Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3246 - Induction Efficacy of Subcutaneous Guselkumab vs Advanced Therapies in Moderately-to-Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Myrlene Sanon, MPH
Johnson & Johnson
Metuchen, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Myrlene Sanon, MPH1, Agathe Neviere, MSc2, Dominik Naessens, PharmD, MBA3, Gabriela Friedrich, 4, Camille Chopardlallier, 5, Zijiang Yang, PhD6, Tim Hoops, MD7, Sumesh Kachroo, PhD7, Katerina Papadimitropoulou, PhD8
1Johnson & Johnson, Metuchen, NJ; 2Amaris Heath Economics and Market Access, Nantes, Pays de la Loire, France; 3Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V., Beerse, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, Belgium; 4Amaris, Barcelona, Madrid, Spain; 5Amaris, Paris, Centre, France; 6Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 7Johnson & Johnson, Horsham, PA; 8Amaris, Lyon, Ile-de-France, France
Introduction: Subcutaneous delivery of biologic agents has become increasingly available as an alternative to IV administration across many disease areas, and a patient’s individual preference is an important factor in treatment selection and shared decision making. Until recently, currently available IL-23p19 subunit inhibitors, the latest class of treatment for Crohn’s disease (CD), require IV induction. Guselkumab (GUS), newly approved for adults with CD, is the first and only IL-23 inhibitor that offers a choice and flexibility between a fully subcutaneous (SC) or an intravenous (IV) induction treatment regimen. This network meta-analysis (NMA) evaluates the comparative induction efficacy of GUS 400mg SC and other available comparators, in overall population and subpopulations including those with inadequate response or intolerance to biologic therapy.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials identified through a systematic literature review were included if they evaluated relevant therapies for induction treatment and reported clinical response/clinical remission between 4 to 12 weeks of treatment. Clinical response and remission rates at the end of induction were jointly analyzed as an ordinal endpoint using a Bayesian network meta-analysis fixed-effect model.
Results: Fourteen trials reported outcomes and were eligible for this induction phase analysis. For clinical response, in the overall population, GUS 400mg SC was more effective than all other comparators followed by guselkumab 200mg IV (Table). For clinical remission, GUS 400mg SC was superior over vedolizumab 300mg IV (OR: 3.71; 95% CrI: 1.70–6.34), mirikizumab 900mg IV (OR: 2.41; 95% CrI: 1.52–4.05), and risankizumab 600mg IV (OR: 1.70; 95%CrI: 1.04–2.91).
GUS 400mg SC and GUS200mg IV consistently ranked first and second per surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) over comparators in both clinical response and clinical remission (Figure).
Findings in the overall population were generally corroborated by subpopulation analyses.
Discussion: In this NMA, GUS 400mg SC demonstrated superior efficacy versus all other advanced therapies, followed by GUS 200mg IV. The findings underscore guselkumab’s robust efficacy profile for induction in both SC and IV treatment regimens relative to other treatment alternatives allowing flexibility with the choice of route of administration for patients and providers while ensuring meaningful induction outcomes.
