Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P4925 - Effectiveness of Dupixent as a Maintenance Therapy in Patients With EOE: A Retrospective Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Dheera Grover, MD
Allegheny Center for Digestive Health
Pittsburgh, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Dheera Grover, MD1, Helene Bloom, DO2, Yin Yue, 3, Sandra El-Hachem, MD1
1Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 2Allegheny Health Network Medicine Institute, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EOE) is non-IgE immune mediated allergic process in the esophagus. Treatment of EOE includes elimination diet, proton pump inhibitors (PPI), topical/systemic steroids or esophageal dilation [1,2]. In May 2022, Dupilumab became the first FDA approved biologic treatment modality for EOE. We aim to determine the long-term effectiveness of Dupilumab as a maintenance therapy.
Methods: Retrospective review of patients in Allegheny Health Network aged 18-89 years with EOE and being treated with Dupilumab was done. Primary outcome included improvement in eosinophils after starting Dupilumab. Secondary outcomes included improvement in dysphagia, admissions for food impaction, and dilations. Post hoc analysis was performed according to the interval between initiation of Dupilumab and latest EGD. ANOVA/Kruskal Wallis’ test and Chi-Square were conducted to compare continuous and categorical variables respectively. P-value less than 0.05 was considered significant
Results: In total, 45 patients were included in the study. Baseline characteristics as in table 1. Mean interval between diagnosis and starting Dupilumab was 3.57 yrs. 37.8%, 64.4%, and 55.6% of patients had seen a nutritionist, allergist and tried diet elimination respectively. Majority of the patients were being treated with PPI (43, 96%) and steroids (38, 84.4%). There was a significant difference between no. of eosinophils between proximal/mid and distal esophagus after starting Dupilumab (Proximal/mid:30 (20-50) vs. 0(0-0); p< 0.001 and Distal: 40(30-50) vs. 0(0-3); p< 0.001). 86.7% of patients reported improvement in dysphagia. Significant difference was noted in EREFS score (pre vs post: 2(2-3) vs. 1(0-2); p < 0.05). There was significant reduction in no. of dilations required and admissions for food impactions post Dupilumab (p< 0.05). Post-hoc analysis was performed according to the latest EGD. 17 patients had EGD within 6 months after Dupilumab, 19 between 6-12 months and 9 after 12 months (up to 31 months). Notably, there was significant difference noted in eosinophils between pre and post EGD in all the three subgroups, however, no difference was noted in EREFS score, no. of dilations and admissions for food impactions.
Discussion: Patients who underwent endoscopic evaluation after starting Dupilumab at 6 months, 6–12 months, and beyond 12 months showed consistent improvement in eosinophil levels across all time points, indicating promising long-term treatment response with continued maintenance therapy.
