Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5826 - Efficacy and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Aanusha Ghouri, MD (she/her/hers)
Luminis Health Anne Arundel Medical Center
Annapolis, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Aanusha Ghouri, MD1, Muhammad Rafay Paracha, 2, Muhammad Ahrar Bin Naeem, 2, Ahmad Noor, 2, Muhammad Hamza Awais Khalid, 2, Maaz Khan, 2, Moeaza Raza Rizvi, 2, Javeeria Arshad, 2, Hamza Ashraf, 2, Hafiza Khadija Shahid, 2, Minahil Ali, 2, Talha Abbas, 2
1Luminis Health Anne Arundel Medical Center, Upper Marlboro, MD; 2Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are now central to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy. A previous meta-analysis demonstrated significant improvements in tumor response and survival outcomes. Since that publication, six randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with updated data have been released. We conducted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis to incorporate these additional trials and evaluate contemporary ICI efficacy and safety in HCC.
Methods: PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library were searched following PRISMA guidelines for RCTs comparing ICIs with standard therapy or placebo in HCC patients. Eligible trials reported objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), survival, and adverse-event outcomes. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) for response metrics and hazard ratios (HRs) for survival endpoints were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results: Eighteen RCTs involving 9,244 patients met inclusion criteria. ICIs significantly improved ORR (OR 3.20; 95% CI 2.44–4.20; P < 0.00001), DCR (OR 1.40; 95% CI 1.08–1.81; P = 0.01), and stable disease rates (OR 2.15; 95% CI 1.16–3.98; P = 0.02). Survival analysis favored ICIs for overall survival (HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.73–0.86; P < 0.00001) and progression-free survival (HR 0.77; 95% CI 0.69–0.87; P < 0.00001). ICIs were associated with higher odds of all-cause grade ≥ 3 adverse events (OR 1.36; 95% CI 1.10–1.67; P = 0.005), with no other significant safety differences observed.
Discussion: This updated meta-analysis confirms that ICIs significantly improve tumor response and survival outcomes in HCC while maintaining an acceptable safety profile. These findings reinforce the role of ICIs as a key component of systemic HCC therapy and highlight the need for further research to optimize treatment combinations and patient selection.
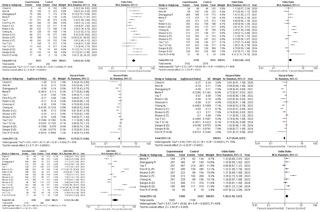
Figure: Significant Outcomes
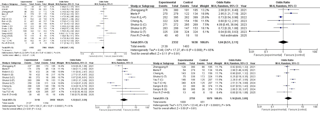
Figure: Non Significant Outcomes
Disclosures:
Aanusha Ghouri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Rafay Paracha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahrar Bin Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Noor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza Awais Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maaz Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moeaza Raza Rizvi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Javeeria Arshad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Ashraf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafiza Khadija Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Abbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aanusha Ghouri, MD1, Muhammad Rafay Paracha, 2, Muhammad Ahrar Bin Naeem, 2, Ahmad Noor, 2, Muhammad Hamza Awais Khalid, 2, Maaz Khan, 2, Moeaza Raza Rizvi, 2, Javeeria Arshad, 2, Hamza Ashraf, 2, Hafiza Khadija Shahid, 2, Minahil Ali, 2, Talha Abbas, 2. P5826 - Efficacy and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Luminis Health Anne Arundel Medical Center, Upper Marlboro, MD; 2Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are now central to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy. A previous meta-analysis demonstrated significant improvements in tumor response and survival outcomes. Since that publication, six randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with updated data have been released. We conducted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis to incorporate these additional trials and evaluate contemporary ICI efficacy and safety in HCC.
Methods: PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library were searched following PRISMA guidelines for RCTs comparing ICIs with standard therapy or placebo in HCC patients. Eligible trials reported objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), survival, and adverse-event outcomes. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) for response metrics and hazard ratios (HRs) for survival endpoints were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results: Eighteen RCTs involving 9,244 patients met inclusion criteria. ICIs significantly improved ORR (OR 3.20; 95% CI 2.44–4.20; P < 0.00001), DCR (OR 1.40; 95% CI 1.08–1.81; P = 0.01), and stable disease rates (OR 2.15; 95% CI 1.16–3.98; P = 0.02). Survival analysis favored ICIs for overall survival (HR 0.79; 95% CI 0.73–0.86; P < 0.00001) and progression-free survival (HR 0.77; 95% CI 0.69–0.87; P < 0.00001). ICIs were associated with higher odds of all-cause grade ≥ 3 adverse events (OR 1.36; 95% CI 1.10–1.67; P = 0.005), with no other significant safety differences observed.
Discussion: This updated meta-analysis confirms that ICIs significantly improve tumor response and survival outcomes in HCC while maintaining an acceptable safety profile. These findings reinforce the role of ICIs as a key component of systemic HCC therapy and highlight the need for further research to optimize treatment combinations and patient selection.

Figure: Significant Outcomes

Figure: Non Significant Outcomes
Disclosures:
Aanusha Ghouri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Rafay Paracha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahrar Bin Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Noor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hamza Awais Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maaz Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moeaza Raza Rizvi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Javeeria Arshad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Ashraf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafiza Khadija Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Abbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aanusha Ghouri, MD1, Muhammad Rafay Paracha, 2, Muhammad Ahrar Bin Naeem, 2, Ahmad Noor, 2, Muhammad Hamza Awais Khalid, 2, Maaz Khan, 2, Moeaza Raza Rizvi, 2, Javeeria Arshad, 2, Hamza Ashraf, 2, Hafiza Khadija Shahid, 2, Minahil Ali, 2, Talha Abbas, 2. P5826 - Efficacy and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
