Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5878 - Mechanistic Meta-Analysis of Cell-Based Immunotherapies Targeting the Hepatic Tumor Microenvironment Across the Cirrhosis-HCC Spectrum
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MK
Meghana Kakarla, MD
Infirmary Health
Mobile, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Meghana Kakarla, MD1, Ashvath Pillai, 2, Giovannie Isaac-Coss, MD3, Muhammad Ali Khan, MBBS4, Gurmanleen Singh. Sohi, MBBS5, Nilay Bhatt, MD6
1Infirmary Health, Mobile, AL; 2SSPM Medical College and Lifetime Hospital, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India; 3Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL; 4Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ; 5Government Medical College,Patiala, Patiala, Punjab, India; 6HCA Houston Clear Lake, Houston, TX
Introduction: Cell-based therapies targeting the hepatic tumor microenvironment (TME) pose as promising approaches for managing patients in the liver cirrhosis-hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) spectrum.This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates their efficacy, safety, and alignment across preclinical and clinical studies.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases from 2007-2023 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, and preclinical experiments on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), CAR-T, and CAR-NK therapies.Primary outcomes were overall survival. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2 (RCTs), ROBINS-I (observational studies), and SYRCLE tools (preclinical studies). Random-effects meta-analysis was performed for homogeneous outcomes, with evidence certainty evaluated using GRADE. Preclinical findings were narratively synthesized for mechanistic insights into biomarker modulation and immune cell interactions.
Results: A total of 18 studies were identified: 4 RCTs (n=378), 6 observational studies, and 8 preclinical experiments were included.
Meta Analysis
"MSC therapy showed a non-significant trend toward reduced mortality (pooled HR=0.74; 95%CI: 0.45-1.22; p=0.241), representing a 25.8% mortality reduction. Sensitivity analysis excluding smaller studies achieved significance (HR=0.626; 95%CI: 0.438-0.895; p< 0.05). Umbilical cord-derived MSCs demonstrated the strongest survival benefit in HBV cirrhosis (HR=0.62; 95%CI: 0.43-0.88). CAR-T Studies: Preliminary efficacy signals observed in advanced HCC with manageable cytokine release syndrome.
Mechanistic Insights
Preclinical studies demonstrated consistent TME remodeling: increased CD8+ T cells and M1 macrophages, decreased regulatory T cells and M2 macrophages, with downregulation of TGF-β and IL-10. Evidence certainty ranged from low to moderate (GRADE assessment).
Discussion: We analysed how cell-based precision immunotherapies hold excellent potential for modifying the hepatic microenvironment and enhancing patient outcomes in HCC through our analysis of trial level data.To reach its full therapeutic potential, larger phase 3 trials, biomarker standardisation, and combinatorial approaches are necessary. High heterogeneity (I² = 77.4%) was attributable to variations in liver pathology, MSC source (autologous vs. allogeneic), and follow-up duration (3–75 months).
