Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P6292 - Beyond the Usual Battle: Refractory Duodenal Ulcer From Overlapping Eosinophilic Enteritis and Esophagitis in a Young Soldier Requiring Combination Biologic Therapy
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- TD
Tyler Doty, DO
Brooke Army Medical Center
Cibolo, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Tyler Doty, DO1, Matthew Robles, DO2, Carl Kay, MD3
1Brooke Army Medical Center, Cibolo, TX; 2Carl R. Darnall Army Medical Center, For Cavazos, TX; 3Carl R. Darnall Army Medical Center, Fort Cavazos, TX
Introduction: Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is rare in adolescents. When ulcers persist without NSAID use or Helicobacter pylori infection, uncommon causes must be considered. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs), including eosinophilic duodenitis (EoD) and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), can rarely present as refractory ulcers. We present a challenging case of persistent PUD in an active-duty soldier with overlapping EGIDs.
Case Description/
Methods: A 19-year-old female soldier presented with recurrent hematemesis, nausea, and epigastric pain. She had a persistent duodenal bulb ulcer despite strict adherence to twice-daily PPI therapy. She denied NSAID use after October 2024, and H. pylori testing was negative. Workup ruled out hypersecretory conditions, Crohn’s disease, malignancy, infections, vascular anomalies, and altered PPI metabolism (Table 1). Push enteroscopy showed a deep, clean-based duodenal bulb ulcer; distal small bowel appeared normal. Biopsies revealed >30 eosinophils per high-power field (hpf). She was started on rabeprazole and a six-food elimination diet without success. Steroids were avoided due to elevated BMI and metabolic risk factors. Repeat EGD in March 2025 showed persistent ulceration and new EoE findings (EREFS 4) with biopsies revealing up to 100 eos/hpf. Vedolizumab was started, leading to partial improvement in epigastric pain but persistent esophageal dysfunction. In May 2025, follow-up EGD confirmed an ongoing duodenal ulcer and active EoE. Dupilumab was added for refractory esophageal symptoms (Figure 1). Peripheral eosinophilia (peak 1220/μL) persisted. She is now improving on combination biologic therapy.
Discussion: This case illustrates a rare presentation of non-healing duodenal ulcer as a manifestation of overlapping EGIDs. While coexisting EoE and EoD is uncommon, managing both can be challenging. Vedolizumab improved small bowel symptoms but was not enough for esophageal dysfunction. Dupilumab was added, representing a novel dual-biologic strategy. To our knowledge, this is the first report of combination vedolizumab and dupilumab for overlapping EGID involving the esophagus and duodenum. This case highlights the need for individualized, segment-specific therapy in complex EGID phenotypes.
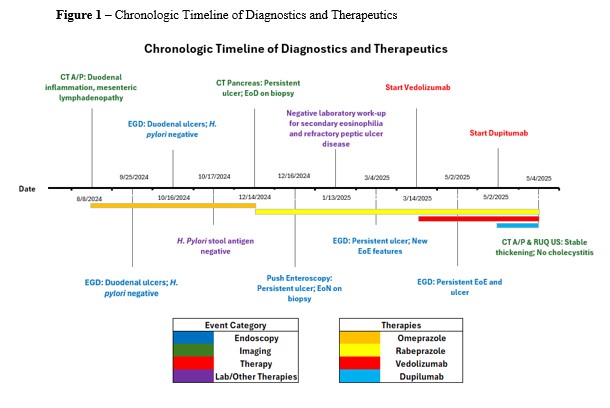
Figure: Table 1. Summary of Eosinophilia and Peptic Ulcer Disease Work-Up (TB - tuberculosis, PAS - Periodic Acid-Schiff Stain , AFB - Acid fast bacilli, tTG - tissue transglutaminase)
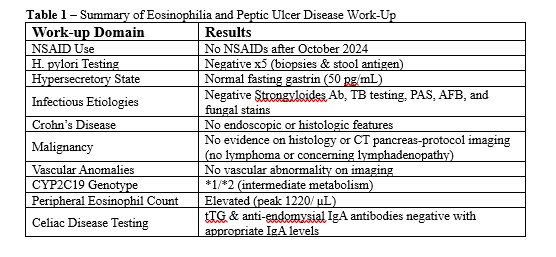
Figure: Figure 1. Chronologic timeline of diagnostics and therapeutics detailing endoscopy, imaging, therapies, and laboratory testing during evaluation of patient. Therapies are denoted as color specific bars under the corresponding dates of therapy and detailed further in the figure's legend.
