Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P5693 - Stent Fixation Using a Tack-and-Suture Device
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Yara Salameh, MD
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Yara Salameh, MD1, Lea Sayegh, MD2, Hadi Khaled. Abou Zeid, MD3, Navtej Buttar, MD3, Louis Wong Kee Song, MD3, Andrew Storm, MD3
1Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, Rochester, MN; 2Yale New Haven Hospital, New Haven, CT; 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Stents are increasingly applied in the management of both benign and malignant gastrointestinal conditions; however, stent migration continues to pose a significant challenge. A novel endoscopic tack-and-suture (TAS) device has been developed, yet evidence supporting its clinical use for stent fixation is limited.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of adult patients who underwent gastrointestinal stent fixation using the TAS device at our institution. Primary outcomes included technical success and early clinical success, defined as absence of migration within predefined dwell times: 60 days for lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) and 70 days for self-expandable metal stents (SEMS). Double-pigtail stents (DPPS) were excluded from LAMS vs SEMS subgroup comparisons.
Results: Among 263 procedures, 42 stent fixations in 35 patients (69% female; mean age 52.1 ± 15.2 years) were included (LAMS: 25; SEMS: 15; DPPS: 2). Technical success was achieved in 100% of cases. Early clinical success was observed in 83.3% (35/42), with significantly lower early migration rates in LAMS (1/25, 4%) compared to SEMS (5/25, 33.3%) (p=0.02). Median time to early migration was significantly longer in LAMS (58 days) than SEMS (20 days; p=0.01). No device-related adverse events were reported. Five post-procedural adverse events (11.9%) occurred; all were managed conservatively, and none were attributed to the TAS device. Reintervention was required in 6 of 7 early migration cases (85.7%), involving either restenting, repositioning, or switching to alternative fixation methods. Late outcomes showed that 20 LAMS and 9 SEMS remained in situ beyond their expected dwell times. Of these, 55% of LAMS and 33.3% of SEMS were electively removed during follow-up, while others migrated spontaneously or remained in place until last follow-up. Median dwell times extended up to 46.9 weeks for LAMS and 74.1 weeks for SEMS. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrated a statistically significant difference in early migration rates (p=0.01) and a borderline difference in overall time to migration favoring LAMS over SEMS (p=0.051).
Discussion: Originally developed for defect closure, the tack-and-suture system proved safe and effective for stent fixation across various stent types. It demonstrated low early migration rates and enabled prolonged dwell times, particularly in LAMS.
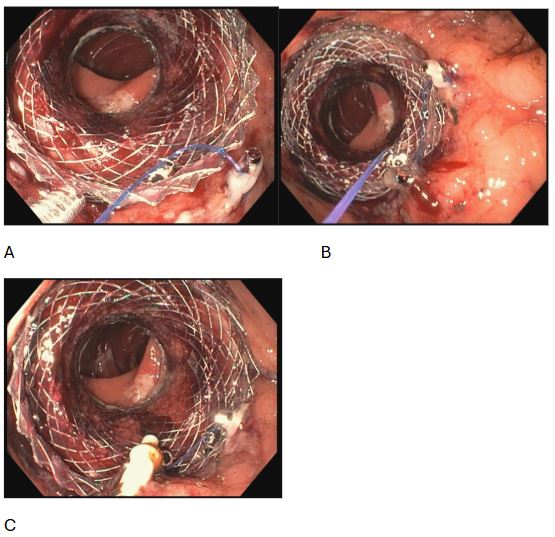
Figure: Figure 1- A, B, C: Lumen apposing metal stent placed across gastrojejunal anastomosis being secured with X-Tack and cinch.
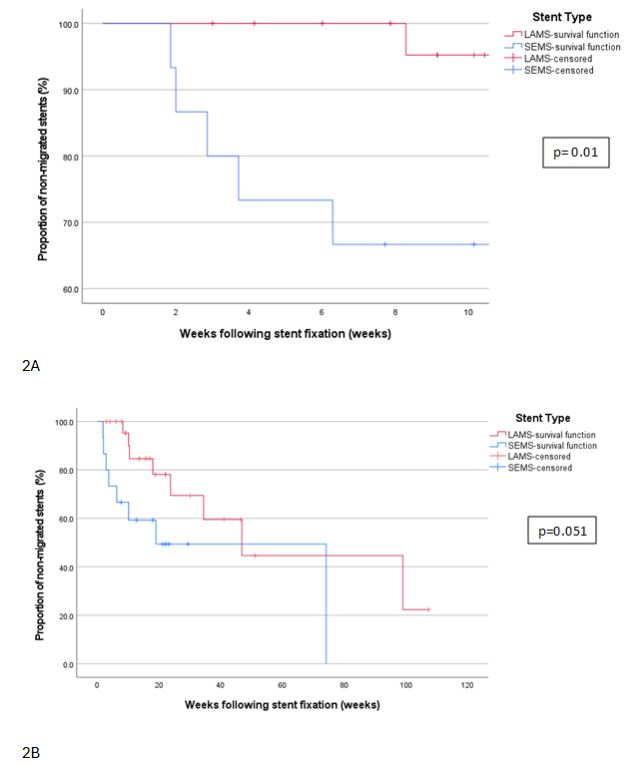
Figure: Figure 2B: Kaplan Meier curve illustrating the overall time to eventual migration of LAMS and SEMS.
