Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3693 - Real-World Comparison of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Aspirin in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Diseases and Obesity: A Propensity-Matched Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Olanrewaju Adeniran, MD (he/him/his)
West Virginia University Morgantown
Morgantown, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MD1, Budoor Alqinai, MBChB, MSc2, Farirai Melania Marwizi, MD3, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD4, Arthur CHIDI. Igbo, MD, MPH5, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD4, Abidemi Akinrinmade, MBBS6, Hamza Almusabeh, MBBS4, Emeka S. Obi, MBBS7, Raja S. Khan, MD4, Swapna Gayam, MD8
1West Virginia University Morgantown, Morgantown, WV; 2West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 3Episcopal Health Services, Queens, NY; 4West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 5Texas Health Resources HEB/Denton Internal Medicine Program, Lewisville, TX; 6University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Monroeville, PA; 7One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 8GI and Hepatology - West Virginia University, West Virginia, VA
Introduction: In the search for a sustainable treatment for patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), recent clinical trials have independently demonstrated the benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) and aspirin. However, no study has compared the efficacy and safety profiles of both medications in this population. This study aims to address this gap by assessing the effects of GLP-1RA and aspirin on the progression of MASLD/MASH and its associated complications.
Methods: Using Trinetx, patients with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m² and MASLD and/or MASH between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2023, were divided into two cohorts: GLP-1RA versus aspirin. The analysis included participants who started either medication after MASLD or MASH diagnosis. Patients with other causes of liver disease were excluded. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance relevant variables (Table 1). Outcomes include the risk of progression to fibrosis, hepatic complications, hepatic medication use, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and all-cause mortality. Cox-regression analysis was used to calculate the hazard ratio.
Results: Before PSM, 59,350 and 77,044 patients were identified in the GLP-1RA and aspirin groups, respectively. After PSM, 35,334 patients were analyzed in both groups. GLP-1RA demonstrates superior safety, with significant reductions in all-cause mortality (1% vs. 3.8%), MACE (3.6% vs. 9.4%), and heart failure (2.7% vs. 3.6%). Hepatic outcomes also favor GLP-1RA, showing significant reductions in overall liver-related morbidity and complications. However, GLP-1RA was associated with an increased risk of progression to cirrhosis, although this finding lacks statistical significance (p = 0.145) (Table 2).
Discussion: In summary, our analysis revealed that GLP-1RA provides significant benefits over aspirin for patients with MASH and obesity. The cardiovascular and mortality advantages, along with the reduced hepatic complications, far outweigh the uncertain fibrosis risk that has been identified, indicating that GLP-1RA offers a net clinical benefit in this high-risk population. This real-world data provides an intriguing perspective on recent and ongoing clinical trials evaluating treatment options for patients with MASLD and MASH.
