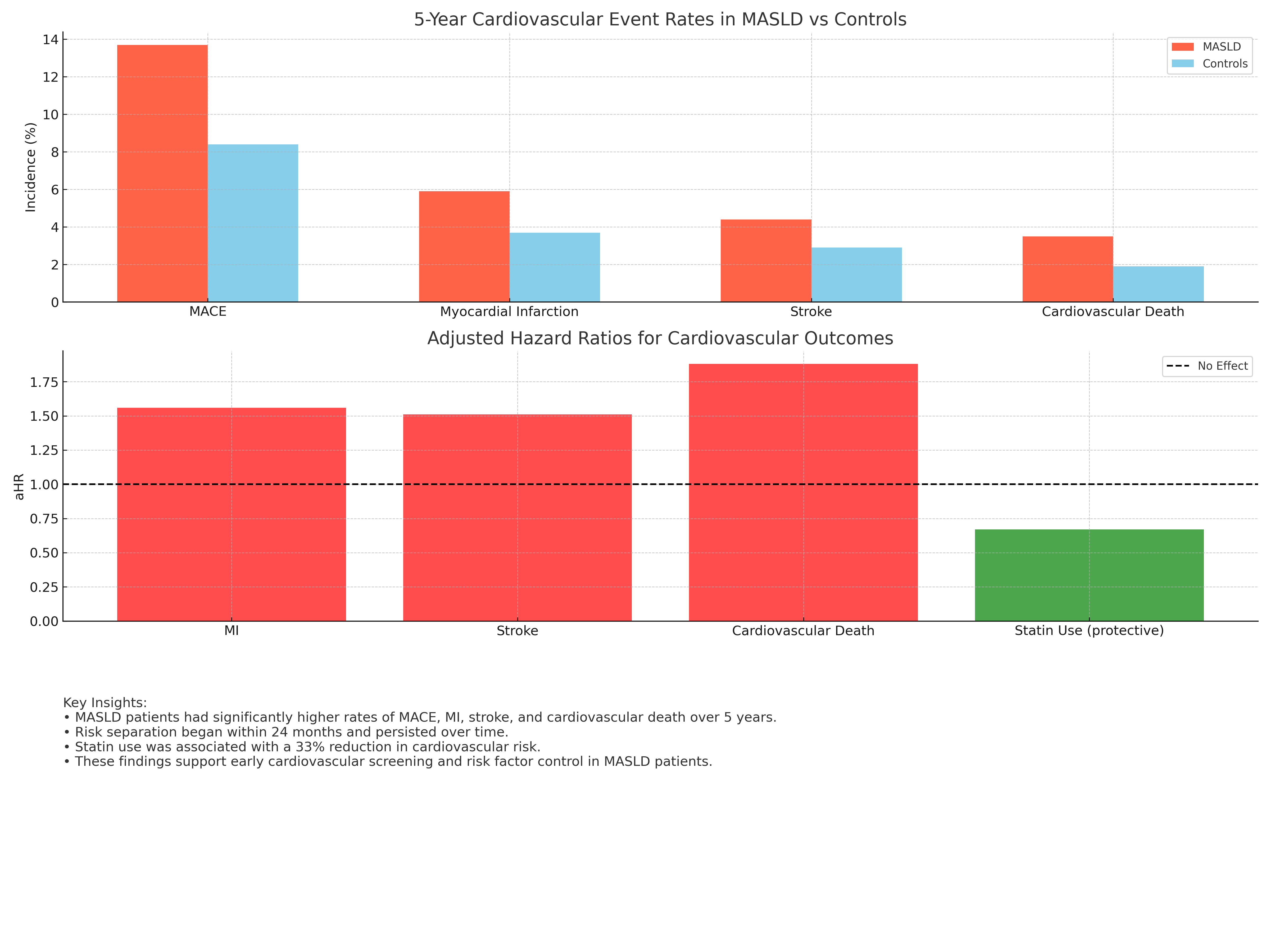
Figure: • MASLD patients had significantly higher rates of MACE, MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death over 5 years.
• Risk separation began within 24 months and persisted over time.
• Statin use was associated with a 33% reduction in cardiovascular risk.
