Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3384 - Beyond the Gut: TNF-Alpha Inhibitor-Induced Demyelinating Neuropathy and Bladder Dysfunction in a Crohn’s Disease Patient With Negative MRI Findings
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- JJ
Jazza Jamil, MBBS
Northwest School of Medicine
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Shaaf Ahmad, MBBS1, Ayesha Siddiqua, MBBS2, Jazza Jamil, MBBS3, Ghias un Nabi Tayyab, MBBS, MRCP4
1University of Lahore Teaching Hospital, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Northwest School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 4Doctors hospital and medical centre lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors are a cornerstone in managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Among them, infliximab-a chimeric monoclonal IgG antibody-has the highest reported incidence of neurological adverse events, including peripheral neuropathy. We report a rare case of infliximab-associated demyelinating neuropathy presenting as urinary incontinence and motor dysfunction, expanding the neurological spectrum of TNF-α inhibitor complications.
Case Description/
Methods: A 25-year-old female presented with a 7-month history of abdominal pain and diarrhea. Stool calprotectin was >1000 µg/g, and colon biopsy confirmed Crohn’s disease with transmural pancolitis and noncaseating granulomas. She was initially treated with dexamethasone and azathioprine with partial symptom control. Subcutaneous infliximab was initiated, improving GI symptoms. However, post-induction, she developed urinary leakage, reduced urine stream, pelvic weakness, difficulty walking, and impaired grip. Physical exam showed right lower limb weakness (4+/5), upgoing plantar response, hyperreflexia, rigidity, and jerky movements. Sensory loss followed a stocking distribution. Urodynamic studies and urethral pressure profilometry indicated neurogenic bladder with low detrusor pressure, reduced flow rate, and intermittent low urethral occlusion pressure. Nerve conduction studies revealed diminished F-wave responses and CMAP amplitude; EMG showed mild neurogenic changes. Brain and spine MRI were negative for central demyelination. Initial management targeted presumed urologic dysfunction, but poor response led to suspicion of infliximab-induced neuropathy. Infliximab was discontinued, and high-dose dexamethasone was initiated, leading to rapid improvement and suggesting an immune-mediated process. After a 3-month steroid taper, she had improved urinary symptoms, with mild residual limb weakness and occasional leakage.
Discussion: Neurological complications of TNF-α inhibitors are rare but clinically significant. This case is unique in that urinary incontinence and pelvic dysfunction were the first manifestations of infliximab-induced demyelinating neuropathy. New-onset urinary or motor symptoms in young patients should prompt early neurologic evaluation and discontinuation of the agent, even with a normal MRI. A delayed diagnosis may result in irreversible deficits.
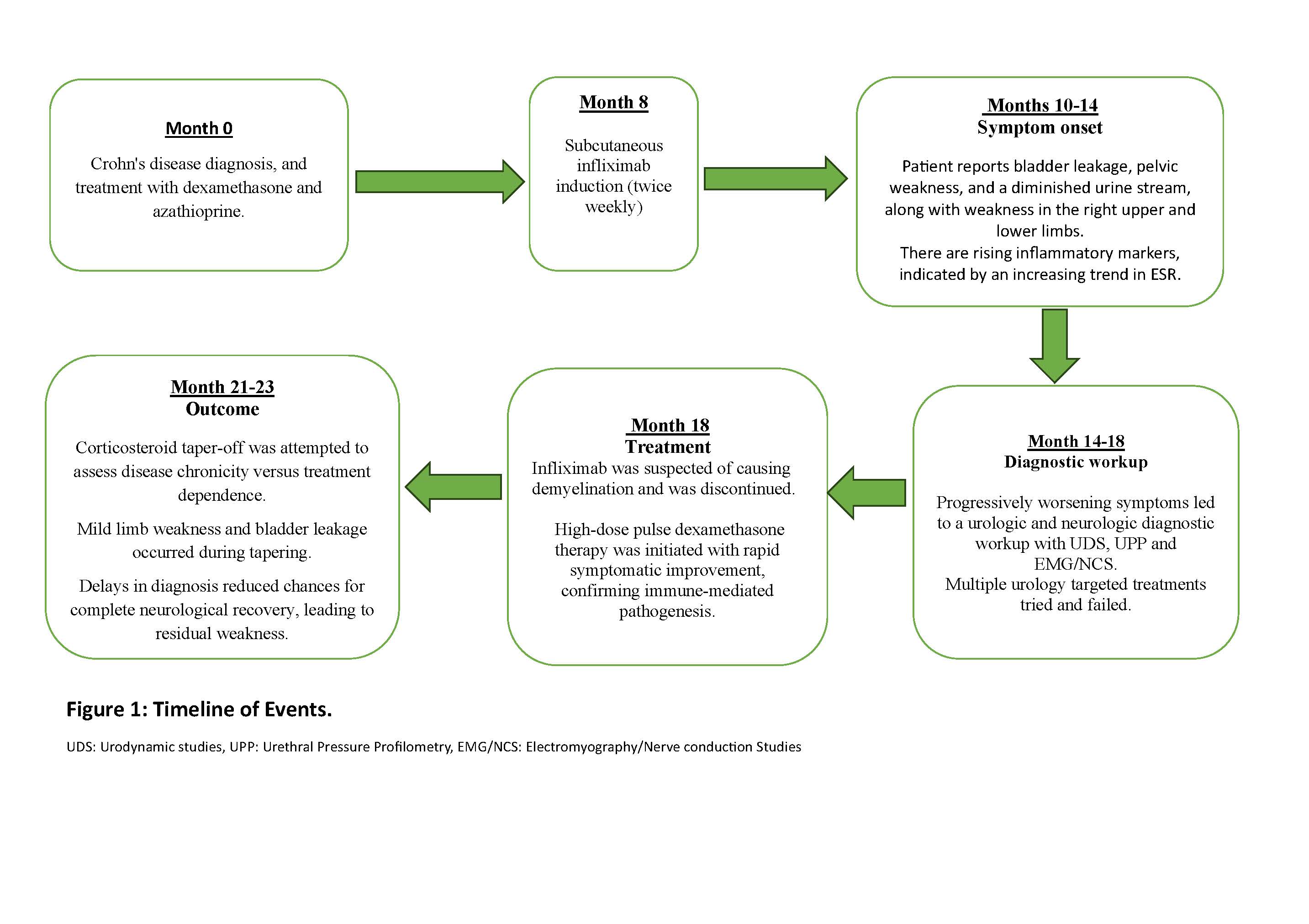
Figure: Timeline of Events
Disclosures:
Shaaf Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Siddiqua indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jazza Jamil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ghias un Nabi Tayyab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaaf Ahmad, MBBS1, Ayesha Siddiqua, MBBS2, Jazza Jamil, MBBS3, Ghias un Nabi Tayyab, MBBS, MRCP4. P3384 - Beyond the Gut: TNF-Alpha Inhibitor-Induced Demyelinating Neuropathy and Bladder Dysfunction in a Crohn’s Disease Patient With Negative MRI Findings, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Lahore Teaching Hospital, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Northwest School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 4Doctors hospital and medical centre lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors are a cornerstone in managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Among them, infliximab-a chimeric monoclonal IgG antibody-has the highest reported incidence of neurological adverse events, including peripheral neuropathy. We report a rare case of infliximab-associated demyelinating neuropathy presenting as urinary incontinence and motor dysfunction, expanding the neurological spectrum of TNF-α inhibitor complications.
Case Description/
Methods: A 25-year-old female presented with a 7-month history of abdominal pain and diarrhea. Stool calprotectin was >1000 µg/g, and colon biopsy confirmed Crohn’s disease with transmural pancolitis and noncaseating granulomas. She was initially treated with dexamethasone and azathioprine with partial symptom control. Subcutaneous infliximab was initiated, improving GI symptoms. However, post-induction, she developed urinary leakage, reduced urine stream, pelvic weakness, difficulty walking, and impaired grip. Physical exam showed right lower limb weakness (4+/5), upgoing plantar response, hyperreflexia, rigidity, and jerky movements. Sensory loss followed a stocking distribution. Urodynamic studies and urethral pressure profilometry indicated neurogenic bladder with low detrusor pressure, reduced flow rate, and intermittent low urethral occlusion pressure. Nerve conduction studies revealed diminished F-wave responses and CMAP amplitude; EMG showed mild neurogenic changes. Brain and spine MRI were negative for central demyelination. Initial management targeted presumed urologic dysfunction, but poor response led to suspicion of infliximab-induced neuropathy. Infliximab was discontinued, and high-dose dexamethasone was initiated, leading to rapid improvement and suggesting an immune-mediated process. After a 3-month steroid taper, she had improved urinary symptoms, with mild residual limb weakness and occasional leakage.
Discussion: Neurological complications of TNF-α inhibitors are rare but clinically significant. This case is unique in that urinary incontinence and pelvic dysfunction were the first manifestations of infliximab-induced demyelinating neuropathy. New-onset urinary or motor symptoms in young patients should prompt early neurologic evaluation and discontinuation of the agent, even with a normal MRI. A delayed diagnosis may result in irreversible deficits.

Figure: Timeline of Events
Disclosures:
Shaaf Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Siddiqua indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jazza Jamil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ghias un Nabi Tayyab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaaf Ahmad, MBBS1, Ayesha Siddiqua, MBBS2, Jazza Jamil, MBBS3, Ghias un Nabi Tayyab, MBBS, MRCP4. P3384 - Beyond the Gut: TNF-Alpha Inhibitor-Induced Demyelinating Neuropathy and Bladder Dysfunction in a Crohn’s Disease Patient With Negative MRI Findings, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
