Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5861 - Liver Fibrosis Progression to Cirrhosis: A Geospatial Mortality Burden Analysis in the United States (1999-2023)
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Haseeb Faiz, MD
Mobile Infirmary Medical Centre
Mobile, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Shamikha Cheema, MBBS1, Shan Muhammad Mughal, MBBS1, Haseeb Faiz, MD2, Laiba Sarfraz, MBBS1, Muhammad Faique Hassan, MBBS1, Muhammad Shaheer Bin Faheem, MBBS3, Hussnain Mushtaq, MBBS1
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Mobile Infirmary Medical Centre, Mobile, AL; 3Karachi Institute of Medical Sciences, KIMS, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis, resulting from chronic liver injury, are major health concerns worldwide. Fibrosis involves excessive scarring, while cirrhosis leads to architectural distortion and loss of liver function, contributing to significant morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Data was extracted from CDC WONDER database (1999-2020 and 2018-2023) involving IDC- 10 Codes – K74 (Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of Liver) using Age-Adjusted Mortality Rate (AAMR) per 1,000,000 individuals. Join point Regression (Version 5.1.0 National Cancer Institute) was used to assess Annual Percent Change (APC) and Average APCs (AAPC) with 95% Confidence Interval. Data analysis was done to assess the significance of mortality trends in different groups.
Results: A total of 951,879 deaths have been reported from 1999-2023. AAMR increased from 1999(107.616) to 2023(125.202) with the AAPC of 0.5872(95%Cl: -0.6072 to 1.7959). AAMR of males (134.9) was higher than females (78.9) but the AAPC of females: 1.3585 (95%Cl: 0.3388 to 2.3886) was more than males: 0.1483 (95%Cl: -0.8756 to 1.1827). South had the highest AAMR (122.3) followed by West (103.1), Midwest (95.8) and Northeast (94.8). All regions except Northeast (AAPC: -0.3278; 95%Cl: -1.3556 to -0.7107) showed an increase in AAPC. South exhibited the highest AAPC of 0.9671 (95%Cl: -0.1592 to 2.1060). AAMR was highest for American Indians (171.054) followed by Whites (108.286), African Americans (98.147) and Asians (60.29) from 1999-2020 where data from 2020 onwards was unavailable. Whites showed the highest AAPC of 0.5509 (95%Cl: -0.4463 to 1.5581). Among the US states, AAMR was highest for Texas (166.399) and lowest for Nebraska (61.115). Greater number of deaths (218308) were recorded in 55-64 year age group with 75-84 years of age group showing the highest AAPC of 1.3446 (95%Cl: 0.6551 to 2.0388). Stata analysis revealed significant association across mortality trend among the following variables: gender, census regions and age groups.
Discussion: Liver failure deaths from fibrosis and cirrhosis rose from 1999–2023, with higher rates among males, southern American region, and American Indians. Older adults and females showed faster increases, highlighting urgent need for targeted prevention and healthcare improvement.
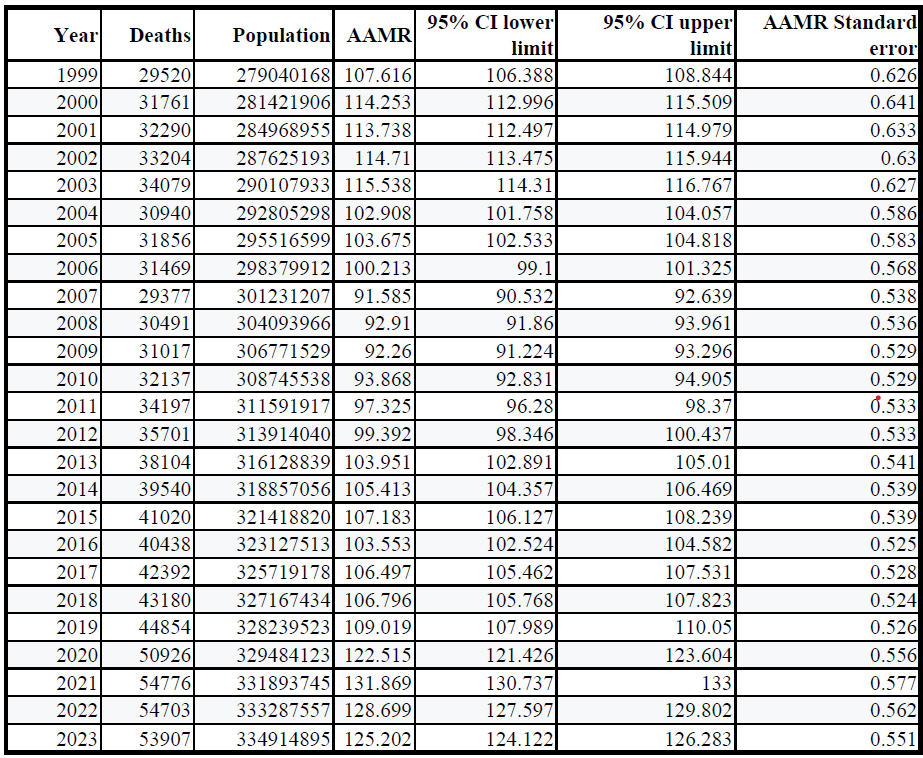
Figure: Liver Fibrosis Progression to Cirrhosis: A Geospatial Mortality Burden Analysis in the United States
Disclosures:
Shamikha Cheema indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shan Muhammad Mughal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Faiz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laiba Sarfraz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Faique Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shaheer Bin Faheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hussnain Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shamikha Cheema, MBBS1, Shan Muhammad Mughal, MBBS1, Haseeb Faiz, MD2, Laiba Sarfraz, MBBS1, Muhammad Faique Hassan, MBBS1, Muhammad Shaheer Bin Faheem, MBBS3, Hussnain Mushtaq, MBBS1. P5861 - Liver Fibrosis Progression to Cirrhosis: A Geospatial Mortality Burden Analysis in the United States (1999-2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Mobile Infirmary Medical Centre, Mobile, AL; 3Karachi Institute of Medical Sciences, KIMS, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis, resulting from chronic liver injury, are major health concerns worldwide. Fibrosis involves excessive scarring, while cirrhosis leads to architectural distortion and loss of liver function, contributing to significant morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Data was extracted from CDC WONDER database (1999-2020 and 2018-2023) involving IDC- 10 Codes – K74 (Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of Liver) using Age-Adjusted Mortality Rate (AAMR) per 1,000,000 individuals. Join point Regression (Version 5.1.0 National Cancer Institute) was used to assess Annual Percent Change (APC) and Average APCs (AAPC) with 95% Confidence Interval. Data analysis was done to assess the significance of mortality trends in different groups.
Results: A total of 951,879 deaths have been reported from 1999-2023. AAMR increased from 1999(107.616) to 2023(125.202) with the AAPC of 0.5872(95%Cl: -0.6072 to 1.7959). AAMR of males (134.9) was higher than females (78.9) but the AAPC of females: 1.3585 (95%Cl: 0.3388 to 2.3886) was more than males: 0.1483 (95%Cl: -0.8756 to 1.1827). South had the highest AAMR (122.3) followed by West (103.1), Midwest (95.8) and Northeast (94.8). All regions except Northeast (AAPC: -0.3278; 95%Cl: -1.3556 to -0.7107) showed an increase in AAPC. South exhibited the highest AAPC of 0.9671 (95%Cl: -0.1592 to 2.1060). AAMR was highest for American Indians (171.054) followed by Whites (108.286), African Americans (98.147) and Asians (60.29) from 1999-2020 where data from 2020 onwards was unavailable. Whites showed the highest AAPC of 0.5509 (95%Cl: -0.4463 to 1.5581). Among the US states, AAMR was highest for Texas (166.399) and lowest for Nebraska (61.115). Greater number of deaths (218308) were recorded in 55-64 year age group with 75-84 years of age group showing the highest AAPC of 1.3446 (95%Cl: 0.6551 to 2.0388). Stata analysis revealed significant association across mortality trend among the following variables: gender, census regions and age groups.
Discussion: Liver failure deaths from fibrosis and cirrhosis rose from 1999–2023, with higher rates among males, southern American region, and American Indians. Older adults and females showed faster increases, highlighting urgent need for targeted prevention and healthcare improvement.

Figure: Liver Fibrosis Progression to Cirrhosis: A Geospatial Mortality Burden Analysis in the United States
Disclosures:
Shamikha Cheema indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shan Muhammad Mughal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Faiz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laiba Sarfraz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Faique Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shaheer Bin Faheem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hussnain Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shamikha Cheema, MBBS1, Shan Muhammad Mughal, MBBS1, Haseeb Faiz, MD2, Laiba Sarfraz, MBBS1, Muhammad Faique Hassan, MBBS1, Muhammad Shaheer Bin Faheem, MBBS3, Hussnain Mushtaq, MBBS1. P5861 - Liver Fibrosis Progression to Cirrhosis: A Geospatial Mortality Burden Analysis in the United States (1999-2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
