Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3302 - Real-World Comparison of Infliximab and Adalimumab for Remission Induction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity-Matched Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Omar Arman, MD, MPH
University at Buffalo
Depew, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Omar Arman, MD, MPH1, Khaled Rafeh, MD2, Laith M.. Haj-Ahmad, MD3, Husam Abu Suilik, MD4, Omar Daas, MD5, Noor Arman, MD5, Ravneet Kaur, MD1, Himaben Gohil, MD1, Mazen Zamzam, BS6, Jad Bou-Abdallah, MD1
1University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 2School of Medicine, The University of Jordan, Shmeisani, 'Amman, Jordan; 3University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 4The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 5University of Jordan School of Medicine, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Infliximab and Adalimumab are widely used biologic therapies for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). While both are effective, few studies have directly compared their roles in remission induction using biomarker-based objective measures across IBD subtypes. This study evaluates the comparative efficacy of Infliximab and Adalimumab in achieving biomarker-based remission in IBD patients.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX data from 93 healthcare organizations. A total of 31,700 adult patients (≥18 years) with IBD treated with Infliximab or Adalimumab between 2018 and 2023 were initially identified. Propensity score matching was performed to balance age, sex, race/ethnicity, disease severity, and comorbidities, resulting in 13,176 matched IBD patients per treatment group (total n = 26,352). The primary outcome was biomarker-based remission, defined as serum C-reactive protein (CRP) ≤5 mg/L or fecal calprotectin ≤150 µg/g, and assessed at 6 months, 1 year, 3 years, and 5 years. Induction of remission rates and Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were reported for the overall IBD cohort and separately for CD and UC subgroups.
Results: Infliximab demonstrated consistently higher remission rates than Adalimumab across all time points (p < 0.001). At 6 months, remission was achieved more frequently with Infliximab in IBD (38.8% vs 29.0%), UC (35.3% vs 25.4%), and CD (38.5% vs 28.3%). This pattern was held at 1 year (IBD: 50.4% vs 43.1%; UC: 46.3% vs 37.1%; CD: 49.8% vs 42.6%), 3 years (IBD: 66.6% vs. 62.8%; UC: 61.9% vs 55.0%; CD: 66.1% vs 62.7%), and 5 years (IBD: 71.4% vs 68.9%; UC: 65.9% vs 60.0%; CD: 71.2% vs 68.5%). Hazard ratios (HR) were directionally standardized to reflect Infliximab over Adalimumab (Infliximab/Adalimumab). Therefore, HR > 1 indicates faster remission with Infliximab. Infliximab was associated with a significantly shorter time to remission across all time points in IBD, CD, and UC (all HRs > 1, p < 0.001). Median time to remission was also consistently shorter with Infliximab compared to Adalimumab across all disease groups. This supports the hazard ratio findings and further shows a faster induction of remission with Infliximab. Table 1 shows a detailed breakdown of these statistics.
Discussion: Infliximab achieves more frequent and faster remission rates across IBD subtypes at all time points. This may help guide biologic therapy selection and early treatment decisions in IBD.
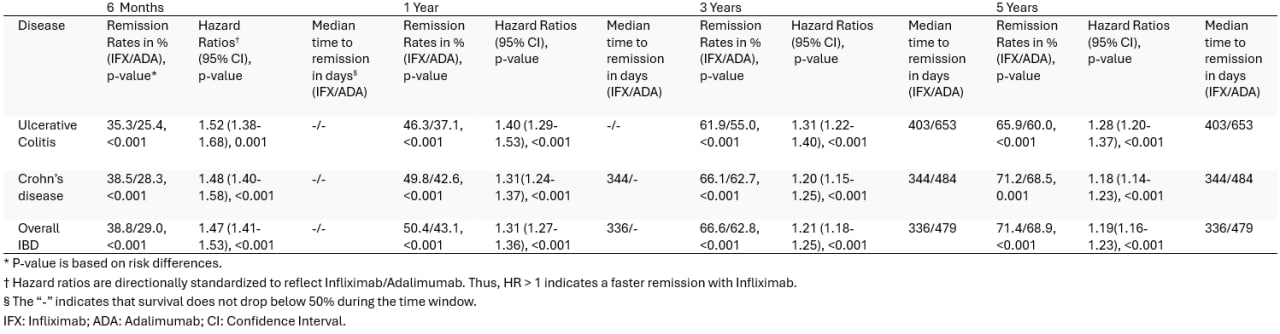
Figure: Table 1. Remission rates, hazard ratios, and median time to remission for Infliximab versus Adalimumab in IBD patients from 6 months to 5 years.