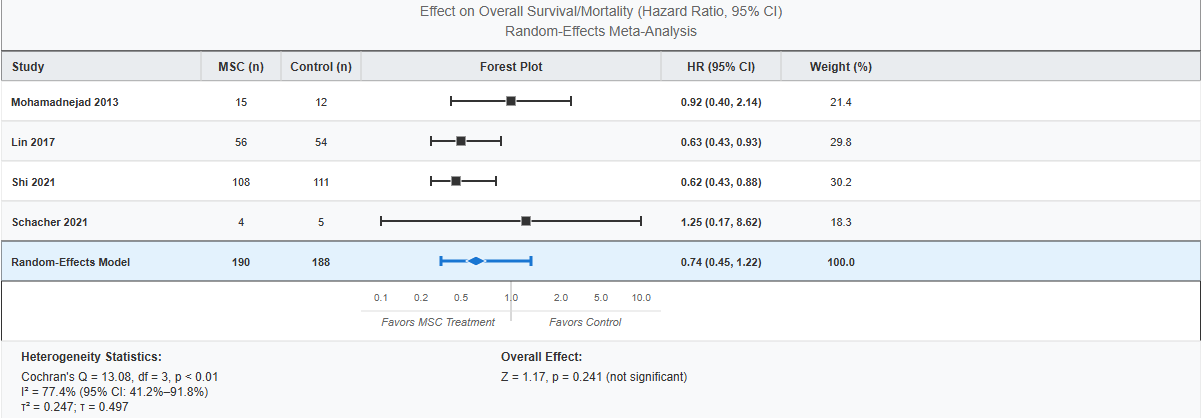
Figure: Forest Plot of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy Effect on Overall Survival/Mortality in HCC
Disclosures:
Meghana Kakarla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashvath Pillai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Giovannie Isaac-Coss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurmanleen Sohi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilay Bhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meghana Kakarla, MD1, Ashvath Pillai, 2, Giovannie Isaac-Coss, MD3, Muhammad Ali Khan, MBBS4, Gurmanleen Singh. Sohi, MBBS5, Nilay Bhatt, MD6. P5878 - Mechanistic Meta-Analysis of Cell-Based Immunotherapies Targeting the Hepatic Tumor Microenvironment Across the Cirrhosis-HCC Spectrum, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Infirmary Health, Mobile, AL; 2SSPM Medical College and Lifetime Hospital, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India; 3Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL; 4Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ; 5Government Medical College,Patiala, Patiala, Punjab, India; 6HCA Houston Clear Lake, Houston, TX
Introduction: Cell-based therapies targeting the hepatic tumor microenvironment (TME) pose as promising approaches for managing patients in the liver cirrhosis-hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) spectrum.This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates their efficacy, safety, and alignment across preclinical and clinical studies.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases from 2007-2023 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, and preclinical experiments on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), CAR-T, and CAR-NK therapies.Primary outcomes were overall survival. Risk of bias was assessed using RoB 2 (RCTs), ROBINS-I (observational studies), and SYRCLE tools (preclinical studies). Random-effects meta-analysis was performed for homogeneous outcomes, with evidence certainty evaluated using GRADE. Preclinical findings were narratively synthesized for mechanistic insights into biomarker modulation and immune cell interactions.
Results: A total of 18 studies were identified: 4 RCTs (n=378), 6 observational studies, and 8 preclinical experiments were included.
Meta Analysis
"MSC therapy showed a non-significant trend toward reduced mortality (pooled HR=0.74; 95%CI: 0.45-1.22; p=0.241), representing a 25.8% mortality reduction. Sensitivity analysis excluding smaller studies achieved significance (HR=0.626; 95%CI: 0.438-0.895; p< 0.05). Umbilical cord-derived MSCs demonstrated the strongest survival benefit in HBV cirrhosis (HR=0.62; 95%CI: 0.43-0.88). CAR-T Studies: Preliminary efficacy signals observed in advanced HCC with manageable cytokine release syndrome.
Mechanistic Insights
Preclinical studies demonstrated consistent TME remodeling: increased CD8+ T cells and M1 macrophages, decreased regulatory T cells and M2 macrophages, with downregulation of TGF-β and IL-10. Evidence certainty ranged from low to moderate (GRADE assessment).
Discussion: We analysed how cell-based precision immunotherapies hold excellent potential for modifying the hepatic microenvironment and enhancing patient outcomes in HCC through our analysis of trial level data.To reach its full therapeutic potential, larger phase 3 trials, biomarker standardisation, and combinatorial approaches are necessary. High heterogeneity (I² = 77.4%) was attributable to variations in liver pathology, MSC source (autologous vs. allogeneic), and follow-up duration (3–75 months).

Figure: Forest Plot of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy Effect on Overall Survival/Mortality in HCC
Disclosures:
Meghana Kakarla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashvath Pillai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Giovannie Isaac-Coss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurmanleen Sohi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilay Bhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meghana Kakarla, MD1, Ashvath Pillai, 2, Giovannie Isaac-Coss, MD3, Muhammad Ali Khan, MBBS4, Gurmanleen Singh. Sohi, MBBS5, Nilay Bhatt, MD6. P5878 - Mechanistic Meta-Analysis of Cell-Based Immunotherapies Targeting the Hepatic Tumor Microenvironment Across the Cirrhosis-HCC Spectrum, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