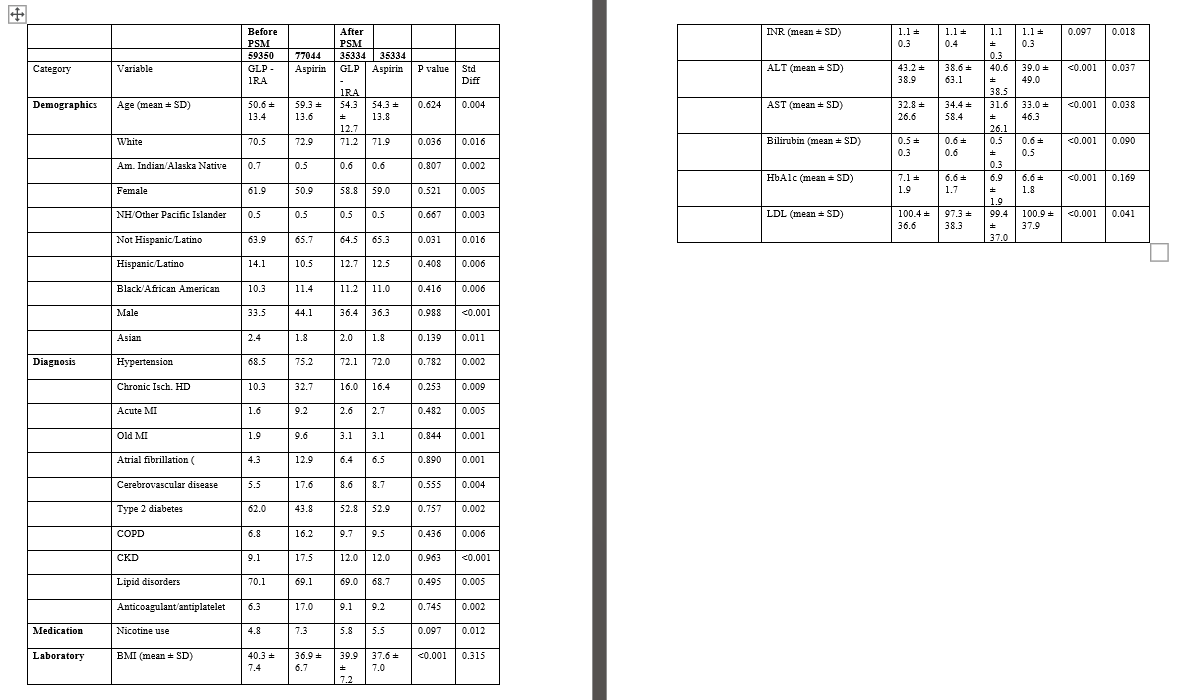
Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics of cohorts before and after propensity score matching (PSM).
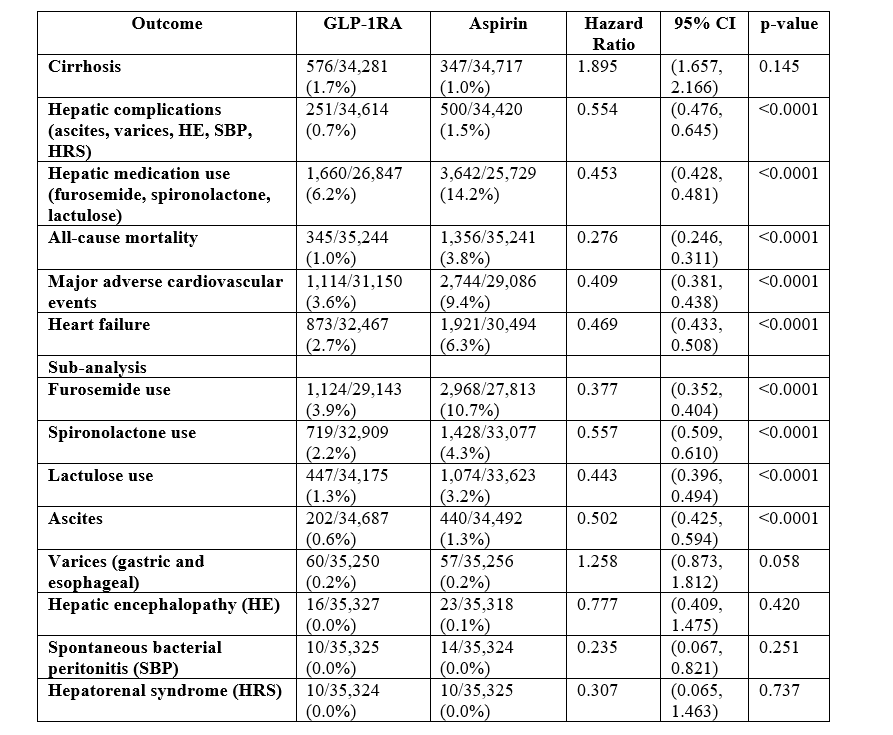
Figure: Table 2: GLP-1RA vs. Aspirin Outcomes Comparison in Patients with MASH and Obesity.
