Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5952 - Trends in Complications and Resource Utilization Among Hospitalized Patients With MASLD: A Nationwide Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MS
Mehul Solanki
Maulana Azad Medical College
Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Mehul Solanki, 1, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD3, Anmol Singh, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS6
1Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 3University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL; 4Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a leading cause of chronic liver disease and liver-related mortality in the United States. Despite its rising prevalence and multisystem involvement, national trends in outcomes and resource utilization among hospitalized patients with MASLD are understudied. This study evaluates the trends in complications and outcomes among hospitalized patients with MASLD using a large, nationally representative cohort.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database was used to identify adult patients with MASLD who were hospitalized from 2016 to 2022. Data were collected on patient demographics, comorbidity burden, and hepatic and systemic complications (including cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), decompensated cirrhosis, acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), in-hospital mortality, cardiovascular and renal complications). Multivariate linear regression was used to determine the trends of various complications and resource utilization.
Results: A total of 5.1 million MASLD-related hospitalizations were identified and included in this study. Between 2016 and 2022, cardiovascular complications showed a significant upward trend: myocardial infarction increased from 2.6% to 4.6% (p< 0.001), stroke from 1.0% to 1.4% (p< 0.001), and congestive heart failure from 20.0% to 24.8% (p< 0.001). Liver-related complications also rose, with decompensated cirrhosis increasing from 20.1% to 22.2% and ACLF from 7.5% to 9.3% (p< 0.001). Notably, the prevalence of chronic kidney disease rose from 22.8% to 24.9% (p< 0.001). Healthcare resource utilization also increased between 2016 and 2022, with mean hospitalization charges rising from $62,114 to $90,809 (p< 0.001) and length of stay increasing from 5.56 to 6.01 days (p< 0.001). The mortality among patients with MASLD rose from 4.6% in 2016 to 5.4% in 2021, and then returned to 4.7% in 2022 (p< 0.001). Trends in complications and resource utilization are illustrated in Figure 1. and Figure 2., respectively.