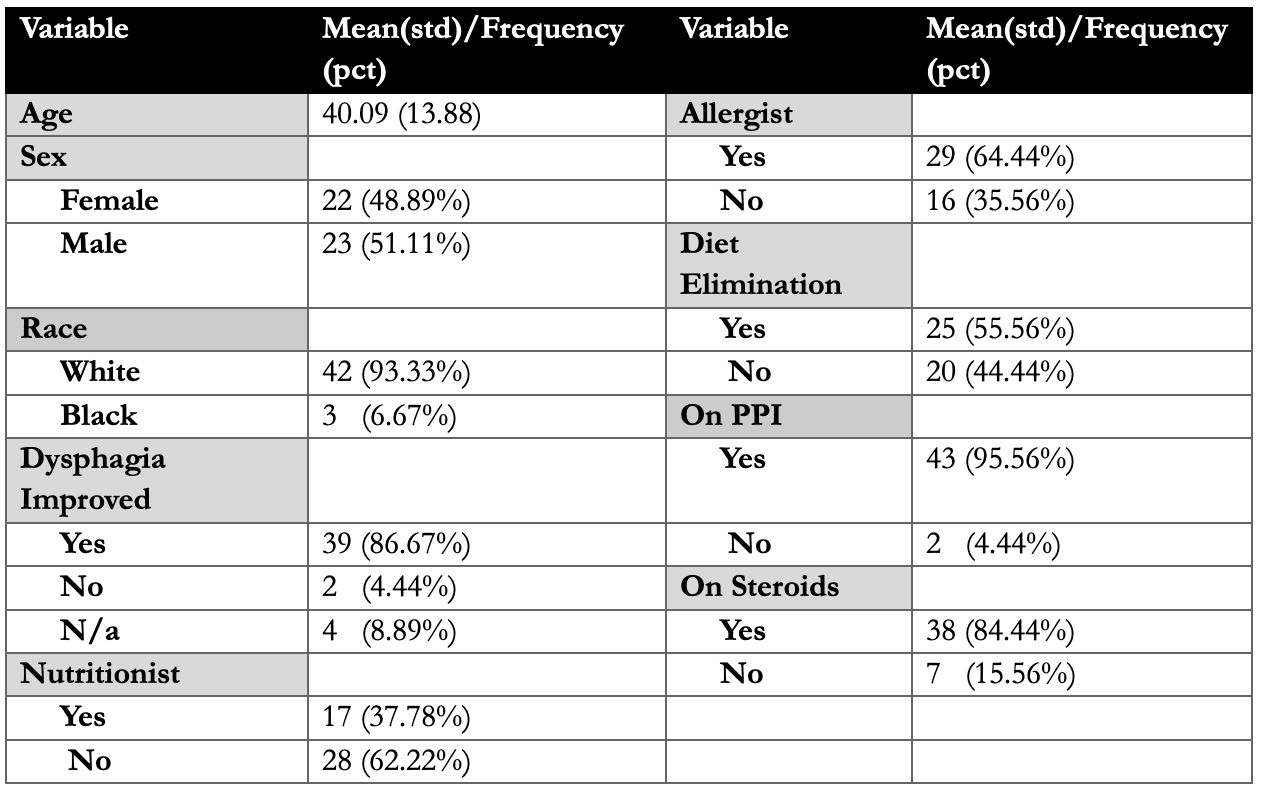
Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics
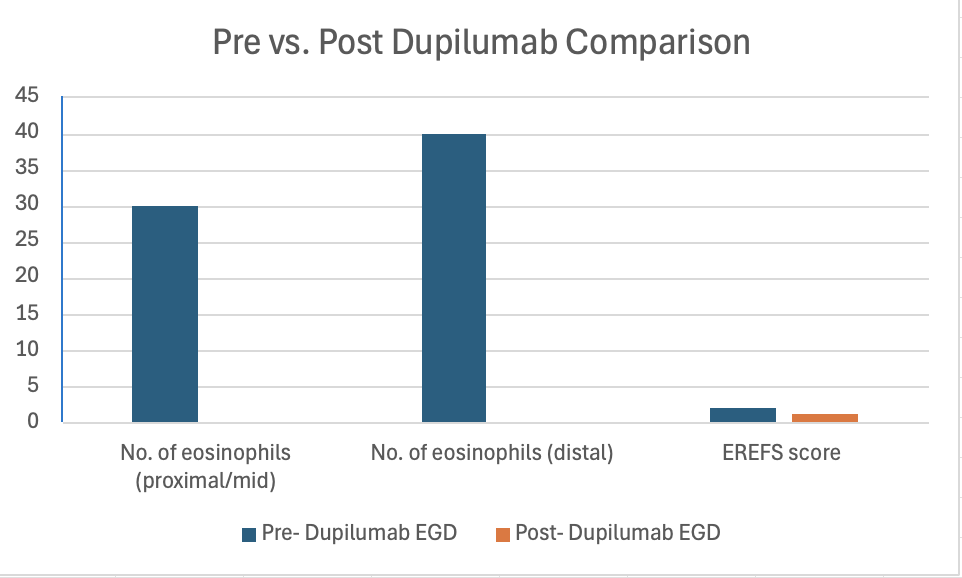
Figure: Image 1: Bar graph depicting the primary endpoints and secondary endpoints of the study pre vs. post Dupilumab including number of eosinophils, and EREFS
Disclosures:
Dheera Grover indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Helene Bloom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yin Yue indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandra El-Hachem: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Briston Myers Squibb – Speakers Bureau. Johnson and Johnson (Janssen ) – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Dheera Grover, MD1, Helene Bloom, DO2, Yin Yue, 3, Sandra El-Hachem, MD1. P4925 - Effectiveness of Dupixent as a Maintenance Therapy in Patients With EOE: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Allegheny Center for Digestive Health, Pittsburgh, PA; 2Allegheny Health Network Medicine Institute, Pittsburgh, PA; 3Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EOE) is non-IgE immune mediated allergic process in the esophagus. Treatment of EOE includes elimination diet, proton pump inhibitors (PPI), topical/systemic steroids or esophageal dilation [1,2]. In May 2022, Dupilumab became the first FDA approved biologic treatment modality for EOE. We aim to determine the long-term effectiveness of Dupilumab as a maintenance therapy.
Methods: Retrospective review of patients in Allegheny Health Network aged 18-89 years with EOE and being treated with Dupilumab was done. Primary outcome included improvement in eosinophils after starting Dupilumab. Secondary outcomes included improvement in dysphagia, admissions for food impaction, and dilations. Post hoc analysis was performed according to the interval between initiation of Dupilumab and latest EGD. ANOVA/Kruskal Wallis’ test and Chi-Square were conducted to compare continuous and categorical variables respectively. P-value less than 0.05 was considered significant
