Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2833 - A Case of PPI-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) With Stricture Responsive to Biologic Therapy
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Huzeifa M. Gulamhusein, MD, MS (he/him/his)
University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Memphis, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Huzeifa M. Gulamhusein, MD, MS1, Leonard Baidoo, MD, FACG1, Chloe Hundman, MD1, Samantha Whitwell, MD2
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 2UTHSC, Memphis, TN
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an infiltrative disease that is driven by eosinophils in a complex interaction between food allergens and patients with underlying genetic predisposition. The prevalence of EoE continues to increase with a rate of 1 in 617 in those < 65 years, and 1 in 1562 in those > 65 years (1). The annual costs attributable to EoE were approximately $1.3 billion dollars in 2024, representing a significant financial burden on the United States Healthcare System (1). We report a case of successful resolution of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) refractory EoE using dupilumab in a patient with esophageal stricture.
Case Description/
Methods: A 26-year-old female with a history of asthma, peanut allergy, and EoE with esophageal stricture presented with persistent dysphagia and recurrent food impaction. Despite the use of PPIs since her initial diagnosis in 2019, food elimination diets, and topical steroids, the patient continued to experience recurrent food impaction with minimal symptomatic relief. The patient underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with biopsy, which demonstrated squamous mucosa with eosinophil counts up to 72 eosinophils/hpf as well as characteristic rings and furrows. Given the PPI-refractory EoE, the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg once weekly. The patient remained on dupilumab for 11 months. Repeat biopsies after 11 months showed squamous mucosa with lamina propria fibrosis and basal cell hyperplasia with a total absence of eosinophils in both the proximal and distal esophagus. Clinically, the patient’s dysphagia had completely resolved allowing her to tolerate a regular diet for the first time since her initial diagnosis in 2019.
Discussion: This case highlights the effectiveness of biologic therapy in a patient with EoE resistant to dietary lifestyle modifications, PPIs, and topical steroids. Dupilumab is effective and well-tolerated in patients with PPI-resistant EoE and can allow patients to return to normalcy with higher quality of life. Our case is also significant as it demonstrates that biologics such as dupilumab shows promise in improving esophageal strictures in patients with PPI-refractory EoE without necessitating dilation which has its known associated risks of deep esophageal bleeding or perforation.
References
1. Thel HL, Anderson C, Xue AZ, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Prevalence and Costs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;23(2):272-80 e8.
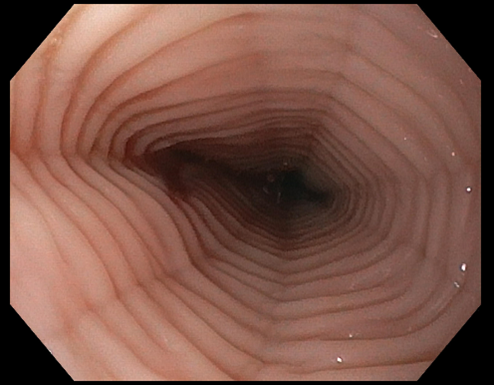
Figure: Before Treatment with Dupilumab
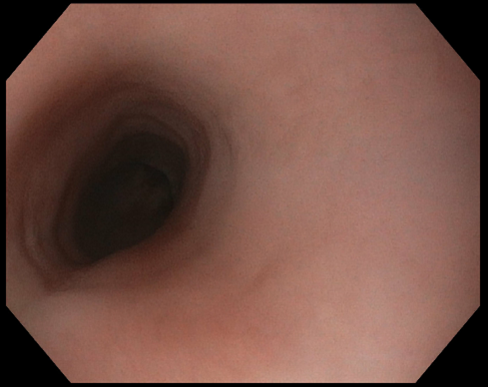
Figure: After Treatment with Dupilumab
Disclosures:
Huzeifa Gulamhusein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leonard Baidoo: Johnson and Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Lily Pharmaceuticals – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau.
Chloe Hundman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samantha Whitwell indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Huzeifa M. Gulamhusein, MD, MS1, Leonard Baidoo, MD, FACG1, Chloe Hundman, MD1, Samantha Whitwell, MD2. P2833 - A Case of PPI-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) With Stricture Responsive to Biologic Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 2UTHSC, Memphis, TN
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an infiltrative disease that is driven by eosinophils in a complex interaction between food allergens and patients with underlying genetic predisposition. The prevalence of EoE continues to increase with a rate of 1 in 617 in those < 65 years, and 1 in 1562 in those > 65 years (1). The annual costs attributable to EoE were approximately $1.3 billion dollars in 2024, representing a significant financial burden on the United States Healthcare System (1). We report a case of successful resolution of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) refractory EoE using dupilumab in a patient with esophageal stricture.
Case Description/
Methods: A 26-year-old female with a history of asthma, peanut allergy, and EoE with esophageal stricture presented with persistent dysphagia and recurrent food impaction. Despite the use of PPIs since her initial diagnosis in 2019, food elimination diets, and topical steroids, the patient continued to experience recurrent food impaction with minimal symptomatic relief. The patient underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with biopsy, which demonstrated squamous mucosa with eosinophil counts up to 72 eosinophils/hpf as well as characteristic rings and furrows. Given the PPI-refractory EoE, the patient was started on dupilumab 300 mg once weekly. The patient remained on dupilumab for 11 months. Repeat biopsies after 11 months showed squamous mucosa with lamina propria fibrosis and basal cell hyperplasia with a total absence of eosinophils in both the proximal and distal esophagus. Clinically, the patient’s dysphagia had completely resolved allowing her to tolerate a regular diet for the first time since her initial diagnosis in 2019.
Discussion: This case highlights the effectiveness of biologic therapy in a patient with EoE resistant to dietary lifestyle modifications, PPIs, and topical steroids. Dupilumab is effective and well-tolerated in patients with PPI-resistant EoE and can allow patients to return to normalcy with higher quality of life. Our case is also significant as it demonstrates that biologics such as dupilumab shows promise in improving esophageal strictures in patients with PPI-refractory EoE without necessitating dilation which has its known associated risks of deep esophageal bleeding or perforation.
References
1. Thel HL, Anderson C, Xue AZ, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Prevalence and Costs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;23(2):272-80 e8.

Figure: Before Treatment with Dupilumab

Figure: After Treatment with Dupilumab
Disclosures:
Huzeifa Gulamhusein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leonard Baidoo: Johnson and Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Lily Pharmaceuticals – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau.
Chloe Hundman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samantha Whitwell indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Huzeifa M. Gulamhusein, MD, MS1, Leonard Baidoo, MD, FACG1, Chloe Hundman, MD1, Samantha Whitwell, MD2. P2833 - A Case of PPI-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) With Stricture Responsive to Biologic Therapy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