Disclosures:
Olanrewaju Adeniran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Budoor Alqinai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farirai Melania Marwizi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayowumi Adekolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arthur Igbo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Kirkpatrick indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abidemi Akinrinmade indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Almusabeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emeka Obi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swapna Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MD1, Budoor Alqinai, MBChB, MSc2, Farirai Melania Marwizi, MD3, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD4, Arthur CHIDI. Igbo, MD, MPH5, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD4, Abidemi Akinrinmade, MBBS6, Hamza Almusabeh, MBBS4, Emeka S. Obi, MBBS7, Raja S. Khan, MD4, Swapna Gayam, MD8. P3693 - Real-World Comparison of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Aspirin in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Diseases and Obesity: A Propensity-Matched Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1West Virginia University Morgantown, Morgantown, WV; 2West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 3Episcopal Health Services, Queens, NY; 4West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 5Texas Health Resources HEB/Denton Internal Medicine Program, Lewisville, TX; 6University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Monroeville, PA; 7One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 8GI and Hepatology - West Virginia University, West Virginia, VA
Introduction: In the search for a sustainable treatment for patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), recent clinical trials have independently demonstrated the benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) and aspirin. However, no study has compared the efficacy and safety profiles of both medications in this population. This study aims to address this gap by assessing the effects of GLP-1RA and aspirin on the progression of MASLD/MASH and its associated complications.
Methods: Using Trinetx, patients with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m² and MASLD and/or MASH between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2023, were divided into two cohorts: GLP-1RA versus aspirin. The analysis included participants who started either medication after MASLD or MASH diagnosis. Patients with other causes of liver disease were excluded. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to balance relevant variables (Table 1). Outcomes include the risk of progression to fibrosis, hepatic complications, hepatic medication use, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and all-cause mortality. Cox-regression analysis was used to calculate the hazard ratio.
Results: Before PSM, 59,350 and 77,044 patients were identified in the GLP-1RA and aspirin groups, respectively. After PSM, 35,334 patients were analyzed in both groups. GLP-1RA demonstrates superior safety, with significant reductions in all-cause mortality (1% vs. 3.8%), MACE (3.6% vs. 9.4%), and heart failure (2.7% vs. 3.6%). Hepatic outcomes also favor GLP-1RA, showing significant reductions in overall liver-related morbidity and complications. However, GLP-1RA was associated with an increased risk of progression to cirrhosis, although this finding lacks statistical significance (p = 0.145) (Table 2).
Discussion: In summary, our analysis revealed that GLP-1RA provides significant benefits over aspirin for patients with MASH and obesity. The cardiovascular and mortality advantages, along with the reduced hepatic complications, far outweigh the uncertain fibrosis risk that has been identified, indicating that GLP-1RA offers a net clinical benefit in this high-risk population. This real-world data provides an intriguing perspective on recent and ongoing clinical trials evaluating treatment options for patients with MASLD and MASH.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics of cohorts before and after propensity score matching (PSM).

Figure: Table 2: GLP-1RA vs. Aspirin Outcomes Comparison in Patients with MASH and Obesity.
Disclosures:
Olanrewaju Adeniran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Budoor Alqinai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farirai Melania Marwizi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayowumi Adekolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arthur Igbo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Kirkpatrick indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abidemi Akinrinmade indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Almusabeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emeka Obi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swapna Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MD1, Budoor Alqinai, MBChB, MSc2, Farirai Melania Marwizi, MD3, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD4, Arthur CHIDI. Igbo, MD, MPH5, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD4, Abidemi Akinrinmade, MBBS6, Hamza Almusabeh, MBBS4, Emeka S. Obi, MBBS7, Raja S. Khan, MD4, Swapna Gayam, MD8. P3693 - Real-World Comparison of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Aspirin in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Diseases and Obesity: A Propensity-Matched Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

