Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5883 - Efficacy and Safety of Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Islam Rajab, MD
St. Joseph's University Medical Center
Paterson, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammad Tanshat, 1, Maram Albandak, MD, MPH2, Mohamed Saad Rakab, 3, Islam Rajab, MD4, AlMothana Manasrah, 5, Nour Fakih, 6, Husam Abu Suilik, MD7, Alshayma Alalawneh, 1, Hashem Al-Gharaibeh, 1, Mai S. Obeidat, 1, Minnat Allah Al Akash, 8, Ahmed Salem, MD9, Alisa Farokhian, 4, Walid Baddoura, MD4
1Faculty of Medicine, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 2Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, Toledo, OH; 3Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 4St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 5United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY, USA, Johnson City, NY; 6School of Dental Medicine, BAU International University, Batumi, Georgia, Batumi, Ajaria, Georgia; 7The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 8Mai S. Obeidat Faculty of Medicine, Yarmouk University Obeidat.s.mai@gmail.com, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 9Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) lacks approved pharmacotherapy. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing semaglutide to placebo on histological, biochemical, metabolic, and safety outcomes in NASH.
Methods: 3 trials (n=1191) were included. Outcomes pooled using random-effects models, reporting risk ratios (RR) or mean differences (MD) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI), P-values, and heterogeneity (I²). PROSPERO ID: CRD420251045059.
