Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5846 - BALAD-2 Emerges as the Most Accurate Prognostic Model in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results From a Biobank-Based Cohort Study
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Coskun O. Demirtas, MD
Marmara University, Institute of Gastroenterology
Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey
Presenting Author(s)
Coskun O. Demirtas, MD1, Fatih Eren, MD, PhD1, Demet Yilmaz, MSc1, Yasemin Armutcuoglu Kaldirim, MD2, Tugba Tolu, MD2, Javid Huseynov, MD2, Ugur Ciftci, MD2, Tuba Yilmaz, MD2, Sehnaz Akin, MD3, Osman C. Ozdogan, MD2
1Marmara University, Institute of Gastroenterology, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 2Marmara University School of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 3Marmara University School of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey
Introduction: Accurate prognostication in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains essential for treatment selection and risk stratification. This study aimed to compare the prognostic performance of individual serum biomarkers (AFP, AFP-L3%, and DCP) and composite scoring models—including GALAD, BALAD, BALAD-2, GAAP, ASAP, Doylestown algorithm, and aMAP—using data from a biobank-based HCC cohort.
Methods: We enrolled 186 patients with confirmed HCC diagnoses with available serum, clinical and follow-up data, between 2019 and 2024 from Marmara University HCC biobank. Serum levels of AFP, AFP-L3% and DCP were measured and used to calculate composite scores using validated formulas. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Prognostic performance was assessed using time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) at 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year intervals and Harrel's concordance index (c-index). Subgroup analyses were performed by treatment intent (curative vs. non-curative) and liver disease etiology (viral vs. non-viral).
Results: The median age was 65 years; 74.7% of patients were male, and 90.3% had underlying cirrhosis. HBV was the most common etiology (49.5%), followed by MASLD (29.0%) and HCV (14.0%). Among all models, BALAD-2 showed the top-performing prognostic accuracy (c-index=0.737) with highest AUROCs at 1-year (0.827), 2-year (0.846), 3-year (0.781), and 5-year (0.716). BALAD-2 consistently showed superior discrimination in both patients treated with curative (c-index=0.698) or non-curative therapies (0.716) with highest c-indexes, and AUROCs across most time points. BALAD-2 demonstrated the best prognostic discriminative accuracy in viral etiology by highest c-index (0.726), and AUROCs at 1-year (0.846), 2-year (0.853), and 5-year (0.758). In non-viral etiology subgroup, BALAD-2 remained among the top performers, although GAAP, ASAP, Doylestown and GALAD showed slightly higher c-index and AUROCs at different time points.