Disclosures:
Omar Arman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Rafeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Haj-Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Daas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Arman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ravneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himaben Gohil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazen Zamzam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jad Bou-Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Arman, MD, MPH1, Khaled Rafeh, MD2, Laith M.. Haj-Ahmad, MD3, Husam Abu Suilik, MD4, Omar Daas, MD5, Noor Arman, MD5, Ravneet Kaur, MD1, Himaben Gohil, MD1, Mazen Zamzam, BS6, Jad Bou-Abdallah, MD1. P3302 - Real-World Comparison of Infliximab and Adalimumab for Remission Induction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 2School of Medicine, The University of Jordan, Shmeisani, 'Amman, Jordan; 3University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 4The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 5University of Jordan School of Medicine, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Infliximab and Adalimumab are widely used biologic therapies for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). While both are effective, few studies have directly compared their roles in remission induction using biomarker-based objective measures across IBD subtypes. This study evaluates the comparative efficacy of Infliximab and Adalimumab in achieving biomarker-based remission in IBD patients.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX data from 93 healthcare organizations. A total of 31,700 adult patients (≥18 years) with IBD treated with Infliximab or Adalimumab between 2018 and 2023 were initially identified. Propensity score matching was performed to balance age, sex, race/ethnicity, disease severity, and comorbidities, resulting in 13,176 matched IBD patients per treatment group (total n = 26,352). The primary outcome was biomarker-based remission, defined as serum C-reactive protein (CRP) ≤5 mg/L or fecal calprotectin ≤150 µg/g, and assessed at 6 months, 1 year, 3 years, and 5 years. Induction of remission rates and Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were reported for the overall IBD cohort and separately for CD and UC subgroups.
Results: Infliximab demonstrated consistently higher remission rates than Adalimumab across all time points (p < 0.001). At 6 months, remission was achieved more frequently with Infliximab in IBD (38.8% vs 29.0%), UC (35.3% vs 25.4%), and CD (38.5% vs 28.3%). This pattern was held at 1 year (IBD: 50.4% vs 43.1%; UC: 46.3% vs 37.1%; CD: 49.8% vs 42.6%), 3 years (IBD: 66.6% vs. 62.8%; UC: 61.9% vs 55.0%; CD: 66.1% vs 62.7%), and 5 years (IBD: 71.4% vs 68.9%; UC: 65.9% vs 60.0%; CD: 71.2% vs 68.5%). Hazard ratios (HR) were directionally standardized to reflect Infliximab over Adalimumab (Infliximab/Adalimumab). Therefore, HR > 1 indicates faster remission with Infliximab. Infliximab was associated with a significantly shorter time to remission across all time points in IBD, CD, and UC (all HRs > 1, p < 0.001). Median time to remission was also consistently shorter with Infliximab compared to Adalimumab across all disease groups. This supports the hazard ratio findings and further shows a faster induction of remission with Infliximab. Table 1 shows a detailed breakdown of these statistics.
Discussion: Infliximab achieves more frequent and faster remission rates across IBD subtypes at all time points. This may help guide biologic therapy selection and early treatment decisions in IBD.

Figure: Table 1. Remission rates, hazard ratios, and median time to remission for Infliximab versus Adalimumab in IBD patients from 6 months to 5 years.
Disclosures:
Omar Arman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Rafeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Haj-Ahmad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Daas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Arman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ravneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himaben Gohil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mazen Zamzam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jad Bou-Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Arman, MD, MPH1, Khaled Rafeh, MD2, Laith M.. Haj-Ahmad, MD3, Husam Abu Suilik, MD4, Omar Daas, MD5, Noor Arman, MD5, Ravneet Kaur, MD1, Himaben Gohil, MD1, Mazen Zamzam, BS6, Jad Bou-Abdallah, MD1. P3302 - Real-World Comparison of Infliximab and Adalimumab for Remission Induction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity-Matched Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
