Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2182 - Use of Novel Agent Purastat® for Post Sphincterotomy Bleeding
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- FK
Faisal Kamal, MD
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Ananya Venkatesh, MD1, Bertilia Tavarez, MD2, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD1, Donna Leet, MD3, Afshin Khan, MD, MPH3, Abdul Kouanda, MD3, Anand Kumar, MD, MPH2, Alana Persaud, MD1, Yasi Xiao, MD1, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Thomas Kowalski, MD1, Faisal Kamal, MD1
1Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 2Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Introduction: Endoscopic sphincterotomy is commonly performed during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Despite being performed by expert endoscopists, endoscopic sphincterotomy (ES) is associated with adverse events such as bleeding and perforation. The incidence of post sphincterotomy bleed has been reported to be 1-3%. PuraStat® is a new synthetic hemostatic gel being used for the prophylaxis and treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding. To date, there are no published reports on the use of PuraStat® for post sphincterotomy bleeding. We aim to report the use and outcomes of PuraStat® for post sphincterotomy bleeding.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of medical records from two institutions. All patients who underwent ES for which PuraStat® was used alongside other hemostatic methods for the treatment of post-sphincterotomy bleeding were included. The aim of this study is to report on the indication, procedural and technical parameters and efficacy and safety of PuraStat for post-sphincterotomy hemorrhage.