Discussion: BALAD-2 outperformed other biomarker-based and clinical composite prognostic models in predicting survival among patients with HCC, regardless of treatment type, with particularly strong performance in those with viral etiologies. These findings support its integration into clinical risk stratification and decision making in HCC management.
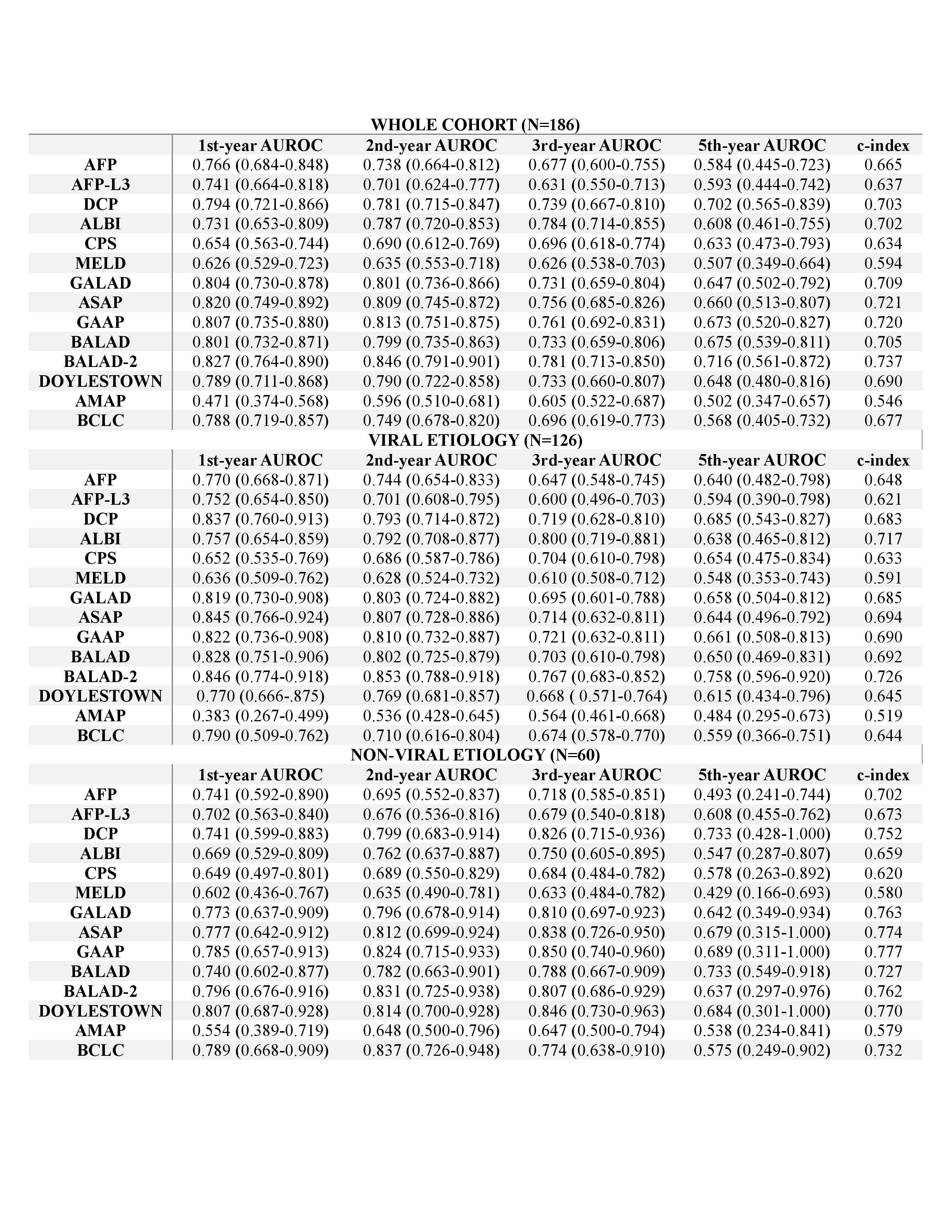
Figure: Table 1. Comparison of the prognostic discriminative ability of biomarkers and prognostic models, including subgroup analyses by liver disease etiology
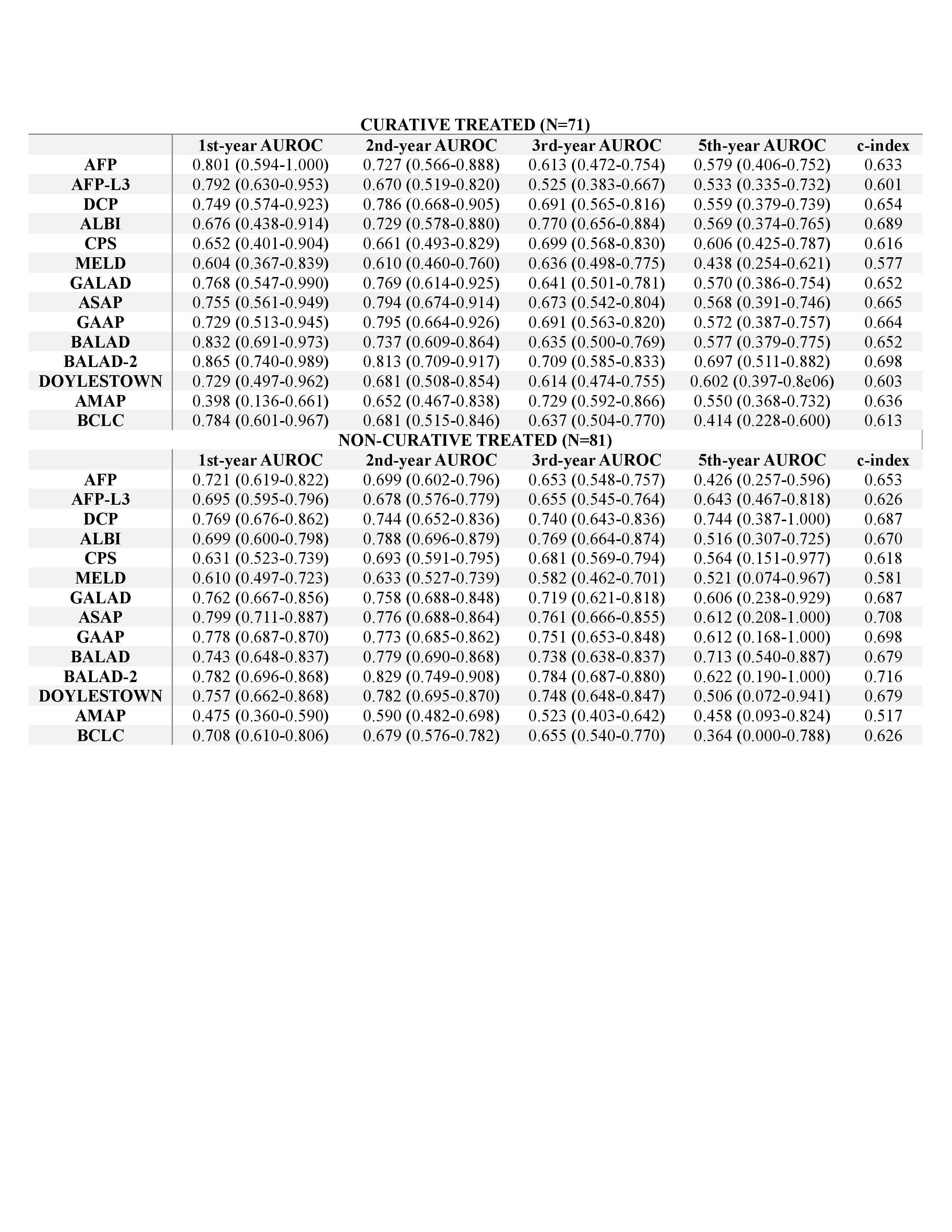
Figure: Table 2. Comparison of the prognostic discriminative ability of individual biomarkers and prognostic models by treatment category
Disclosures:
Coskun Demirtas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatih Eren indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Demet Yilmaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasemin Armutcuoglu Kaldirim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tugba Tolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Javid Huseynov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ugur Ciftci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tuba Yilmaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sehnaz Akin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osman Ozdogan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Coskun O. Demirtas, MD1, Fatih Eren, MD, PhD1, Demet Yilmaz, MSc1, Yasemin Armutcuoglu Kaldirim, MD2, Tugba Tolu, MD2, Javid Huseynov, MD2, Ugur Ciftci, MD2, Tuba Yilmaz, MD2, Sehnaz Akin, MD3, Osman C. Ozdogan, MD2. P5846 - BALAD-2 Emerges as the Most Accurate Prognostic Model in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results From a Biobank-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Marmara University, Institute of Gastroenterology, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 2Marmara University School of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey; 3Marmara University School of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey
Introduction: Accurate prognostication in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains essential for treatment selection and risk stratification. This study aimed to compare the prognostic performance of individual serum biomarkers (AFP, AFP-L3%, and DCP) and composite scoring models—including GALAD, BALAD, BALAD-2, GAAP, ASAP, Doylestown algorithm, and aMAP—using data from a biobank-based HCC cohort.
Methods: We enrolled 186 patients with confirmed HCC diagnoses with available serum, clinical and follow-up data, between 2019 and 2024 from Marmara University HCC biobank. Serum levels of AFP, AFP-L3% and DCP were measured and used to calculate composite scores using validated formulas. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Prognostic performance was assessed using time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) at 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year intervals and Harrel's concordance index (c-index). Subgroup analyses were performed by treatment intent (curative vs. non-curative) and liver disease etiology (viral vs. non-viral).
