Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P4931 - The Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in the Management of Zenker’s Diverticulum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Khadija Mohib, MD (she/her/hers)
Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS1, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS2, Khadija Mohib, MD3, Abu-Bakr Ahmed, BA3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Mian Uman Anwer, MBBS6, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD7
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Punjab Medical College, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD) causing dysphagia in older adults is a false pulsion diverticulum. Zenker’s peroral endoscopic myotomy (Z-POEM), a novel approach utilizing the submucosal layer to fully visualize and cut the septum, offers a minimally invasive alternative to conventional endoscopic septotomy. This meta-analysis aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of the POEM technique in ZD management.
Methods: The electronic databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library and ScienceDirect were searched from inception till January 2025. This review followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. The pooled analysis was conducted under the random effects model in R version 4.2.3 and employed the “metaprop” package. The primary and secondary outcomes of interest were clinical success, technical success, symptom recurrence, and adverse events. The quality of studies was judged by the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. Publication bias was assessed through visual inspection of the funnel plots. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to investigate heterogeneity.
Results: Twenty studies pooling a total of 713 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled clinical success rate was 93% (95% confidence interval:[89-96%]; I2=9.5%). The technical success rate was 99% (95% confidence interval:[97-100%]; I2=0%). Regarding the recurrence of the symptoms, the pooled rate was 6% (95% CI:[4-11%]; I2=1.3%) whereas the pooled rate of adverse events was 7% (95% CI:[5-11%]; I2=0%).
Discussion: Zenker's peroral endoscopic myotomy demonstrates high clinical and technical success rates with low rates of symptom recurrence and adverse events establishing it as a safe and effective minimally invasive approach for managing Zenker’s diverticulum. These findings highlight Z-POEM's potential as a superior alternative to conventional endoscopic techniques in older adults
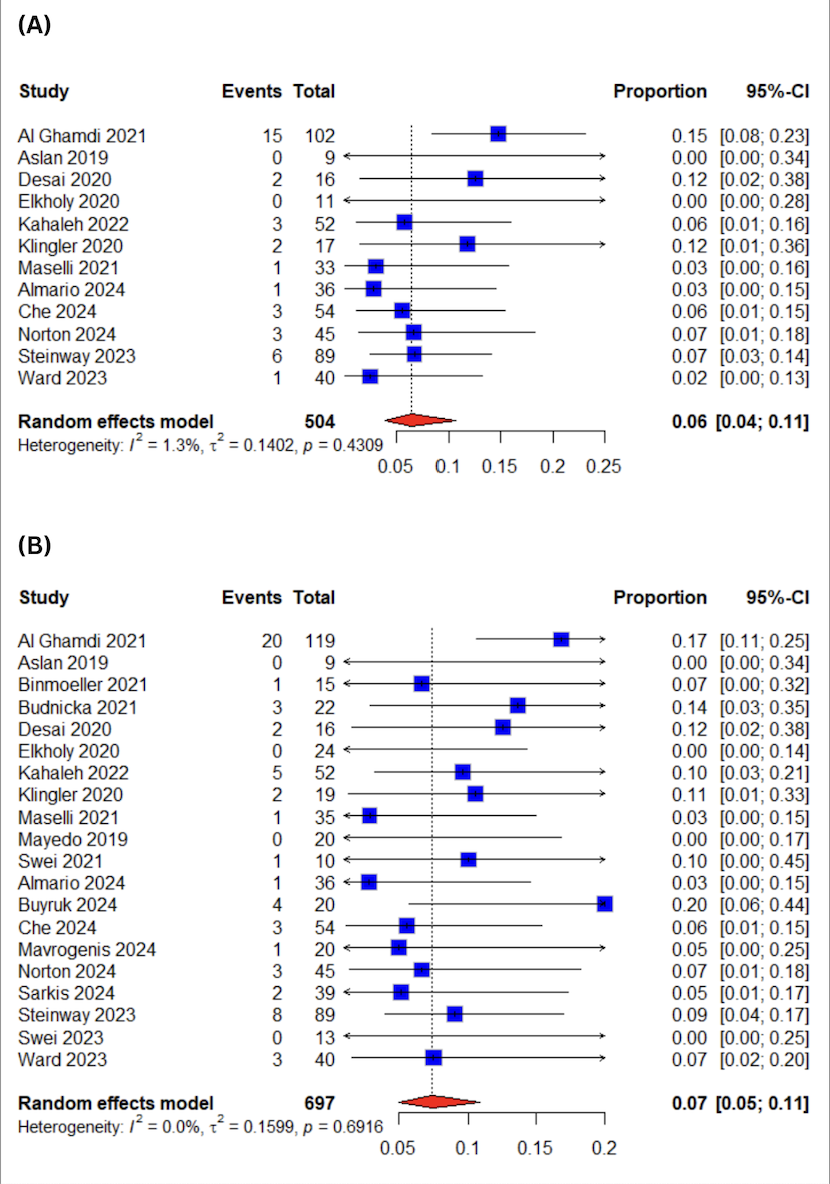
Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plots for (A)Clinical Success (B)Technical Success
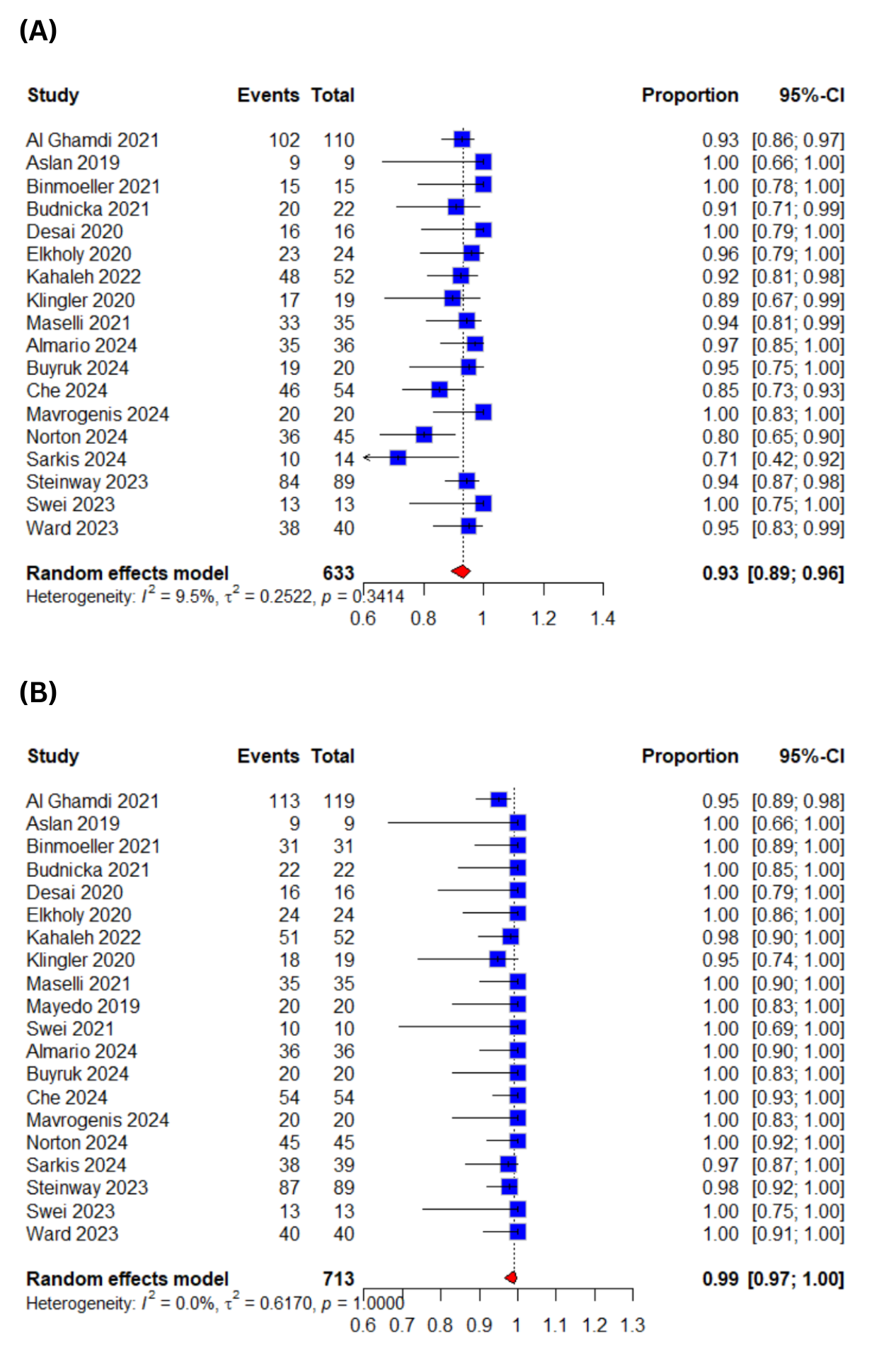
Figure: Figure 2: Forest Plots for (A)Symptoms Recurrence (B)Adverse Events
Disclosures:
