Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5799 - Impact of Seizures on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Liver Failure: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ayman Elawad, MD (he/him/his)
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Ayman Elawad, MD1, Ali Osman, MD, MSCI Candidate2, Abdellatif Ismail, MD3, Khalid Ahmed, MD4, Miqdad Dafaallah, MD5, Mohammad Adam, MD, MSc6, Nur Sena Cagatay, MD7, Thuraya Mussa, MD8, Nihal Babiker, MBBS9, Amna Ahmed, MBBS10, Mohammad Bilal, MD, FACG11, Abdelhaleem Sideeg, MD12, Mohamed Abdallah, MD13
1Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 2Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Ballwin, MO; 3University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 4University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN; 5Mercyone Des Moines Medical Center, Iowa, IA; 6University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 7Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 8Michigan State University, Lansing, MI; 9Zafazig University, Zagazig, Ash Sharqiyah, Egypt; 10University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan; 11University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 12virginia mason medical center, Seattle, WA; 13Corewell Health, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Acute liver failure (ALF) is a dynamic syndrome hallmarked by sudden hepatic dysfunction, coagulopathy, and onset of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in patients without prior history of liver disease. Seizures (SE) and cerebral edema (CE) are closely linked with ALF and are associated with poor outcomes.3,4 The impact of developing SE on the clinical outcomes in ALF patients remains inadequately defined. This study aims to examine the impact and clinical outcomes of SE in ALF patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used the TriNetX database to identify patients with ALF complicated by new-onset SE from 2008 to 2024. ALF patients were determined based on the AALSD criteria. Patients with a history of liver cirrhosis or pre-existing epilepsy were excluded. Cohort 1 included patients with ALF with evidence of INR >2.5 and HE with new-onset SE. Cohort 2 included patients with ALF with INR >2.5 and HE without SE. Both had a total illness duration of less than 26 weeks. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed based on demographics and comorbidities. The primary outcome was mortality. Secondary outcomes included CE, mechanical ventilation (MV), renal replacement therapy (RRT), and liver transplantation (LT). Each outcome's risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: 412 patients were included after propensity score matching (206 patients in cohorts 1 and 2, respectively). 30-day mortality was higher in the seizure group (56.8% vs. 47.6%), though the difference did not reach statistical significance (RR 9.2%; 95% CI –0.4 to 18.8; p=0.061). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed lower survival probability in the SE group. However, this was not statistically significant (35.2% vs. 42.6%; p=0.386). RRT was significantly more common in the SE group (22.8% vs. 10.7%; p=0.001). LT occurred significantly more frequently in the SE group (12.1% vs 5.3%; p=0.015).
Discussion: Patients with ALF and new-onset SE are more likely to receive LT and need RRT compared to patients without SE. 30-day mortality was higher in the SE group; however, this difference was not statistically significant. Our study underscores the clinical importance of seizures as a marker for disease severity in patients with ALF, particularly patients undergoing LT evaluation. Further studies are needed to study the determinants of outcomes in patients with ALF.
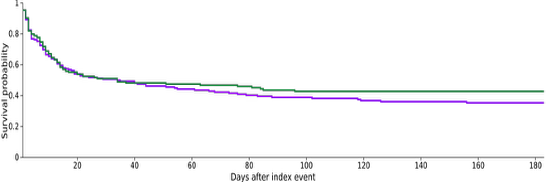
Figure: Figure 1. Mortality Kaplan–Meier survival analysis
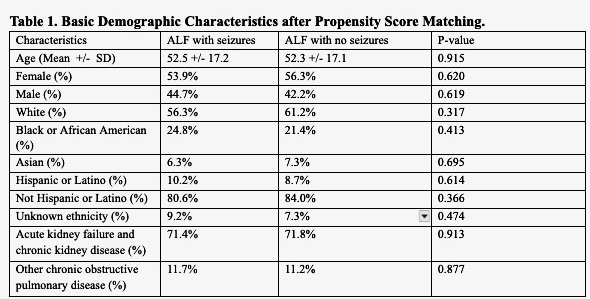
Figure: Table 1. Basic Demographic Characteristics after Propensity Score Matching.