Discussion: Over the past decade, hospitalizations related to MASLD have been marked by a growing burden of cardiovascular and renal complications, as well as liver decompensation, despite stable mortality rates. These findings underscore the importance of early identification, multidisciplinary management, and preventive strategies to mitigate systemic complications and optimize the utilization of healthcare resources in this high-risk population.
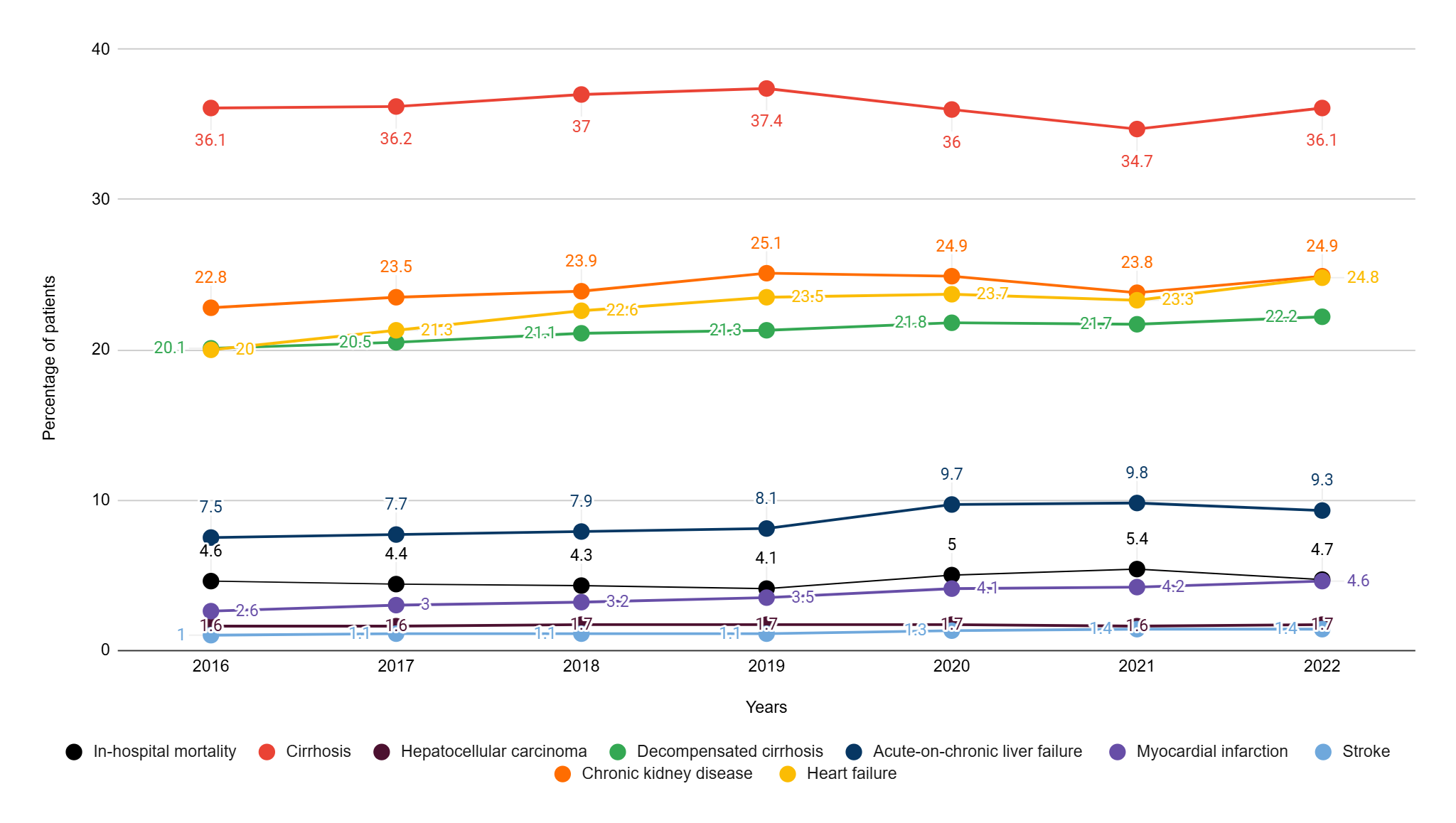
Figure: Figure 1. Trends in complications each year from 2016-2022.
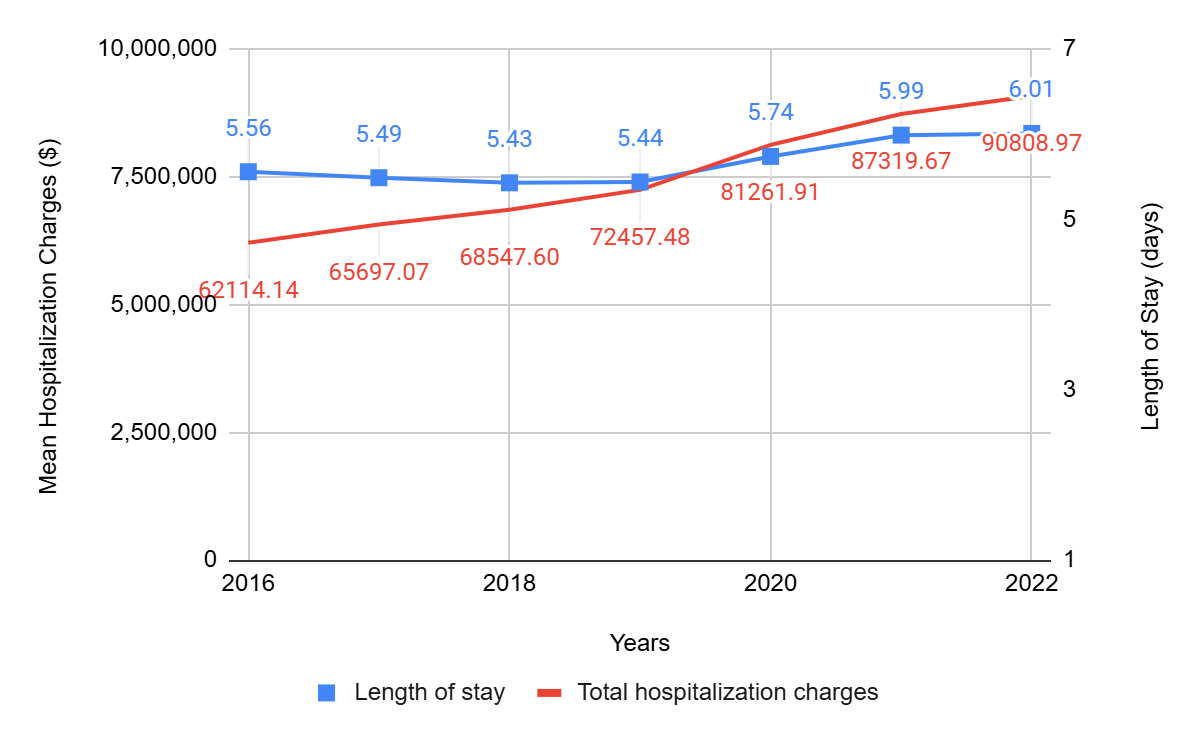
Figure: Figure 2. Trends in resource utilization each year from 2016-2022.
Disclosures:
Mehul Solanki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsimran Kalsi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Divyesh Sejpal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Grant/Research Support.
Mehul Solanki, 1, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD3, Anmol Singh, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS6. P5952 - Trends in Complications and Resource Utilization Among Hospitalized Patients With MASLD: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 3University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL; 4Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a leading cause of chronic liver disease and liver-related mortality in the United States. Despite its rising prevalence and multisystem involvement, national trends in outcomes and resource utilization among hospitalized patients with MASLD are understudied. This study evaluates the trends in complications and outcomes among hospitalized patients with MASLD using a large, nationally representative cohort.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database was used to identify adult patients with MASLD who were hospitalized from 2016 to 2022. Data were collected on patient demographics, comorbidity burden, and hepatic and systemic complications (including cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), decompensated cirrhosis, acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), in-hospital mortality, cardiovascular and renal complications). Multivariate linear regression was used to determine the trends of various complications and resource utilization.