• These findings support early cardiovascular screening and risk factor control in MASLD
Disclosures:
Ahmed Salem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Meribout indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hazem Abosheaishaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abusuliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abdelhalim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatima Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Mujtaba Baqir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samantha Ehrlich indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samar Pal Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajdeep Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Rajab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Barberan Parraga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avleen Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nakul Mahajan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Hussein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanuj Chokshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Menand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
MariaLisa Itzoe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bani Roland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yuriy Tsirlin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gerard Mullin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Alomari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Tokayer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Salem, MD1, Sarah Meribout, MD1, Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD2, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD3, Neha Sharma, MD1, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Islam Mohamed, MD5, Fatima Khan, MD1, Syed Mujtaba Baqir, MD1, Samantha Ehrlich, MD1, Samar Pal S. Sandhu, MBBS1, Rajdeep Singh, MD6, Islam Rajab, MD7, Carla Barberan Parraga, MD1, Avleen Kaur, MD8, Nakul Mahajan, MBBS1, Abdallah Hussein, MD9, Tanuj Chokshi, MD1, Joseph Menand, MD1, MariaLisa Itzoe, DO, MPH1, Bani Roland, MD10, Yuriy Tsirlin, MD1, Gerard Mullin, MD11, Mohammad Alomari, MD12, Mauricio Garcia, MD13, Aaron Z. Tokayer, MD, MHS1. P5806 - Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Multicenter Propensity-Matched Longitudinal Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Mount Sinai West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 3Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 5University of Missouri Columbia, Columbia, MO; 6PEACEHEALTH, Longview, WA; 7St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 8SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 9Virtua Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital, Camden, NJ; 10Brooklyn VA Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 11Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 12University of Arkansas, Little Rock, AR; 13University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction:
Background:
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) is increasingly recognized as a systemic metabolic condition. While it has been associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), the long-term real-world magnitude of this risk remains underexplored.
Aim:
To assess the incidence and predictors of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with MASLD compared to matched non-MASLD controls.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective multicenter cohort study using TriNetX, a U.S.-based network of longitudinal electronic health records. Adults (≥18 years) diagnosed with MAFLD (ICD-10: K76.0) from Jan 1, 2010, to Dec 31, 2023, were included. Exclusion criteria: prior MI, stroke, cardiovascular procedures, alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, or cirrhosis at baseline.
Controls were matched 1:1 for age, sex, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, tobacco use, and use of statins or antiplatelets.
The primary outcome was 5-year incidence of MACE: MI, stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), and cardiovascular death. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) were estimated via Cox models controlling for metabolic syndrome, HbA1c, and medications. Kaplan-Meier analysis illustrated cumulative risk.
Results: After matching, 48,552 patients (24,276 per group) were included. Mean age: 57.4 years; 52.8% female. Median follow-up: 5.2 years.
MASLD patients had significantly higher 5-year MACE incidence:
MACE: 13.7% vs 8.4% (p< 0.001)
MI: 5.9% vs 3.7%; aHR 1.56 (95% CI: 1.39–1.74)
Stroke: 4.4% vs 2.9%; aHR 1.51 (95% CI: 1.32–1.73)
CV death: 3.5% vs 1.9%; aHR 1.88 (95% CI: 1.55–2.29)
Statin use was protective in both groups (aHR 0.67; 95% CI: 0.56–0.80). Sensitivity analyses confirmed findings across subgroups by diabetes, sex, LDL, and BMI. Kaplan-Meier curves showed divergence by 24 months, with sustained separation over 5 years.
Discussion: MASLD is independently linked to increased long-term risk of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death. These real-world findings support classifying MASLD as a systemic disease and underscore the need for early cardiovascular screening, aggressive risk management, and statin therapy.

Figure: • MASLD patients had significantly higher rates of MACE, MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death over 5 years.
• Risk separation began within 24 months and persisted over time.
• Statin use was associated with a 33% reduction in cardiovascular risk.
• These findings support early cardiovascular screening and risk factor control in MASLD
Disclosures:
Ahmed Salem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Meribout indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hazem Abosheaishaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abusuliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abdelhalim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatima Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Mujtaba Baqir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samantha Ehrlich indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samar Pal Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajdeep Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Rajab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carla Barberan Parraga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avleen Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nakul Mahajan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallah Hussein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanuj Chokshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Menand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
MariaLisa Itzoe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bani Roland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yuriy Tsirlin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gerard Mullin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Alomari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Tokayer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Salem, MD1, Sarah Meribout, MD1, Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD2, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD3, Neha Sharma, MD1, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Islam Mohamed, MD5, Fatima Khan, MD1, Syed Mujtaba Baqir, MD1, Samantha Ehrlich, MD1, Samar Pal S. Sandhu, MBBS1, Rajdeep Singh, MD6, Islam Rajab, MD7, Carla Barberan Parraga, MD1, Avleen Kaur, MD8, Nakul Mahajan, MBBS1, Abdallah Hussein, MD9, Tanuj Chokshi, MD1, Joseph Menand, MD1, MariaLisa Itzoe, DO, MPH1, Bani Roland, MD10, Yuriy Tsirlin, MD1, Gerard Mullin, MD11, Mohammad Alomari, MD12, Mauricio Garcia, MD13, Aaron Z. Tokayer, MD, MHS1. P5806 - Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Multicenter Propensity-Matched Longitudinal Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
