Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5825 - Rising Burden of MASLD-Related Liver Cancer in the US Amid Increasing Socio-Demographic Development: A State Level Analysis (1990-2021)
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD
Hunt Regional Medical Center
Greenville, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD2, John Guardiola, MD2, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD3
1Hunt Regional Medical Center, Greenville, TX; 2Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 3University of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Primary liver cancer (PLC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally. Despite declining rates of viral hepatitis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is emerging as a dominant etiology in the Unites States (US). This study examines the burden of MASLD-related PLC in the US from 1990 to 2021, contextualized within evolving Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) trends.
Methods: US-specific data were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database (1990–2021), focusing on age-standardized mortality rates (ASMR), incidence rates (ASIR), and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for MASLD-related PLC. SDI data were obtained for all 50 states. Trends were stratified by sex and state. Correlation and spatial analyses were conducted to assess the relationship between SDI and liver cancer burden.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, ASMR rose from 0.20 to 0.47 per 100,000 (+135%), ASIR increased from 0.22 to 0.58 per 100,000 (+164%), and DALYs nearly doubled from 4.51 to 10.59 per 100,000 (+135%). Despite a national SDI increase from ~0.76 to ~0.86, MASLD-related liver cancer burden rose sharply. Males consistently had higher ASMRs than females. In 2021, Hawaii had the highest state-level mortality (0.68), while Montana had the lowest (0.44). High fasting plasma glucose emerged as the leading risk factor, increasing from 19.2% to 35.4% of attributable deaths, while smoking’s contribution declined slightly.
Discussion: The rising burden of MASLD-related liver cancer in the US contrasts with improving SDI, highlighting a growing metabolic health crisis. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions addressing metabolic risk factors, in both high- and low-SDI states.
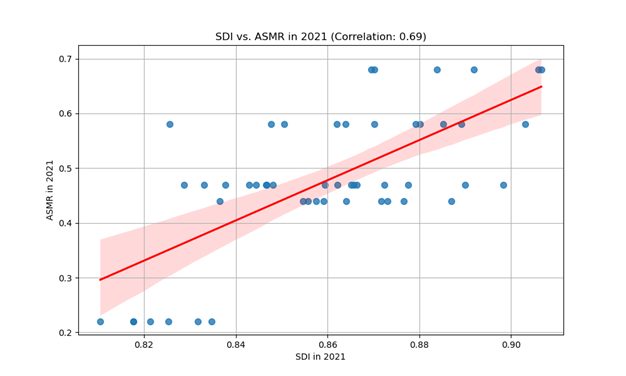
Figure: Positive correlation between SDI and MASLD-associated PLC ASMR in 2021
Disclosures:
Mohammed Y. Youssef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azizullah Beran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Guardiola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Indira Bhavsar-Burke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD2, John Guardiola, MD2, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD3. P5825 - Rising Burden of MASLD-Related Liver Cancer in the US Amid Increasing Socio-Demographic Development: A State Level Analysis (1990-2021), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Hunt Regional Medical Center, Greenville, TX; 2Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 3University of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Primary liver cancer (PLC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally. Despite declining rates of viral hepatitis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is emerging as a dominant etiology in the Unites States (US). This study examines the burden of MASLD-related PLC in the US from 1990 to 2021, contextualized within evolving Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) trends.
Methods: US-specific data were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database (1990–2021), focusing on age-standardized mortality rates (ASMR), incidence rates (ASIR), and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for MASLD-related PLC. SDI data were obtained for all 50 states. Trends were stratified by sex and state. Correlation and spatial analyses were conducted to assess the relationship between SDI and liver cancer burden.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, ASMR rose from 0.20 to 0.47 per 100,000 (+135%), ASIR increased from 0.22 to 0.58 per 100,000 (+164%), and DALYs nearly doubled from 4.51 to 10.59 per 100,000 (+135%). Despite a national SDI increase from ~0.76 to ~0.86, MASLD-related liver cancer burden rose sharply. Males consistently had higher ASMRs than females. In 2021, Hawaii had the highest state-level mortality (0.68), while Montana had the lowest (0.44). High fasting plasma glucose emerged as the leading risk factor, increasing from 19.2% to 35.4% of attributable deaths, while smoking’s contribution declined slightly.
Discussion: The rising burden of MASLD-related liver cancer in the US contrasts with improving SDI, highlighting a growing metabolic health crisis. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions addressing metabolic risk factors, in both high- and low-SDI states.

Figure: Positive correlation between SDI and MASLD-associated PLC ASMR in 2021
Disclosures:
Mohammed Y. Youssef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azizullah Beran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Guardiola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Indira Bhavsar-Burke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD1, Azizullah Beran, MD2, John Guardiola, MD2, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD3. P5825 - Rising Burden of MASLD-Related Liver Cancer in the US Amid Increasing Socio-Demographic Development: A State Level Analysis (1990-2021), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