Results: A total of 11 patients met our inclusion criteria. 55% of patients were female and mean age was 59 years. 18% of patients had significant renal dysfunction (GFR < 60) and 9% had abnormal platelets at the time of intervention. 82% of patients had intraprocedural/immediate bleeding during sphincterotomy (Table 1). 18% of the patients required hospitalization due to immediate bleeding. A variety of hemostatic methods were used with 36% of the patient requiring bipolar cautery. 82% of the patients had complete cessation of the bleeding during index procedure after PuraStat® application. None of the patients experienced recurrent (< 2 weeks) bleeding after hemostatic agent use (Table 2).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates the efficacy of PuraStat® in the management of post-sphincterotomy bleeding and none of the patients experienced recurrent bleeding after its use. The use of this novel agent proves to be safe and efficacious when used alongside other hemostatic methods. Larger scale multicenter studies are required to further validate these findings.
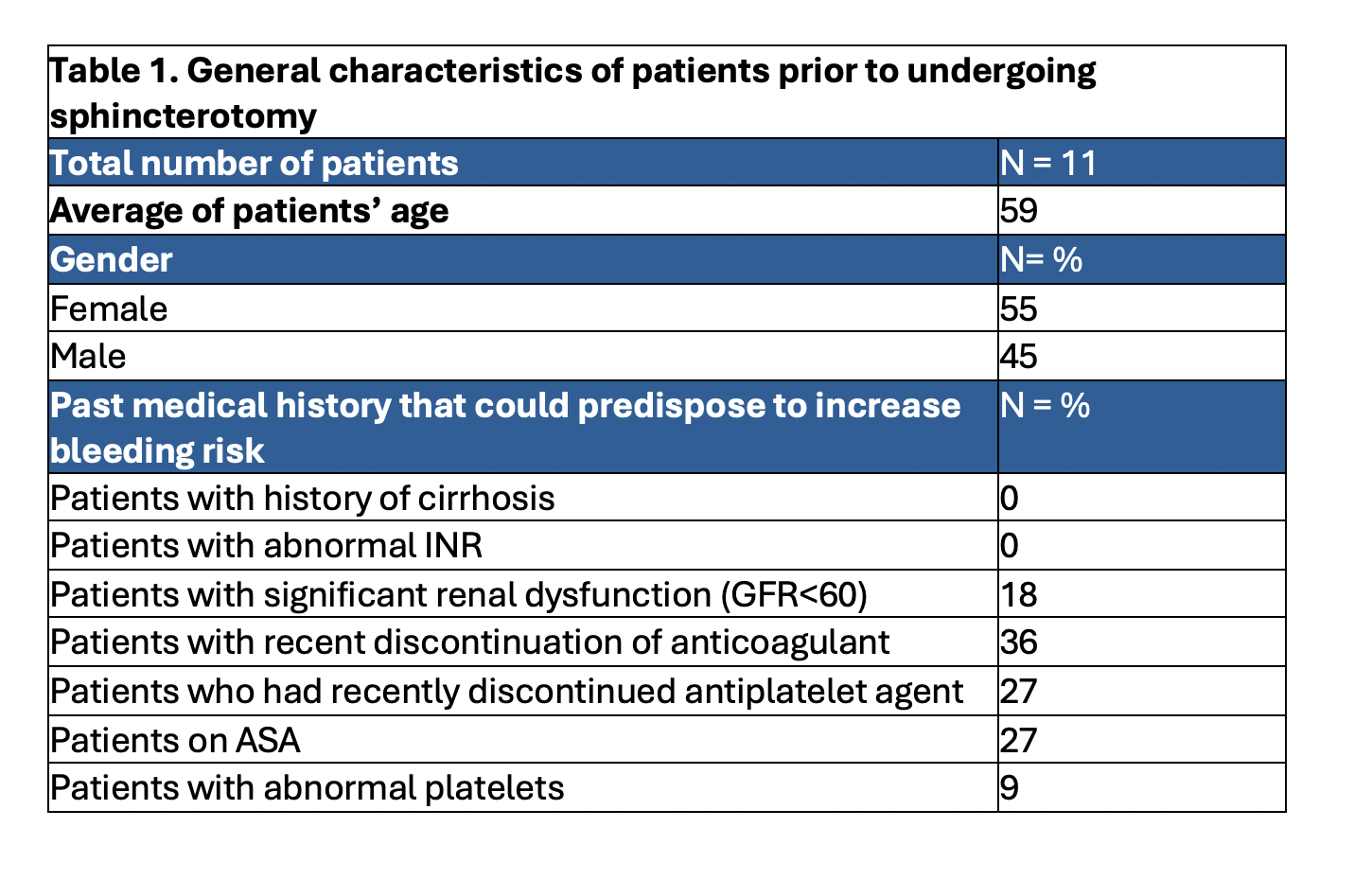
Figure: Table 1. General characteristics of patients prior to undergoing sphincterotomy
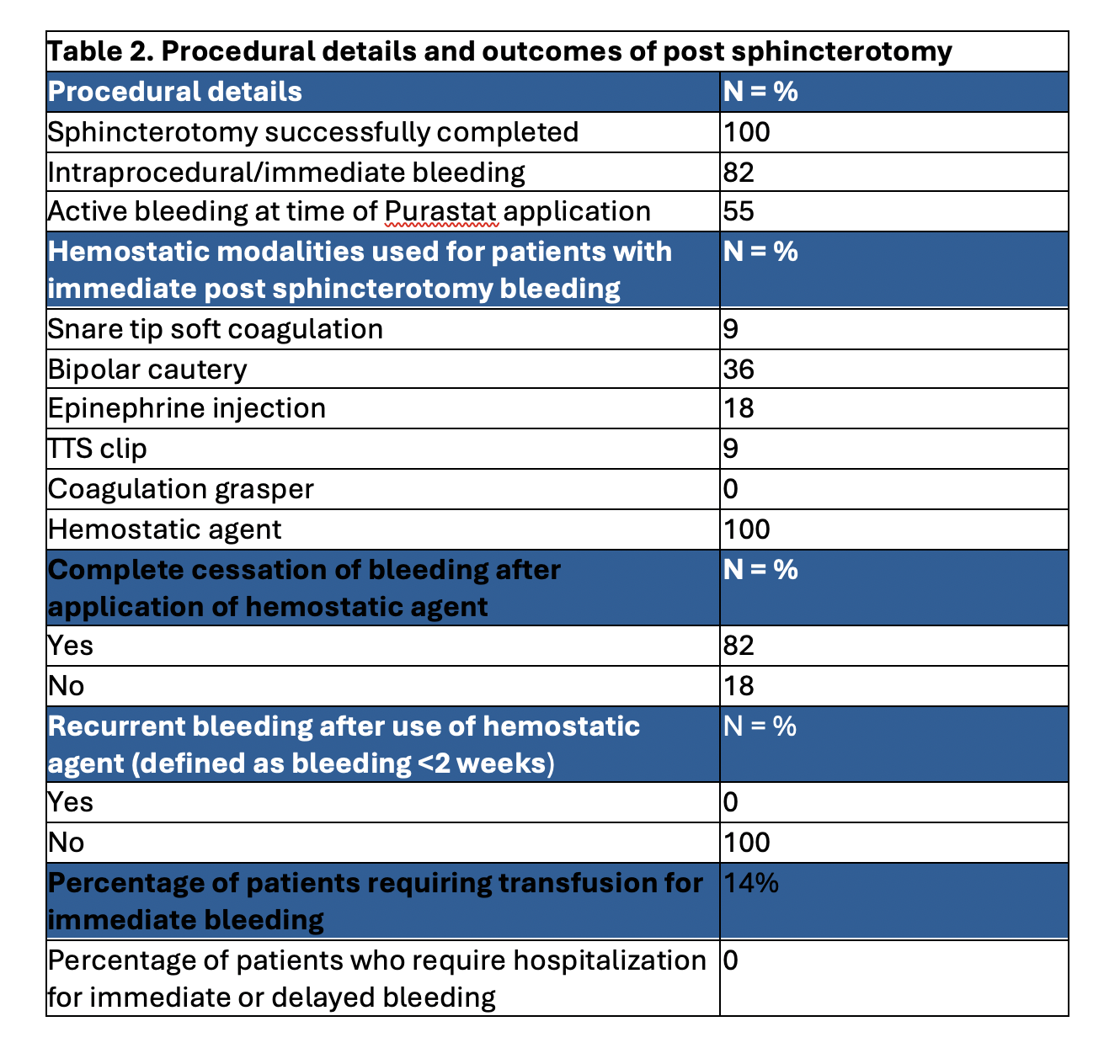
Figure: Table 2. Procedural details and outcomes of post sphincterotomy
Disclosures:
Ananya Venkatesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bertilia Tavarez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Palacios Argueta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donna Leet: Neptune Medical – Consultant.