Disclosures:
Ayman Elawad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Osman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdellatif Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miqdad Dafaallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Adam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nur Sena Cagatay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thuraya Mussa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Babiker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Bilal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook endoscopy – Paid speaker. Steris Endoscopy – Consultant.
Abdelhaleem Sideeg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayman Elawad, MD1, Ali Osman, MD, MSCI Candidate2, Abdellatif Ismail, MD3, Khalid Ahmed, MD4, Miqdad Dafaallah, MD5, Mohammad Adam, MD, MSc6, Nur Sena Cagatay, MD7, Thuraya Mussa, MD8, Nihal Babiker, MBBS9, Amna Ahmed, MBBS10, Mohammad Bilal, MD, FACG11, Abdelhaleem Sideeg, MD12, Mohamed Abdallah, MD13. P5799 - Impact of Seizures on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Liver Failure: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 2Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Ballwin, MO; 3University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 4University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN; 5Mercyone Des Moines Medical Center, Iowa, IA; 6University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 7Wayne State University, Detroit, MI; 8Michigan State University, Lansing, MI; 9Zafazig University, Zagazig, Ash Sharqiyah, Egypt; 10University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan; 11University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 12virginia mason medical center, Seattle, WA; 13Corewell Health, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Acute liver failure (ALF) is a dynamic syndrome hallmarked by sudden hepatic dysfunction, coagulopathy, and onset of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in patients without prior history of liver disease. Seizures (SE) and cerebral edema (CE) are closely linked with ALF and are associated with poor outcomes.3,4 The impact of developing SE on the clinical outcomes in ALF patients remains inadequately defined. This study aims to examine the impact and clinical outcomes of SE in ALF patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used the TriNetX database to identify patients with ALF complicated by new-onset SE from 2008 to 2024. ALF patients were determined based on the AALSD criteria. Patients with a history of liver cirrhosis or pre-existing epilepsy were excluded. Cohort 1 included patients with ALF with evidence of INR >2.5 and HE with new-onset SE. Cohort 2 included patients with ALF with INR >2.5 and HE without SE. Both had a total illness duration of less than 26 weeks. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed based on demographics and comorbidities. The primary outcome was mortality. Secondary outcomes included CE, mechanical ventilation (MV), renal replacement therapy (RRT), and liver transplantation (LT). Each outcome's risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: 412 patients were included after propensity score matching (206 patients in cohorts 1 and 2, respectively). 30-day mortality was higher in the seizure group (56.8% vs. 47.6%), though the difference did not reach statistical significance (RR 9.2%; 95% CI –0.4 to 18.8; p=0.061). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed lower survival probability in the SE group. However, this was not statistically significant (35.2% vs. 42.6%; p=0.386). RRT was significantly more common in the SE group (22.8% vs. 10.7%; p=0.001). LT occurred significantly more frequently in the SE group (12.1% vs 5.3%; p=0.015).
Discussion: Patients with ALF and new-onset SE are more likely to receive LT and need RRT compared to patients without SE. 30-day mortality was higher in the SE group; however, this difference was not statistically significant. Our study underscores the clinical importance of seizures as a marker for disease severity in patients with ALF, particularly patients undergoing LT evaluation. Further studies are needed to study the determinants of outcomes in patients with ALF.

Figure: Figure 1. Mortality Kaplan–Meier survival analysis

Figure: Table 1. Basic Demographic Characteristics after Propensity Score Matching.
Disclosures:
Ayman Elawad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Osman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdellatif Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miqdad Dafaallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Adam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nur Sena Cagatay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thuraya Mussa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Babiker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Bilal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook endoscopy – Paid speaker. Steris Endoscopy – Consultant.
Abdelhaleem Sideeg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayman Elawad, MD1, Ali Osman, MD, MSCI Candidate2, Abdellatif Ismail, MD3, Khalid Ahmed, MD4, Miqdad Dafaallah, MD5, Mohammad Adam, MD, MSc6, Nur Sena Cagatay, MD7, Thuraya Mussa, MD8, Nihal Babiker, MBBS9, Amna Ahmed, MBBS10, Mohammad Bilal, MD, FACG11, Abdelhaleem Sideeg, MD12, Mohamed Abdallah, MD13. P5799 - Impact of Seizures on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Liver Failure: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