Results: A total of 5.1 million MASLD-related hospitalizations were identified and included in this study. Between 2016 and 2022, cardiovascular complications showed a significant upward trend: myocardial infarction increased from 2.6% to 4.6% (p< 0.001), stroke from 1.0% to 1.4% (p< 0.001), and congestive heart failure from 20.0% to 24.8% (p< 0.001). Liver-related complications also rose, with decompensated cirrhosis increasing from 20.1% to 22.2% and ACLF from 7.5% to 9.3% (p< 0.001). Notably, the prevalence of chronic kidney disease rose from 22.8% to 24.9% (p< 0.001). Healthcare resource utilization also increased between 2016 and 2022, with mean hospitalization charges rising from $62,114 to $90,809 (p< 0.001) and length of stay increasing from 5.56 to 6.01 days (p< 0.001). The mortality among patients with MASLD rose from 4.6% in 2016 to 5.4% in 2021, and then returned to 4.7% in 2022 (p< 0.001). Trends in complications and resource utilization are illustrated in Figure 1. and Figure 2., respectively.
Discussion: Over the past decade, hospitalizations related to MASLD have been marked by a growing burden of cardiovascular and renal complications, as well as liver decompensation, despite stable mortality rates. These findings underscore the importance of early identification, multidisciplinary management, and preventive strategies to mitigate systemic complications and optimize the utilization of healthcare resources in this high-risk population.

Figure: Figure 1. Trends in complications each year from 2016-2022.

Figure: Figure 2. Trends in resource utilization each year from 2016-2022.
Disclosures:
Mehul Solanki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsimran Kalsi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Divyesh Sejpal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Grant/Research Support.
Mehul Solanki, 1, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD3, Anmol Singh, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Divyesh Sejpal, MD, MS6. P5952 - Trends in Complications and Resource Utilization Among Hospitalized Patients With MASLD: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
