Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5786 - Clinical Burden of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients Hospitalized With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Shivangini Duggal, MD
Department of Internal Medicine at Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso TX, USA
El Paso, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Shivangini Duggal, MD1, Sakar Khattar, MS2, Lakshmi Kattamuri, MD3, Swati Mahapatra, DO4, Bhavi Trivedi, MD3, Alejandro Robles, MD5, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD6, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD3
1Department of Internal Medicine at Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso TX, USA, El Paso, TX; 2Google Inc., Santa Clara, CA; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 4Texas A&M, El Paso, TX; 5Department of Gastroenterology, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso, El Paso , TX, El Paso, TX; 6Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX., El Paso, TX
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) affects approximately 10–30% of the U.S. population, with prevalence increasing five-fold over recent decades. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of mortality among individuals with MASLD. Emerging evidence suggests MASLD is independently associated with adverse cardiac remodeling, diastolic dysfunction, and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), largely driven by shared pathophysiologic mechanisms such as metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, systemic inflammation, and impaired myocardial energetics. However, data elucidating the interplay between MASLD and HFpEF remain limited. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of HFpEF on clinical outcomes in MASLD patients.
Methods: The Nationwide Inpatient Sample database was queried to identify adult hospitalizations with MASLD and coexisting HFpEF between 2012 and 2021 using ICD-9/10-CM codes. Patients were stratified according to HFpEF status, and comparisons were made across demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes. Statistical analyses were conducted using R software.
Results: Among 5,327,034 MASLD hospitalizations, 262,820 (4.9%) had concurrent HFpEF. HFpEF group had higher age (mean 69.9 vs 57.1 years, p< 0.001), longer hospital stays (7.19 vs 5.34 days, p< 0.001), and higher hospitalization costs (mean $79,560 vs $65,564, p< 0.001). HFpEF group demonstrated greater burden of arrhythmias (44.9% vs 11.4%, p< 0.001), mechanical ventilation (6.5% vs 4.0%, p< 0.001), acute liver failure (14.2% vs 9.9%, p< 0.001), venous thromboembolism (9.0% vs 7.2%, p< 0.001) and sudden cardiac arrest (1.45% vs 0.75%, p< 0.001). HFpEF group also had lower liver transplant rates (0.10% vs 0.24%, p< 0.001) and endoscopy utilization (9.11% vs 10.03%, p< 0.001). Mortality was significantly higher in the HFpEF group (6.02% vs 2.89%, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: This large real-world data analysis showed that MASLD patients with coexisting HFpEF exhibit substantially higher morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization. The observed interplay reflects shared metabolic derangements including insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and disproportionate ectopic fat deposition contributing to both hepatic fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction. These findings highlight the importance of early recognition and integrated management of hepatic and cardiac comorbidities in this expanding patient population.
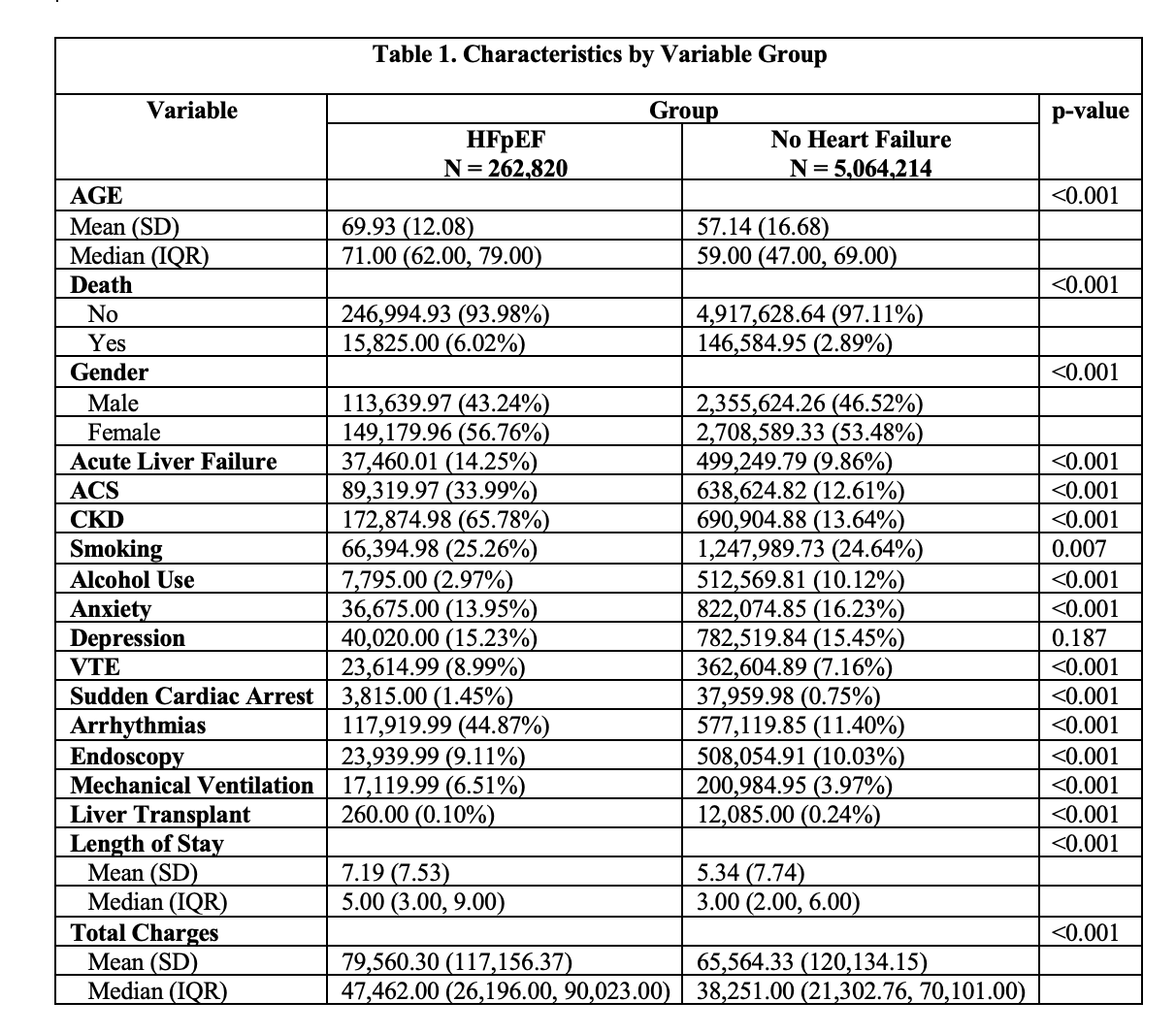
Figure: Table 1. Displays the patient characteristics in HFpEF group and no heart failure group.
Disclosures:
Shivangini Duggal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sakar Khattar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lakshmi Kattamuri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swati Mahapatra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavi Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marc Zuckerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivangini Duggal, MD1, Sakar Khattar, MS2, Lakshmi Kattamuri, MD3, Swati Mahapatra, DO4, Bhavi Trivedi, MD3, Alejandro Robles, MD5, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD6, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD3. P5786 - Clinical Burden of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients Hospitalized With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Department of Internal Medicine at Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso TX, USA, El Paso, TX; 2Google Inc., Santa Clara, CA; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 4Texas A&M, El Paso, TX; 5Department of Gastroenterology, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso, El Paso , TX, El Paso, TX; 6Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX., El Paso, TX
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) affects approximately 10–30% of the U.S. population, with prevalence increasing five-fold over recent decades. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of mortality among individuals with MASLD. Emerging evidence suggests MASLD is independently associated with adverse cardiac remodeling, diastolic dysfunction, and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), largely driven by shared pathophysiologic mechanisms such as metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, systemic inflammation, and impaired myocardial energetics. However, data elucidating the interplay between MASLD and HFpEF remain limited. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of HFpEF on clinical outcomes in MASLD patients.
Methods: The Nationwide Inpatient Sample database was queried to identify adult hospitalizations with MASLD and coexisting HFpEF between 2012 and 2021 using ICD-9/10-CM codes. Patients were stratified according to HFpEF status, and comparisons were made across demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes. Statistical analyses were conducted using R software.
Results: Among 5,327,034 MASLD hospitalizations, 262,820 (4.9%) had concurrent HFpEF. HFpEF group had higher age (mean 69.9 vs 57.1 years, p< 0.001), longer hospital stays (7.19 vs 5.34 days, p< 0.001), and higher hospitalization costs (mean $79,560 vs $65,564, p< 0.001). HFpEF group demonstrated greater burden of arrhythmias (44.9% vs 11.4%, p< 0.001), mechanical ventilation (6.5% vs 4.0%, p< 0.001), acute liver failure (14.2% vs 9.9%, p< 0.001), venous thromboembolism (9.0% vs 7.2%, p< 0.001) and sudden cardiac arrest (1.45% vs 0.75%, p< 0.001). HFpEF group also had lower liver transplant rates (0.10% vs 0.24%, p< 0.001) and endoscopy utilization (9.11% vs 10.03%, p< 0.001). Mortality was significantly higher in the HFpEF group (6.02% vs 2.89%, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: This large real-world data analysis showed that MASLD patients with coexisting HFpEF exhibit substantially higher morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization. The observed interplay reflects shared metabolic derangements including insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and disproportionate ectopic fat deposition contributing to both hepatic fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction. These findings highlight the importance of early recognition and integrated management of hepatic and cardiac comorbidities in this expanding patient population.

Figure: Table 1. Displays the patient characteristics in HFpEF group and no heart failure group.
Disclosures:
Shivangini Duggal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sakar Khattar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lakshmi Kattamuri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swati Mahapatra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhavi Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marc Zuckerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivangini Duggal, MD1, Sakar Khattar, MS2, Lakshmi Kattamuri, MD3, Swati Mahapatra, DO4, Bhavi Trivedi, MD3, Alejandro Robles, MD5, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD6, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD3. P5786 - Clinical Burden of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Patients Hospitalized With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