Disclosures:
Tyler Doty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carl Kay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tyler Doty, DO1, Matthew Robles, DO2, Carl Kay, MD3. P6292 - Beyond the Usual Battle: Refractory Duodenal Ulcer From Overlapping Eosinophilic Enteritis and Esophagitis in a Young Soldier Requiring Combination Biologic Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brooke Army Medical Center, Cibolo, TX; 2Carl R. Darnall Army Medical Center, For Cavazos, TX; 3Carl R. Darnall Army Medical Center, Fort Cavazos, TX
Introduction: Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is rare in adolescents. When ulcers persist without NSAID use or Helicobacter pylori infection, uncommon causes must be considered. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs), including eosinophilic duodenitis (EoD) and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), can rarely present as refractory ulcers. We present a challenging case of persistent PUD in an active-duty soldier with overlapping EGIDs.
Case Description/
Methods: A 19-year-old female soldier presented with recurrent hematemesis, nausea, and epigastric pain. She had a persistent duodenal bulb ulcer despite strict adherence to twice-daily PPI therapy. She denied NSAID use after October 2024, and H. pylori testing was negative. Workup ruled out hypersecretory conditions, Crohn’s disease, malignancy, infections, vascular anomalies, and altered PPI metabolism (Table 1). Push enteroscopy showed a deep, clean-based duodenal bulb ulcer; distal small bowel appeared normal. Biopsies revealed >30 eosinophils per high-power field (hpf). She was started on rabeprazole and a six-food elimination diet without success. Steroids were avoided due to elevated BMI and metabolic risk factors. Repeat EGD in March 2025 showed persistent ulceration and new EoE findings (EREFS 4) with biopsies revealing up to 100 eos/hpf. Vedolizumab was started, leading to partial improvement in epigastric pain but persistent esophageal dysfunction. In May 2025, follow-up EGD confirmed an ongoing duodenal ulcer and active EoE. Dupilumab was added for refractory esophageal symptoms (Figure 1). Peripheral eosinophilia (peak 1220/μL) persisted. She is now improving on combination biologic therapy.
Discussion: This case illustrates a rare presentation of non-healing duodenal ulcer as a manifestation of overlapping EGIDs. While coexisting EoE and EoD is uncommon, managing both can be challenging. Vedolizumab improved small bowel symptoms but was not enough for esophageal dysfunction. Dupilumab was added, representing a novel dual-biologic strategy. To our knowledge, this is the first report of combination vedolizumab and dupilumab for overlapping EGID involving the esophagus and duodenum. This case highlights the need for individualized, segment-specific therapy in complex EGID phenotypes.

Figure: Table 1. Summary of Eosinophilia and Peptic Ulcer Disease Work-Up (TB - tuberculosis, PAS - Periodic Acid-Schiff Stain , AFB - Acid fast bacilli, tTG - tissue transglutaminase)

Figure: Figure 1. Chronologic timeline of diagnostics and therapeutics detailing endoscopy, imaging, therapies, and laboratory testing during evaluation of patient. Therapies are denoted as color specific bars under the corresponding dates of therapy and detailed further in the figure's legend.
Disclosures:
Tyler Doty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carl Kay indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tyler Doty, DO1, Matthew Robles, DO2, Carl Kay, MD3. P6292 - Beyond the Usual Battle: Refractory Duodenal Ulcer From Overlapping Eosinophilic Enteritis and Esophagitis in a Young Soldier Requiring Combination Biologic Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
