Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2183 - Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- FK
Faisal Kamal, MD
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Abdullah Rasheed, MBBS4, Ahmad Sabah, MBBS4, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Abdul Mateen, MBBS4, Marjan Haider, MD5, Muhammad Elahi, MD6, Muhammad Kamal, MD7, Sam Dabit, 8, Amman Yousaf, MD9, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Janak Shah, MD10, Faisal Kamal, MD11
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3King Edward Medical University, Chattanooga, TN; 4Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 6West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 7Hackensack Meridian Health, Edison, NJ; 8South Central Regional Medical Center, Laurel, MS; 9Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Hattiesburg, MS; 10Ochsner Health System, New Orleans, LA; 11Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a leading cause of hospital admissions in the United States. Up to 20% of AP cases can progress to acute necrotizing pancreatitis (ANP). Inflammation-induced dysregulation of the coagulation cascade and vascular stasis in hospitalized patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis (ANP) serve as a milieu for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are often underrecognized. In this meta-analysis, we have evaluated the incidence of VTE and associated worse outcomes in patients with ANP.
Methods: We reviewed several databases from inception to April 28, 2025, to identify studies that reported the incidence of VTE in patients with ANP. Our outcomes of interest were the rate of VTE, DVT, PE, and splanchnic venous thrombosis, and comparison of all-cause mortality, intensive care admissions, and organ failure in ANP patients with and without venous thrombosis. We calculated pooled rates with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for our outcomes of interest. Pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated for comparatives outcomes. Data was analyzed using random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistic.
Results: We included 8 studies with 83425 patients with ANP. The mean age of the patients was 51.6(1.9) years. Pooled rates (95% CI) of VTE in patients with the ANP were 15% (6.7%, 32%) (Figure 1A). Pooled rates (95% CI) of DVT in patients with the ANP group were 7.4% (1%, 30%) (Figure 1B). Pooled rates (95% CI) of pulmonary embolism in patients with the ANP group were 3% (1%, 6.6%). Pooled rates (95% CI) of splanchnic venous thrombosis in patients with the ANP were 29% (10%, 58%). Rates of all-cause mortality, OR 1.50 (1.06, 2.11), p=0.02, I² =91% (Figure 2A) and intensive care admissions, OR 1.86 (1.78, 1.95), p< 0.00001, I² =0% (Figure 2B) were significantly higher in VTE group compared to no VTE group.