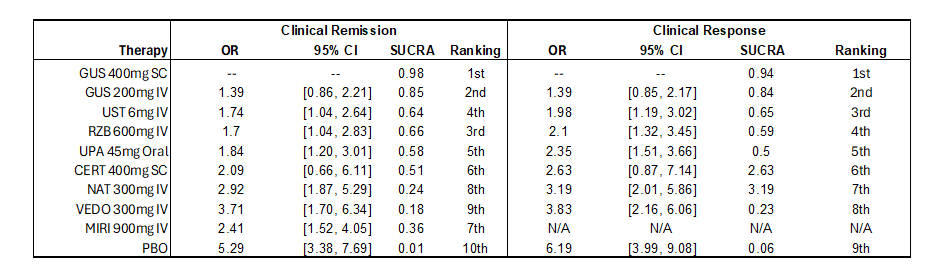
Figure: Table. Odds ratio, 95% credible intervals, and ranking of comparators versus guselkumab 400mg SC
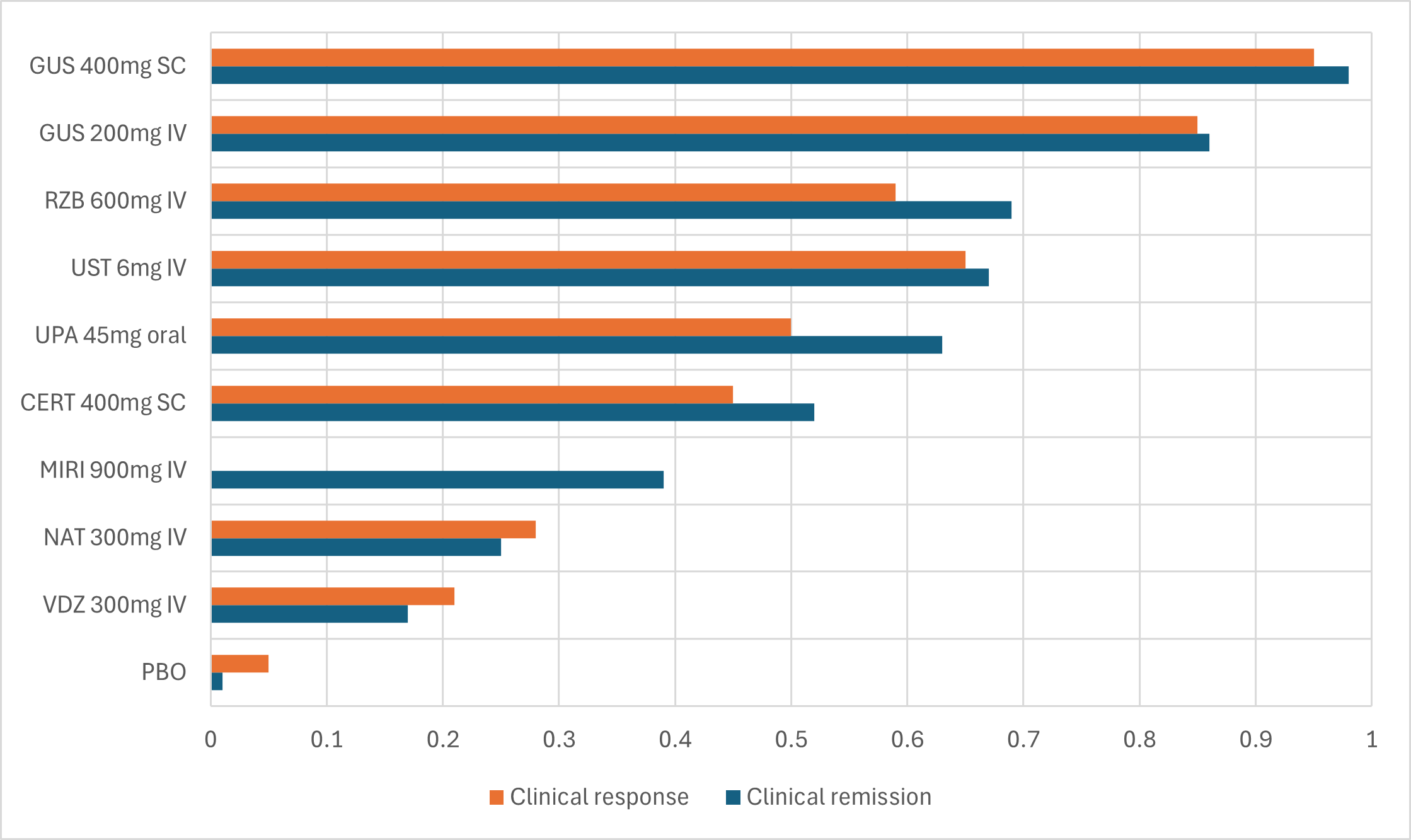
Figure: Figure. Bar plot of SUCRA values for Clinical Remission NMA across all treatments. SUCRA values range from 0 to 1 and represent the percentage of efficacy that a treatment achieves relative to an ideal treatment.
Disclosures:
Myrlene Sanon: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Agathe Neviere indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dominik Naessens: Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V., – Employee.
Gabriela Friedrich: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Camille Chopardlallier: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Zijiang Yang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Tim Hoops: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Sumesh Kachroo: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options.