Results: In total, 45 patients were included in the study. Baseline characteristics as in table 1. Mean interval between diagnosis and starting Dupilumab was 3.57 yrs. 37.8%, 64.4%, and 55.6% of patients had seen a nutritionist, allergist and tried diet elimination respectively. Majority of the patients were being treated with PPI (43, 96%) and steroids (38, 84.4%). There was a significant difference between no. of eosinophils between proximal/mid and distal esophagus after starting Dupilumab (Proximal/mid:30 (20-50) vs. 0(0-0); p< 0.001 and Distal: 40(30-50) vs. 0(0-3); p< 0.001). 86.7% of patients reported improvement in dysphagia. Significant difference was noted in EREFS score (pre vs post: 2(2-3) vs. 1(0-2); p < 0.05). There was significant reduction in no. of dilations required and admissions for food impactions post Dupilumab (p< 0.05). Post-hoc analysis was performed according to the latest EGD. 17 patients had EGD within 6 months after Dupilumab, 19 between 6-12 months and 9 after 12 months (up to 31 months). Notably, there was significant difference noted in eosinophils between pre and post EGD in all the three subgroups, however, no difference was noted in EREFS score, no. of dilations and admissions for food impactions.
Discussion: Patients who underwent endoscopic evaluation after starting Dupilumab at 6 months, 6–12 months, and beyond 12 months showed consistent improvement in eosinophil levels across all time points, indicating promising long-term treatment response with continued maintenance therapy.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics

Figure: Image 1: Bar graph depicting the primary endpoints and secondary endpoints of the study pre vs. post Dupilumab including number of eosinophils, and EREFS
Disclosures:
Dheera Grover indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Helene Bloom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yin Yue indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandra El-Hachem: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Briston Myers Squibb – Speakers Bureau. Johnson and Johnson (Janssen ) – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Dheera Grover, MD1, Helene Bloom, DO2, Yin Yue, 3, Sandra El-Hachem, MD1. P4925 - Effectiveness of Dupixent as a Maintenance Therapy in Patients With EOE: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