Afshin Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Kouanda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anand Kumar: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Pentax – Paid Speaker.
Alana Persaud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasi Xiao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Schlachterman: Boston Scientific – Consultant. FujiFilm – Consultant. Laborie – Consultant. Lumendi – Consultant. Microtech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Thomas Kowalski: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Venkatesh, MD1, Bertilia Tavarez, MD2, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD1, Donna Leet, MD3, Afshin Khan, MD, MPH3, Abdul Kouanda, MD3, Anand Kumar, MD, MPH2, Alana Persaud, MD1, Yasi Xiao, MD1, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Thomas Kowalski, MD1, Faisal Kamal, MD1. P2182 - Use of Novel Agent Purastat® for Post Sphincterotomy Bleeding, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 2Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Introduction: Endoscopic sphincterotomy is commonly performed during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Despite being performed by expert endoscopists, endoscopic sphincterotomy (ES) is associated with adverse events such as bleeding and perforation. The incidence of post sphincterotomy bleed has been reported to be 1-3%. PuraStat® is a new synthetic hemostatic gel being used for the prophylaxis and treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding. To date, there are no published reports on the use of PuraStat® for post sphincterotomy bleeding. We aim to report the use and outcomes of PuraStat® for post sphincterotomy bleeding.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of medical records from two institutions. All patients who underwent ES for which PuraStat® was used alongside other hemostatic methods for the treatment of post-sphincterotomy bleeding were included. The aim of this study is to report on the indication, procedural and technical parameters and efficacy and safety of PuraStat for post-sphincterotomy hemorrhage.
Results: A total of 11 patients met our inclusion criteria. 55% of patients were female and mean age was 59 years. 18% of patients had significant renal dysfunction (GFR < 60) and 9% had abnormal platelets at the time of intervention. 82% of patients had intraprocedural/immediate bleeding during sphincterotomy (Table 1). 18% of the patients required hospitalization due to immediate bleeding. A variety of hemostatic methods were used with 36% of the patient requiring bipolar cautery. 82% of the patients had complete cessation of the bleeding during index procedure after PuraStat® application. None of the patients experienced recurrent (< 2 weeks) bleeding after hemostatic agent use (Table 2).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates the efficacy of PuraStat® in the management of post-sphincterotomy bleeding and none of the patients experienced recurrent bleeding after its use. The use of this novel agent proves to be safe and efficacious when used alongside other hemostatic methods. Larger scale multicenter studies are required to further validate these findings.

Figure: Table 1. General characteristics of patients prior to undergoing sphincterotomy

Figure: Table 2. Procedural details and outcomes of post sphincterotomy
Disclosures:
Ananya Venkatesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bertilia Tavarez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Palacios Argueta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donna Leet: Neptune Medical – Consultant.
Afshin Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Kouanda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anand Kumar: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Pentax – Paid Speaker.
Alana Persaud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yasi Xiao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Schlachterman: Boston Scientific – Consultant. FujiFilm – Consultant. Laborie – Consultant. Lumendi – Consultant. Microtech – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Thomas Kowalski: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Venkatesh, MD1, Bertilia Tavarez, MD2, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD1, Donna Leet, MD3, Afshin Khan, MD, MPH3, Abdul Kouanda, MD3, Anand Kumar, MD, MPH2, Alana Persaud, MD1, Yasi Xiao, MD1, Alexander Schlachterman, MD1, Thomas Kowalski, MD1, Faisal Kamal, MD1. P2182 - Use of Novel Agent Purastat® for Post Sphincterotomy Bleeding, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