Results: Semaglutide markedly increased NASH resolution without fibrosis worsening (RR 3.55, P < 0.0001) but did not significantly improve fibrosis stage (RR 1.31, P = 0.61). It reduced liver-stiffness final scores (MD –1.95, P = 0.02) and Enhanced Liver Fibrosis scores (MD –1.65, P = 0.007). Semaglutide also lowered AST (MD –11.23 U/L, P < 0.0001), ALT (MD –15.21 U/L, P < 0.0001), and GGT (MD –24.00 U/L, P < 0.0001). Metabolic benefits included greater weight loss (MD –13.65 kg, P < 0.0001) and HbA1c reduction (MD –1.59 %, P < 0.0001). Overall adverse events were comparable (RR 1.02, P = 0.42), with increased gastrointestinal events; nausea (RR 2.88), constipation (RR 2.16), diarrhea (RR 2.07), vomiting (RR 3.98), and decreased appetite (RR 4.59, all P < 0.0001). Serious and other non-GI adverse events did not differ.
Discussion: Semaglutide significantly improves histological, biochemical, and metabolic parameters in NASH with an acceptable safety profile, though gastrointestinal tolerability warrants monitoring.
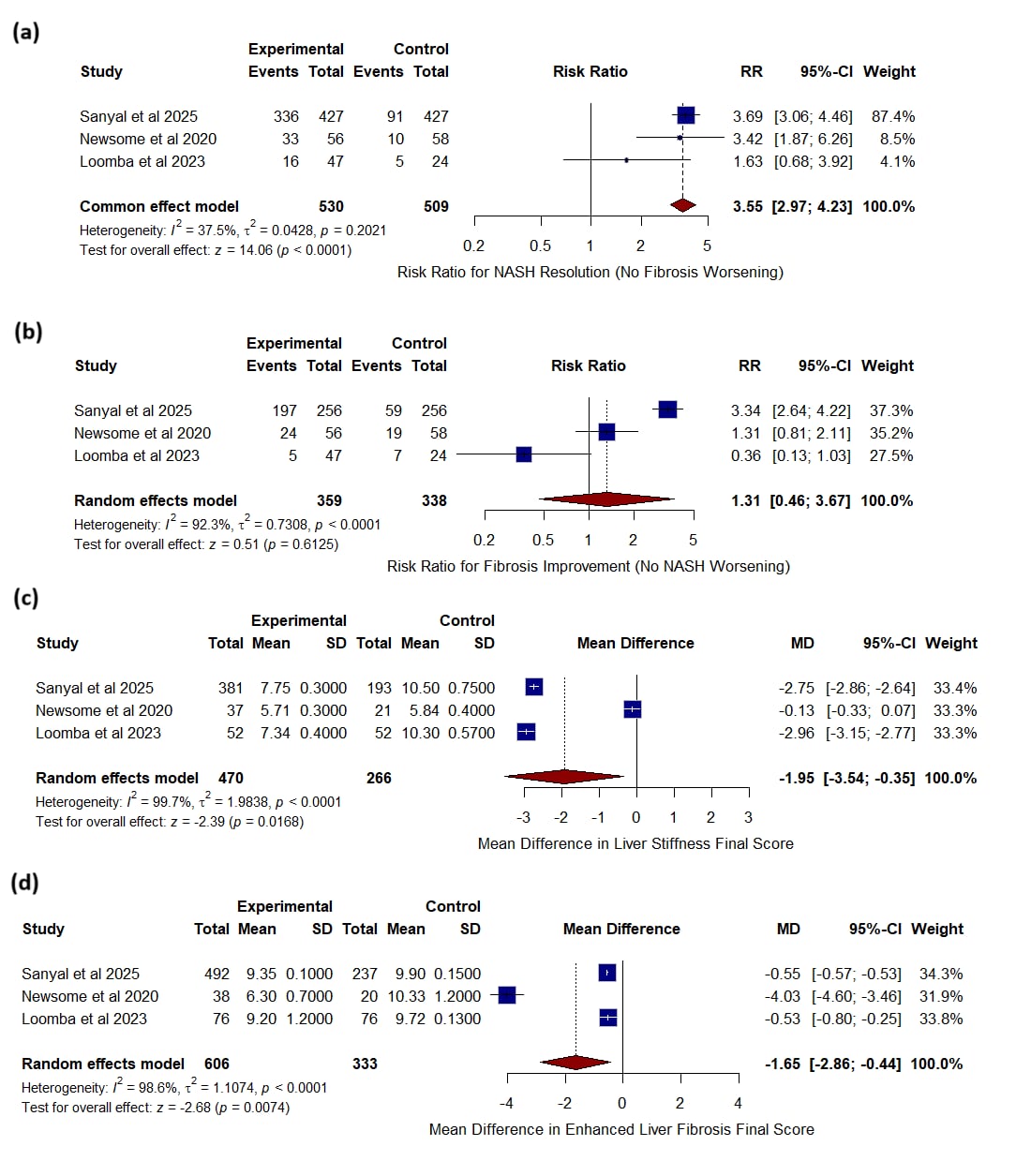
Figure: Figure 1 . Forest plots showing the effect of semaglutide versus control on (a) NASH resolution without fibrosis worsening, (b) fibrosis improvement without NASH worsening, (c) liver stiffness final score, and (d) enhanced liver fibrosis final score.
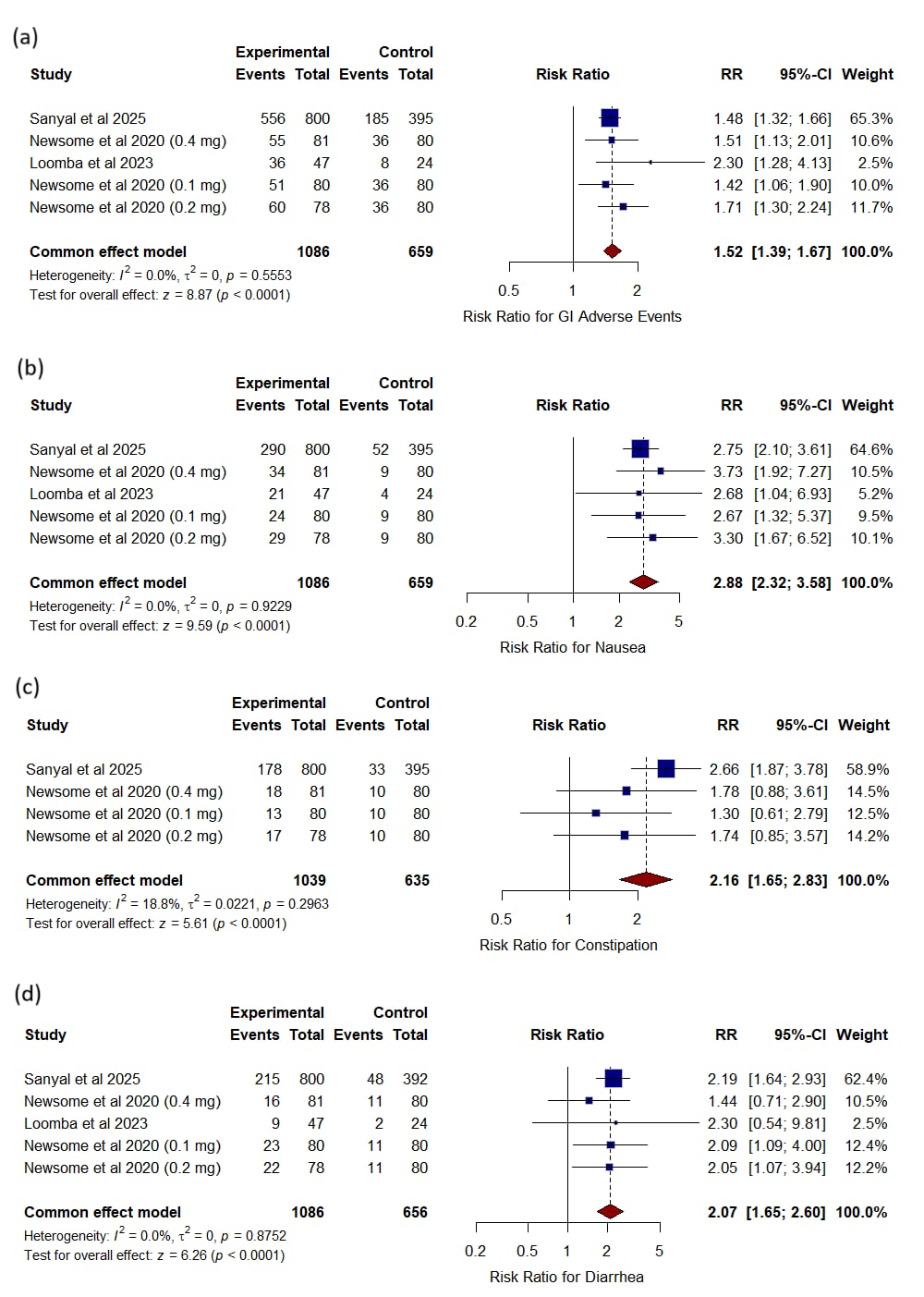
Figure: Figure2. Forest plots showing the risk ratio for (a) GI adverse events, (b) nausea, (c) constipation, and (d) diarrhea, in patients receiving semaglutide compared to control.