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Mohib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abu-Bakr Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mian Uman Anwer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS1, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS2, Khadija Mohib, MD3, Abu-Bakr Ahmed, BA3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Mian Uman Anwer, MBBS6, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD7. P4931 - The Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in the Management of Zenker’s Diverticulum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Punjab Medical College, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD) causing dysphagia in older adults is a false pulsion diverticulum. Zenker’s peroral endoscopic myotomy (Z-POEM), a novel approach utilizing the submucosal layer to fully visualize and cut the septum, offers a minimally invasive alternative to conventional endoscopic septotomy. This meta-analysis aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of the POEM technique in ZD management.
Methods: The electronic databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library and ScienceDirect were searched from inception till January 2025. This review followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. The pooled analysis was conducted under the random effects model in R version 4.2.3 and employed the “metaprop” package. The primary and secondary outcomes of interest were clinical success, technical success, symptom recurrence, and adverse events. The quality of studies was judged by the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. Publication bias was assessed through visual inspection of the funnel plots. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to investigate heterogeneity.
Results: Twenty studies pooling a total of 713 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled clinical success rate was 93% (95% confidence interval:[89-96%]; I2=9.5%). The technical success rate was 99% (95% confidence interval:[97-100%]; I2=0%). Regarding the recurrence of the symptoms, the pooled rate was 6% (95% CI:[4-11%]; I2=1.3%) whereas the pooled rate of adverse events was 7% (95% CI:[5-11%]; I2=0%).
Discussion: Zenker's peroral endoscopic myotomy demonstrates high clinical and technical success rates with low rates of symptom recurrence and adverse events establishing it as a safe and effective minimally invasive approach for managing Zenker’s diverticulum. These findings highlight Z-POEM's potential as a superior alternative to conventional endoscopic techniques in older adults

Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plots for (A)Clinical Success (B)Technical Success

Figure: Figure 2: Forest Plots for (A)Symptoms Recurrence (B)Adverse Events
Disclosures:
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Mohib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abu-Bakr Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mian Uman Anwer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS1, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS2, Khadija Mohib, MD3, Abu-Bakr Ahmed, BA3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Mian Uman Anwer, MBBS6, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD7. P4931 - The Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in the Management of Zenker’s Diverticulum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