Discussion: Patients with ANP are at increased risk of VTE. VTE is associated with elevated risk of mortality and intensive care admissions in patients with ANP.
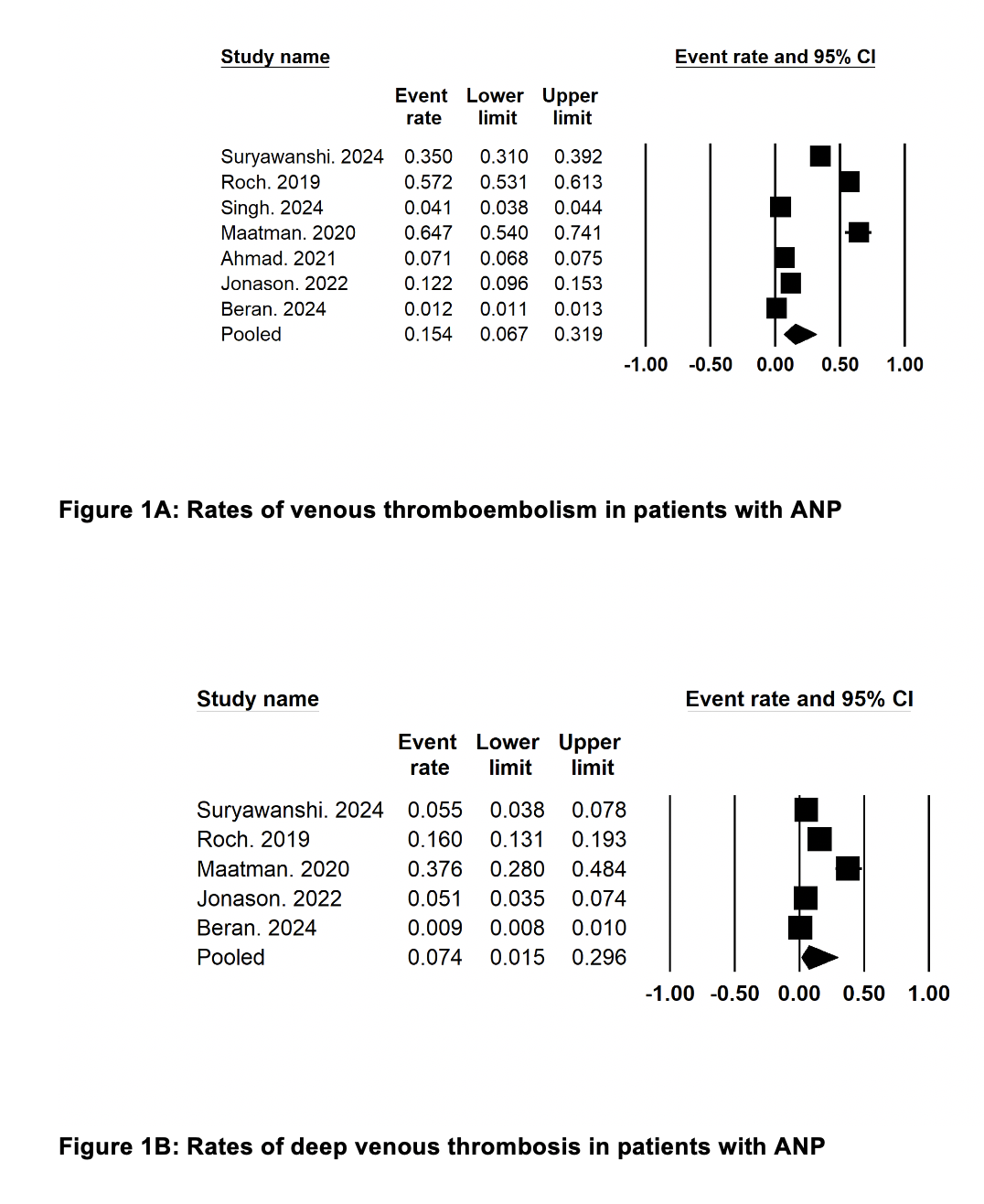
Figure: Figure 1: Rates of venous thromboembolism and deep venous thrombosis in patients with ANP
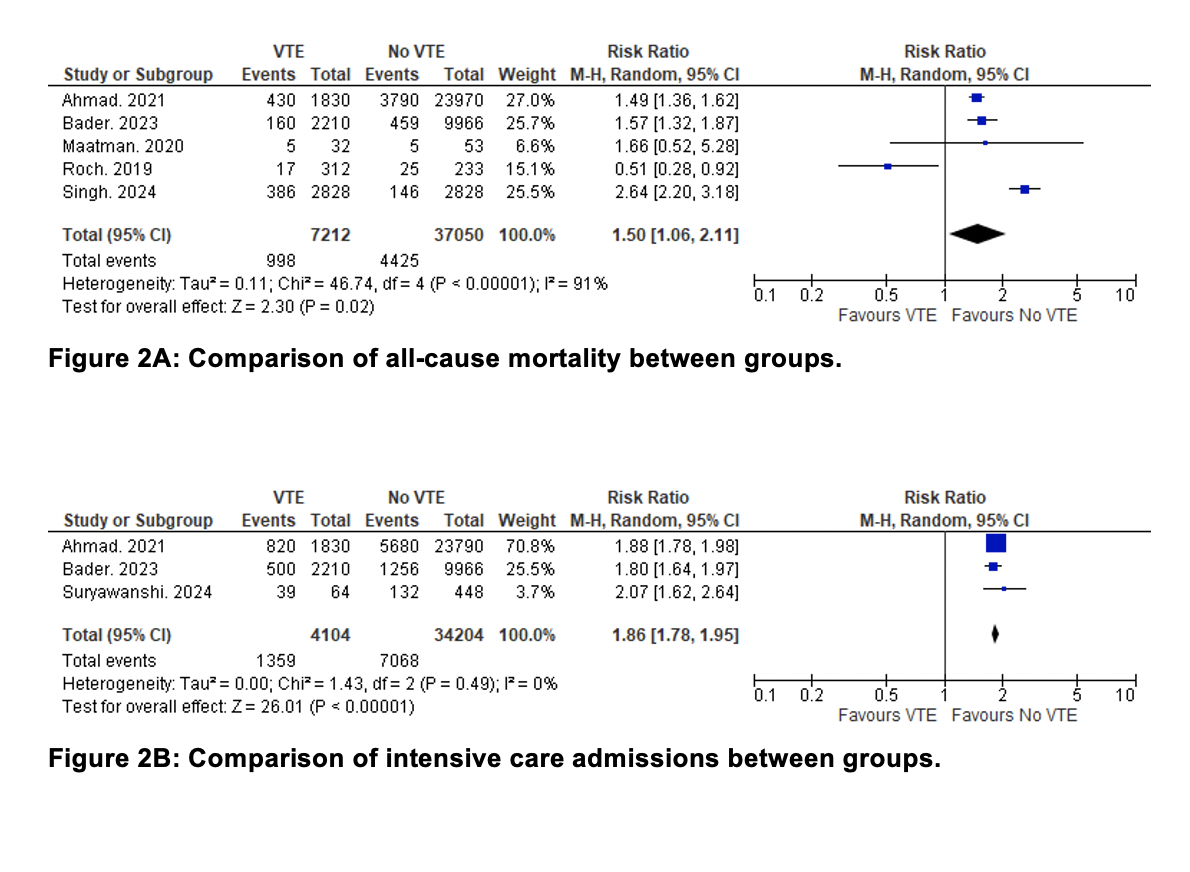
Figure: Figure 2: Comparison of all cause mortality and intensive care admissions between groups
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hina Akbar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Rasheed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Sabah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Yousuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Mateen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marjan Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Elahi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sam Dabit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amman Yousaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Radlinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Janak Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Abdullah Rasheed, MBBS4, Ahmad Sabah, MBBS4, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Abdul Mateen, MBBS4, Marjan Haider, MD5, Muhammad Elahi, MD6, Muhammad Kamal, MD7, Sam Dabit, 8, Amman Yousaf, MD9, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Janak Shah, MD10, Faisal Kamal, MD11. P2183 - Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3King Edward Medical University, Chattanooga, TN; 4Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 6West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 7Hackensack Meridian Health, Edison, NJ; 8South Central Regional Medical Center, Laurel, MS; 9Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Hattiesburg, MS; 10Ochsner Health System, New Orleans, LA; 11Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a leading cause of hospital admissions in the United States. Up to 20% of AP cases can progress to acute necrotizing pancreatitis (ANP). Inflammation-induced dysregulation of the coagulation cascade and vascular stasis in hospitalized patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis (ANP) serve as a milieu for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are often underrecognized. In this meta-analysis, we have evaluated the incidence of VTE and associated worse outcomes in patients with ANP.
