Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5934 - Nationwide Trends and Inequities in Hepatorenal Syndrome Mortality in the United States: A 24-Year Population-Based Study (1999-2022)
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool
Mayo Clinic
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Usama Idrees, MBBS1, Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool, 2, Akshit Bhambri, MBBS3, Humza Saeed, 4, Safa Nasir, MBBS5, Usama Qamar, MBBS6, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS7, Khansha Saeed, MBBS8, Talha Ashraf Zia, MBBS9, Ali Dheyaa Marsool, 10
1Khawaja Muhammad Safdar Medical College, Sialkot, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ; 3ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 4Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 7Services Institute of Medical Sciences, New Haven, CT; 8Rashid Latif Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 9King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 10Al-Kindy College of Medicine, Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
Introduction: Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of advanced liver disease, resulting in progressive renal dysfunction and poor clinical outcomes. Despite advancements in liver disease management, HRS continues to carry high morbidity and mortality. However, long-term national trends and sociodemographic disparities in HRS-related mortality remain relatively understudied.
Methods: We conducted a population-based analysis using data from the CDC WONDER database from 1999 to 2022, identifying HRS-related deaths in U.S. adults via ICD-10 code K76.7. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated and stratified by age, sex, race/ethnicity and geographic location. Joinpoint regression was used to evaluate temporal trends, reporting annual percent changes (APCs) with 95% confidence intervals. Statistical significance was defined as p< 0.05.
Results: A total of 107,615 U.S. adults died from HRS between 1999 and 2022, with 75% deaths reported in the medical facilities. The overall AAMR per 100,000 declined significantly from 2.43 in 1999 to 1.83 in 2008 (APC: –3.44; p< 0.01), followed by a non-significant increase to 1.90 in 2018 (APC: 0.52; p=0.35), and then a significant rise to 2.33 by 2022 (APC: 6.90; p< 0.01) (Figure 1). Males consistently exhibited higher AAMRs than females (2.78 vs 1.38). While older adults had the highest overall AAMR (3.97), younger adults experienced the sharpest increase from 2017 to 2022 (APC: 15.92; p< 0.01). Racial disparities were evident, with the highest AAMRs observed among non-Hispanic (NH) American Indian or Alaska Native individuals (8.34), followed by Hispanic (2.94), NH White (1.97), NH Black (1.84), and NH Asian or Pacific Islander (1.11) groups. Non-metropolitan areas had higher AAMRs (2.44) than metropolitan areas (1.91). Regionally, the West reported the highest overall AAMR (2.62) while lowest one was noted in Midwest (1.73). State level analysis revealed highest death rates in New Mexico (7.16) followed by Wyoming (6.56).
Discussion: These findings reveal a concerning resurgence in HRS mortality in recent years, reversing earlier declines. The highest AAMRs were observed among NH American Indian or Alaska Native individuals, males, older adults, and residents of non-metropolitan and Western regions. These disparities urgently call for equity-focused interventions, improved access to specialized liver and renal care, and culturally tailored strategies to reduce the growing burden of HRS among vulnerable populations.
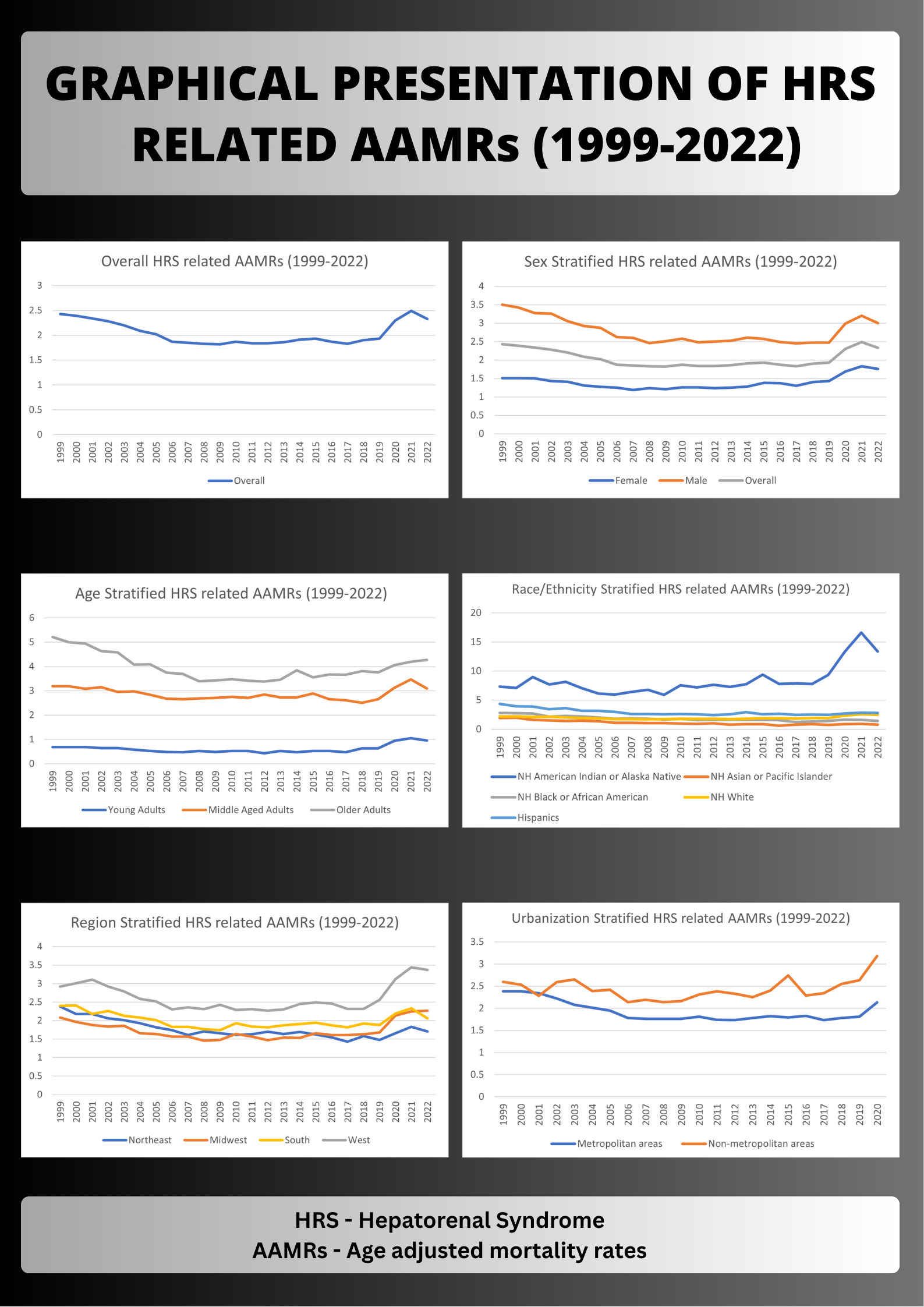
Figure: Graphical figures
Disclosures:
Usama Idrees indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akshit Bhambri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humza Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Safa Nasir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Qamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khansha Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Ashraf Zia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Dheyaa Marsool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Idrees, MBBS1, Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool, 2, Akshit Bhambri, MBBS3, Humza Saeed, 4, Safa Nasir, MBBS5, Usama Qamar, MBBS6, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS7, Khansha Saeed, MBBS8, Talha Ashraf Zia, MBBS9, Ali Dheyaa Marsool, 10. P5934 - Nationwide Trends and Inequities in Hepatorenal Syndrome Mortality in the United States: A 24-Year Population-Based Study (1999-2022), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Khawaja Muhammad Safdar Medical College, Sialkot, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, AZ; 3ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 4Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 7Services Institute of Medical Sciences, New Haven, CT; 8Rashid Latif Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 9King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 10Al-Kindy College of Medicine, Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
Introduction: Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of advanced liver disease, resulting in progressive renal dysfunction and poor clinical outcomes. Despite advancements in liver disease management, HRS continues to carry high morbidity and mortality. However, long-term national trends and sociodemographic disparities in HRS-related mortality remain relatively understudied.
Methods: We conducted a population-based analysis using data from the CDC WONDER database from 1999 to 2022, identifying HRS-related deaths in U.S. adults via ICD-10 code K76.7. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated and stratified by age, sex, race/ethnicity and geographic location. Joinpoint regression was used to evaluate temporal trends, reporting annual percent changes (APCs) with 95% confidence intervals. Statistical significance was defined as p< 0.05.
Results: A total of 107,615 U.S. adults died from HRS between 1999 and 2022, with 75% deaths reported in the medical facilities. The overall AAMR per 100,000 declined significantly from 2.43 in 1999 to 1.83 in 2008 (APC: –3.44; p< 0.01), followed by a non-significant increase to 1.90 in 2018 (APC: 0.52; p=0.35), and then a significant rise to 2.33 by 2022 (APC: 6.90; p< 0.01) (Figure 1). Males consistently exhibited higher AAMRs than females (2.78 vs 1.38). While older adults had the highest overall AAMR (3.97), younger adults experienced the sharpest increase from 2017 to 2022 (APC: 15.92; p< 0.01). Racial disparities were evident, with the highest AAMRs observed among non-Hispanic (NH) American Indian or Alaska Native individuals (8.34), followed by Hispanic (2.94), NH White (1.97), NH Black (1.84), and NH Asian or Pacific Islander (1.11) groups. Non-metropolitan areas had higher AAMRs (2.44) than metropolitan areas (1.91). Regionally, the West reported the highest overall AAMR (2.62) while lowest one was noted in Midwest (1.73). State level analysis revealed highest death rates in New Mexico (7.16) followed by Wyoming (6.56).
Discussion: These findings reveal a concerning resurgence in HRS mortality in recent years, reversing earlier declines. The highest AAMRs were observed among NH American Indian or Alaska Native individuals, males, older adults, and residents of non-metropolitan and Western regions. These disparities urgently call for equity-focused interventions, improved access to specialized liver and renal care, and culturally tailored strategies to reduce the growing burden of HRS among vulnerable populations.

Figure: Graphical figures
Disclosures:
Usama Idrees indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akshit Bhambri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humza Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Safa Nasir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Qamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khansha Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Ashraf Zia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Dheyaa Marsool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Idrees, MBBS1, Mohammed Dheyaa Marsool, 2, Akshit Bhambri, MBBS3, Humza Saeed, 4, Safa Nasir, MBBS5, Usama Qamar, MBBS6, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS7, Khansha Saeed, MBBS8, Talha Ashraf Zia, MBBS9, Ali Dheyaa Marsool, 10. P5934 - Nationwide Trends and Inequities in Hepatorenal Syndrome Mortality in the United States: A 24-Year Population-Based Study (1999-2022), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