Katerina Papadimitropoulou: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Myrlene Sanon, MPH1, Agathe Neviere, MSc2, Dominik Naessens, PharmD, MBA3, Gabriela Friedrich, 4, Camille Chopardlallier, 5, Zijiang Yang, PhD6, Tim Hoops, MD7, Sumesh Kachroo, PhD7, Katerina Papadimitropoulou, PhD8. P3246 - Induction Efficacy of Subcutaneous Guselkumab vs Advanced Therapies in Moderately-to-Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Johnson & Johnson, Metuchen, NJ; 2Amaris Heath Economics and Market Access, Nantes, Pays de la Loire, France; 3Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V., Beerse, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, Belgium; 4Amaris, Barcelona, Madrid, Spain; 5Amaris, Paris, Centre, France; 6Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 7Johnson & Johnson, Horsham, PA; 8Amaris, Lyon, Ile-de-France, France
Introduction: Subcutaneous delivery of biologic agents has become increasingly available as an alternative to IV administration across many disease areas, and a patient’s individual preference is an important factor in treatment selection and shared decision making. Until recently, currently available IL-23p19 subunit inhibitors, the latest class of treatment for Crohn’s disease (CD), require IV induction. Guselkumab (GUS), newly approved for adults with CD, is the first and only IL-23 inhibitor that offers a choice and flexibility between a fully subcutaneous (SC) or an intravenous (IV) induction treatment regimen. This network meta-analysis (NMA) evaluates the comparative induction efficacy of GUS 400mg SC and other available comparators, in overall population and subpopulations including those with inadequate response or intolerance to biologic therapy.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials identified through a systematic literature review were included if they evaluated relevant therapies for induction treatment and reported clinical response/clinical remission between 4 to 12 weeks of treatment. Clinical response and remission rates at the end of induction were jointly analyzed as an ordinal endpoint using a Bayesian network meta-analysis fixed-effect model.
Results: Fourteen trials reported outcomes and were eligible for this induction phase analysis. For clinical response, in the overall population, GUS 400mg SC was more effective than all other comparators followed by guselkumab 200mg IV (Table). For clinical remission, GUS 400mg SC was superior over vedolizumab 300mg IV (OR: 3.71; 95% CrI: 1.70–6.34), mirikizumab 900mg IV (OR: 2.41; 95% CrI: 1.52–4.05), and risankizumab 600mg IV (OR: 1.70; 95%CrI: 1.04–2.91).
GUS 400mg SC and GUS200mg IV consistently ranked first and second per surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) over comparators in both clinical response and clinical remission (Figure).
Findings in the overall population were generally corroborated by subpopulation analyses.
Discussion: In this NMA, GUS 400mg SC demonstrated superior efficacy versus all other advanced therapies, followed by GUS 200mg IV. The findings underscore guselkumab’s robust efficacy profile for induction in both SC and IV treatment regimens relative to other treatment alternatives allowing flexibility with the choice of route of administration for patients and providers while ensuring meaningful induction outcomes.

Figure: Table. Odds ratio, 95% credible intervals, and ranking of comparators versus guselkumab 400mg SC

Figure: Figure. Bar plot of SUCRA values for Clinical Remission NMA across all treatments. SUCRA values range from 0 to 1 and represent the percentage of efficacy that a treatment achieves relative to an ideal treatment.
Disclosures:
Myrlene Sanon: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Agathe Neviere indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dominik Naessens: Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V., – Employee.
Gabriela Friedrich: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Camille Chopardlallier: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Zijiang Yang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Tim Hoops: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Sumesh Kachroo: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options.
Katerina Papadimitropoulou: Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Myrlene Sanon, MPH1, Agathe Neviere, MSc2, Dominik Naessens, PharmD, MBA3, Gabriela Friedrich, 4, Camille Chopardlallier, 5, Zijiang Yang, PhD6, Tim Hoops, MD7, Sumesh Kachroo, PhD7, Katerina Papadimitropoulou, PhD8. P3246 - Induction Efficacy of Subcutaneous Guselkumab vs Advanced Therapies in Moderately-to-Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