Methods: We reviewed several databases from inception to April 28, 2025, to identify studies that reported the incidence of VTE in patients with ANP. Our outcomes of interest were the rate of VTE, DVT, PE, and splanchnic venous thrombosis, and comparison of all-cause mortality, intensive care admissions, and organ failure in ANP patients with and without venous thrombosis. We calculated pooled rates with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for our outcomes of interest. Pooled odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated for comparatives outcomes. Data was analyzed using random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistic.
Results: We included 8 studies with 83425 patients with ANP. The mean age of the patients was 51.6(1.9) years. Pooled rates (95% CI) of VTE in patients with the ANP were 15% (6.7%, 32%) (Figure 1A). Pooled rates (95% CI) of DVT in patients with the ANP group were 7.4% (1%, 30%) (Figure 1B). Pooled rates (95% CI) of pulmonary embolism in patients with the ANP group were 3% (1%, 6.6%). Pooled rates (95% CI) of splanchnic venous thrombosis in patients with the ANP were 29% (10%, 58%). Rates of all-cause mortality, OR 1.50 (1.06, 2.11), p=0.02, I² =91% (Figure 2A) and intensive care admissions, OR 1.86 (1.78, 1.95), p< 0.00001, I² =0% (Figure 2B) were significantly higher in VTE group compared to no VTE group.
Discussion: Patients with ANP are at increased risk of VTE. VTE is associated with elevated risk of mortality and intensive care admissions in patients with ANP.

Figure: Figure 1: Rates of venous thromboembolism and deep venous thrombosis in patients with ANP

Figure: Figure 2: Comparison of all cause mortality and intensive care admissions between groups
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hina Akbar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Rasheed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Sabah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Yousuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Mateen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marjan Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Elahi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sam Dabit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amman Yousaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Radlinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Janak Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Abdullah Rasheed, MBBS4, Ahmad Sabah, MBBS4, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Abdul Mateen, MBBS4, Marjan Haider, MD5, Muhammad Elahi, MD6, Muhammad Kamal, MD7, Sam Dabit, 8, Amman Yousaf, MD9, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Janak Shah, MD10, Faisal Kamal, MD11. P2183 - Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