Disclosures:
Mohammad Tanshat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maram Albandak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Saad Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Rajab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
AlMothana Manasrah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nour Fakih indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alshayma Alalawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hashem Al-Gharaibeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mai S. Obeidat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minnat Allah Al Akash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Salem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alisa Farokhian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walid Baddoura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Tanshat, 1, Maram Albandak, MD, MPH2, Mohamed Saad Rakab, 3, Islam Rajab, MD4, AlMothana Manasrah, 5, Nour Fakih, 6, Husam Abu Suilik, MD7, Alshayma Alalawneh, 1, Hashem Al-Gharaibeh, 1, Mai S. Obeidat, 1, Minnat Allah Al Akash, 8, Ahmed Salem, MD9, Alisa Farokhian, 4, Walid Baddoura, MD4. P5883 - Efficacy and Safety of Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Faculty of Medicine, Yarmouk University, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 2Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, Toledo, OH; 3Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 4St. Joseph's University Medical Center, Paterson, NJ; 5United Health Services, Wilson Medical Center, Johnson City, NY, USA, Johnson City, NY; 6School of Dental Medicine, BAU International University, Batumi, Georgia, Batumi, Ajaria, Georgia; 7The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 8Mai S. Obeidat Faculty of Medicine, Yarmouk University Obeidat.s.mai@gmail.com, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 9Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) lacks approved pharmacotherapy. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing semaglutide to placebo on histological, biochemical, metabolic, and safety outcomes in NASH.
Methods: 3 trials (n=1191) were included. Outcomes pooled using random-effects models, reporting risk ratios (RR) or mean differences (MD) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI), P-values, and heterogeneity (I²). PROSPERO ID: CRD420251045059.
Results: Semaglutide markedly increased NASH resolution without fibrosis worsening (RR 3.55, P < 0.0001) but did not significantly improve fibrosis stage (RR 1.31, P = 0.61). It reduced liver-stiffness final scores (MD –1.95, P = 0.02) and Enhanced Liver Fibrosis scores (MD –1.65, P = 0.007). Semaglutide also lowered AST (MD –11.23 U/L, P < 0.0001), ALT (MD –15.21 U/L, P < 0.0001), and GGT (MD –24.00 U/L, P < 0.0001). Metabolic benefits included greater weight loss (MD –13.65 kg, P < 0.0001) and HbA1c reduction (MD –1.59 %, P < 0.0001). Overall adverse events were comparable (RR 1.02, P = 0.42), with increased gastrointestinal events; nausea (RR 2.88), constipation (RR 2.16), diarrhea (RR 2.07), vomiting (RR 3.98), and decreased appetite (RR 4.59, all P < 0.0001). Serious and other non-GI adverse events did not differ.
Discussion: Semaglutide significantly improves histological, biochemical, and metabolic parameters in NASH with an acceptable safety profile, though gastrointestinal tolerability warrants monitoring.

Figure: Figure 1 . Forest plots showing the effect of semaglutide versus control on (a) NASH resolution without fibrosis worsening, (b) fibrosis improvement without NASH worsening, (c) liver stiffness final score, and (d) enhanced liver fibrosis final score.

Figure: Figure2. Forest plots showing the risk ratio for (a) GI adverse events, (b) nausea, (c) constipation, and (d) diarrhea, in patients receiving semaglutide compared to control.
Disclosures:
Mohammad Tanshat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maram Albandak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Saad Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Rajab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
AlMothana Manasrah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nour Fakih indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alshayma Alalawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hashem Al-Gharaibeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mai S. Obeidat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minnat Allah Al Akash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Salem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alisa Farokhian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Walid Baddoura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Tanshat, 1, Maram Albandak, MD, MPH2, Mohamed Saad Rakab, 3, Islam Rajab, MD4, AlMothana Manasrah, 5, Nour Fakih, 6, Husam Abu Suilik, MD7, Alshayma Alalawneh, 1, Hashem Al-Gharaibeh, 1, Mai S. Obeidat, 1, Minnat Allah Al Akash, 8, Ahmed Salem, MD9, Alisa Farokhian, 4, Walid Baddoura, MD4. P5883 - Efficacy and Safety of Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