Results: The median age was 65 years; 74.7% of patients were male, and 90.3% had underlying cirrhosis. HBV was the most common etiology (49.5%), followed by MASLD (29.0%) and HCV (14.0%). Among all models, BALAD-2 showed the top-performing prognostic accuracy (c-index=0.737) with highest AUROCs at 1-year (0.827), 2-year (0.846), 3-year (0.781), and 5-year (0.716). BALAD-2 consistently showed superior discrimination in both patients treated with curative (c-index=0.698) or non-curative therapies (0.716) with highest c-indexes, and AUROCs across most time points. BALAD-2 demonstrated the best prognostic discriminative accuracy in viral etiology by highest c-index (0.726), and AUROCs at 1-year (0.846), 2-year (0.853), and 5-year (0.758). In non-viral etiology subgroup, BALAD-2 remained among the top performers, although GAAP, ASAP, Doylestown and GALAD showed slightly higher c-index and AUROCs at different time points.
Discussion: BALAD-2 outperformed other biomarker-based and clinical composite prognostic models in predicting survival among patients with HCC, regardless of treatment type, with particularly strong performance in those with viral etiologies. These findings support its integration into clinical risk stratification and decision making in HCC management.

Figure: Table 1. Comparison of the prognostic discriminative ability of biomarkers and prognostic models, including subgroup analyses by liver disease etiology

Figure: Table 2. Comparison of the prognostic discriminative ability of individual biomarkers and prognostic models by treatment category
Disclosures:
Coskun Demirtas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatih Eren indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Demet Yilmaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasemin Armutcuoglu Kaldirim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tugba Tolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Javid Huseynov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ugur Ciftci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tuba Yilmaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sehnaz Akin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osman Ozdogan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Coskun O. Demirtas, MD1, Fatih Eren, MD, PhD1, Demet Yilmaz, MSc1, Yasemin Armutcuoglu Kaldirim, MD2, Tugba Tolu, MD2, Javid Huseynov, MD2, Ugur Ciftci, MD2, Tuba Yilmaz, MD2, Sehnaz Akin, MD3, Osman C. Ozdogan, MD2. P5846 - BALAD-2 Emerges as the Most Accurate Prognostic Model in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results From a Biobank-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