Figure 2A: Kaplan Meier curve illustrating the time to early migration of LAMS and SEMS.
Disclosures:
Yara Salameh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lea Sayegh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hadi Abou Zeid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navtej Buttar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Louis Wong Kee Song: Noah Medical, Inc. – Consultant. Olympus Corp. – Consultant. Steris Inc. – Consultant.
Andrew Storm: Ambu – Consultant. Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Cook – Consultant. Endogenex – Grant/Research Support. Endo-Tagss – Grant/Research Support. Enterasense – Grant/Research Support. Envision Endoscopy – Grant/Research Support. Intuitive – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. MGI Medical – Grant/Research Support. Microtech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. OnePass – Grant/Research Support. SofTac – Grant/Research Support. Sotelix – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Yara Salameh, MD1, Lea Sayegh, MD2, Hadi Khaled. Abou Zeid, MD3, Navtej Buttar, MD3, Louis Wong Kee Song, MD3, Andrew Storm, MD3. P5693 - Stent Fixation Using a Tack-and-Suture Device, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, Rochester, MN; 2Yale New Haven Hospital, New Haven, CT; 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Stents are increasingly applied in the management of both benign and malignant gastrointestinal conditions; however, stent migration continues to pose a significant challenge. A novel endoscopic tack-and-suture (TAS) device has been developed, yet evidence supporting its clinical use for stent fixation is limited.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of adult patients who underwent gastrointestinal stent fixation using the TAS device at our institution. Primary outcomes included technical success and early clinical success, defined as absence of migration within predefined dwell times: 60 days for lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) and 70 days for self-expandable metal stents (SEMS). Double-pigtail stents (DPPS) were excluded from LAMS vs SEMS subgroup comparisons.
Results: Among 263 procedures, 42 stent fixations in 35 patients (69% female; mean age 52.1 ± 15.2 years) were included (LAMS: 25; SEMS: 15; DPPS: 2). Technical success was achieved in 100% of cases. Early clinical success was observed in 83.3% (35/42), with significantly lower early migration rates in LAMS (1/25, 4%) compared to SEMS (5/25, 33.3%) (p=0.02). Median time to early migration was significantly longer in LAMS (58 days) than SEMS (20 days; p=0.01). No device-related adverse events were reported. Five post-procedural adverse events (11.9%) occurred; all were managed conservatively, and none were attributed to the TAS device. Reintervention was required in 6 of 7 early migration cases (85.7%), involving either restenting, repositioning, or switching to alternative fixation methods. Late outcomes showed that 20 LAMS and 9 SEMS remained in situ beyond their expected dwell times. Of these, 55% of LAMS and 33.3% of SEMS were electively removed during follow-up, while others migrated spontaneously or remained in place until last follow-up. Median dwell times extended up to 46.9 weeks for LAMS and 74.1 weeks for SEMS. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrated a statistically significant difference in early migration rates (p=0.01) and a borderline difference in overall time to migration favoring LAMS over SEMS (p=0.051).
Discussion: Originally developed for defect closure, the tack-and-suture system proved safe and effective for stent fixation across various stent types. It demonstrated low early migration rates and enabled prolonged dwell times, particularly in LAMS.

Figure: Figure 1- A, B, C: Lumen apposing metal stent placed across gastrojejunal anastomosis being secured with X-Tack and cinch.

Figure: Figure 2B: Kaplan Meier curve illustrating the overall time to eventual migration of LAMS and SEMS.
Figure 2A: Kaplan Meier curve illustrating the time to early migration of LAMS and SEMS.
Disclosures:
Yara Salameh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lea Sayegh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hadi Abou Zeid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navtej Buttar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Louis Wong Kee Song: Noah Medical, Inc. – Consultant. Olympus Corp. – Consultant. Steris Inc. – Consultant.
Andrew Storm: Ambu – Consultant. Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Cook – Consultant. Endogenex – Grant/Research Support. Endo-Tagss – Grant/Research Support. Enterasense – Grant/Research Support. Envision Endoscopy – Grant/Research Support. Intuitive – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. MGI Medical – Grant/Research Support. Microtech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. OnePass – Grant/Research Support. SofTac – Grant/Research Support. Sotelix – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Yara Salameh, MD1, Lea Sayegh, MD2, Hadi Khaled. Abou Zeid, MD3, Navtej Buttar, MD3, Louis Wong Kee Song, MD3, Andrew Storm, MD3. P5693 - Stent Fixation Using a Tack-and-Suture Device, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
