Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4636 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Metastasizing to the Gastrointestinal Tract
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AA
Ahmad Afzal, MD
Houston Methodist Hospital
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Scott Berger, MD1, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Ronan Allencherril, MD1, Mojgan Amrikachi, MD3, Mary R. Schwartz, MD1, Rachel Schiesser, MD1
1Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 2Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3MD, Houston, TX
Introduction: Primary pulmonary adenocarcinoma presenting as metastasis to the gastrointestinal tract is a rare (< 2%) occurrence. The most common GI sites for lung cancer metastasis are the small intestine and colon. Presentations often include bowel obstruction or GI bleeding.
Case Description/
Methods: We present the case of a 66-year-old male with history of recent small bowel obstruction (SBO) who presented with abdominal pain and melena. He was admitted for nausea and vomiting. Computed tomography (CT) confirmed a SBO with transition points in the right lower quadrant with circumferential wall thickening of multiple segments of the small bowel and a lytic T10 spinal lesion. Further work-up with CT of the chest demonstrated a left upper lung lobe mass invading the anterior mediastinum. A subsequent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy revealed four 0.5-2cm ulcerated masses in the second portion of the duodenum and 2cm masses, one in the hepatic flexure and one in the rectum. Biopsies of these masses revealed poorly differentiated carcinoma with focal sarcomatoid features. Bronchoscopy and biopsies of the left upper lung mass showed poorly differentiated pulmonary adenocarcinoma with PD-L1 expression in 30% of the cells. The tumor in the GI tract biopsies was histologically similar to the lung primary. Oncology was consulted for management of stage IV lung carcinoma and patient was started on pembrolizumab, carboplatin, and pemetrexed. Unfortunately, he continued to have multiple episodes of partial SBOs requiring hospital admissions which were managed conservatively. At 6 months from his diagnosis, he continues to receive chemotherapy and is pending a palliative G tube placement.
Discussion: Patients with lung adenocarcinoma with colonic metastasis generally have a poor prognosis, with median survival rate measured in months after GI involvement is detected. Treatment options include systemic chemotherapy, with first line therapy being pembrolizumab, carboplatin and pemetrexed for non-squamous cell lung cancer. Although chemotherapy decreases GI bleeding, the risk of obstruction and perforation remains unchanged, supported in a study by Hu et al (1). Palliative surgical intervention for obstruction can often improve patients’ quality of life.
References:
1. Hu Y, Feit N, Huang Y, Xu W, Zheng S, Li X. Gastrointestinal metastasis of primary lung cancer: An analysis of 366 cases. Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):9766-9776. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8575. Epub 2018 Apr 25. PMID: 29928351; PMCID: PMC6004691.
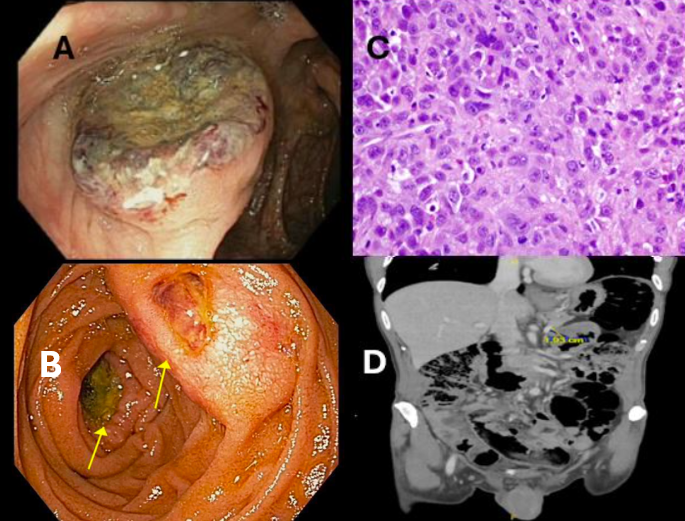
Figure: Figure A: colonoscopy image of hepatic flexure mass. Figure B: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy image of the ulcerated duodenal mass. Figure C: Photomicrograph of hepatic mass biopsy showing poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Figure D: CT abdomen image showing heterogenous hypodense 1.9 cm nodular focus, suggesting infiltrative process.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Berger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apaar Dadlani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ronan Allencherril indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mojgan Amrikachi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Schwartz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Schiesser indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Scott Berger, MD1, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Ronan Allencherril, MD1, Mojgan Amrikachi, MD3, Mary R. Schwartz, MD1, Rachel Schiesser, MD1. P4636 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Metastasizing to the Gastrointestinal Tract, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX; 2Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 3MD, Houston, TX
Introduction: Primary pulmonary adenocarcinoma presenting as metastasis to the gastrointestinal tract is a rare (< 2%) occurrence. The most common GI sites for lung cancer metastasis are the small intestine and colon. Presentations often include bowel obstruction or GI bleeding.
Case Description/
Methods: We present the case of a 66-year-old male with history of recent small bowel obstruction (SBO) who presented with abdominal pain and melena. He was admitted for nausea and vomiting. Computed tomography (CT) confirmed a SBO with transition points in the right lower quadrant with circumferential wall thickening of multiple segments of the small bowel and a lytic T10 spinal lesion. Further work-up with CT of the chest demonstrated a left upper lung lobe mass invading the anterior mediastinum. A subsequent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy revealed four 0.5-2cm ulcerated masses in the second portion of the duodenum and 2cm masses, one in the hepatic flexure and one in the rectum. Biopsies of these masses revealed poorly differentiated carcinoma with focal sarcomatoid features. Bronchoscopy and biopsies of the left upper lung mass showed poorly differentiated pulmonary adenocarcinoma with PD-L1 expression in 30% of the cells. The tumor in the GI tract biopsies was histologically similar to the lung primary. Oncology was consulted for management of stage IV lung carcinoma and patient was started on pembrolizumab, carboplatin, and pemetrexed. Unfortunately, he continued to have multiple episodes of partial SBOs requiring hospital admissions which were managed conservatively. At 6 months from his diagnosis, he continues to receive chemotherapy and is pending a palliative G tube placement.
Discussion: Patients with lung adenocarcinoma with colonic metastasis generally have a poor prognosis, with median survival rate measured in months after GI involvement is detected. Treatment options include systemic chemotherapy, with first line therapy being pembrolizumab, carboplatin and pemetrexed for non-squamous cell lung cancer. Although chemotherapy decreases GI bleeding, the risk of obstruction and perforation remains unchanged, supported in a study by Hu et al (1). Palliative surgical intervention for obstruction can often improve patients’ quality of life.
References:
1. Hu Y, Feit N, Huang Y, Xu W, Zheng S, Li X. Gastrointestinal metastasis of primary lung cancer: An analysis of 366 cases. Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):9766-9776. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8575. Epub 2018 Apr 25. PMID: 29928351; PMCID: PMC6004691.

Figure: Figure A: colonoscopy image of hepatic flexure mass. Figure B: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy image of the ulcerated duodenal mass. Figure C: Photomicrograph of hepatic mass biopsy showing poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Figure D: CT abdomen image showing heterogenous hypodense 1.9 cm nodular focus, suggesting infiltrative process.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Berger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apaar Dadlani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Basit Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ronan Allencherril indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mojgan Amrikachi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Schwartz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Schiesser indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Afzal, MD1, Scott Berger, MD1, Apaar Dadlani, MD1, Abdul Basit Afzal, MBBS2, Ronan Allencherril, MD1, Mojgan Amrikachi, MD3, Mary R. Schwartz, MD1, Rachel Schiesser, MD1. P4636 - A Rare Case of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Metastasizing to the Gastrointestinal Tract, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
