Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3197 - Efficacy of Biologics and Small Molecules for Maintenance of Response and Remission in Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Shahryar Khan, MD
University of Kansas Medical Center
Kansas City, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Shahryar Khan, MD1, Asad Ur Rahman, MD2, Noor Ehsan, MD3, Ryan Nazari, BS4, Manav Nayeni, BMSc4, Azzah Muhammad Hayat, MD5, Ahmad Khan, 5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Sayed Tauseef Ahmad Jan, MD7, Shadi Hamdeh, MD, FACG1
1University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS; 2Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, FL; 3Gulab Devi Teaching Hospital, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Kansas City University, Kansas City, MO; 5Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 7University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics, Iowa City, IA
Introduction: Fistulizing Crohn’s disease (FCD) is a debilitating complication associated with high rates of recurrence and long-term morbidity. While the induction of fistula closure is essential, sustained maintenance of remission and response remains a key therapeutic challenge. Despite the availability of biologics and small molecules, the comparative efficacy of these agents in sustaining fistula healing over extended follow-up periods remains poorly defined. This network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed to evaluate and rank the efficacy of advanced therapies for maintaining clinical remission and response in patients with FCD.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and frequentist random-effects NMA of RCTs evaluating biologics and small molecules for maintenance therapy in FCD over a 12-month period. Fistula remission was defined as complete closure of all external draining fistulas, and response as a ≥50% reduction in the number of draining fistulas from baseline without new fistula formation. A frequentist random-effects NMA was performed using the netmeta package in R to estimate the odds ratios and P-scores for treatment ranking.
Results: Ten RCTs were included to evaluate the efficacy of nine advanced therapies for maintaining fistula remission and response with a mean follow-up duration of 13.5 months. Perianal FCD was the predominant phenotype observed in the study population. Adalimumab (OR 3.34; 95% CI 1.24-9.01), Infliximab 5 mg/kg (OR 2.80; 95% CI 1.50-5.21), and Ustekinumab (OR 6.50; 95% CI 1.09-38.8) significantly increased the odds of maintaining complete fistula remission compared to placebo (Fig 1, Fig 2). Only five studies reported maintenance of fistula response; infliximab 5 mg/kg showed significant improvement with fistula response (OR 1.88; 95% CI 1.15-3.07); however, Upadacitinib 15 mg (OR 9.86; 95% CI 0.47-206) and upadacitinib 30 mg (OR 7.67; 95% CI 0.35-166) demonstrated favorable trends, although the differences did not reach statistical significance (Fig 3, Fig 4). Vedolizumab did not demonstrate superiority over placebo in the maintenance of either fistula remission or response.
Discussion: This NMA supports the use of anti-TNF agents and Ustekinumab for maintaining fistula remission. These findings support the continued use of select biologics for long-term fistula management, though data on newer IL-23 inhibitors remain limited, highlighting the need for further studies to define their role in maintenance therapy.
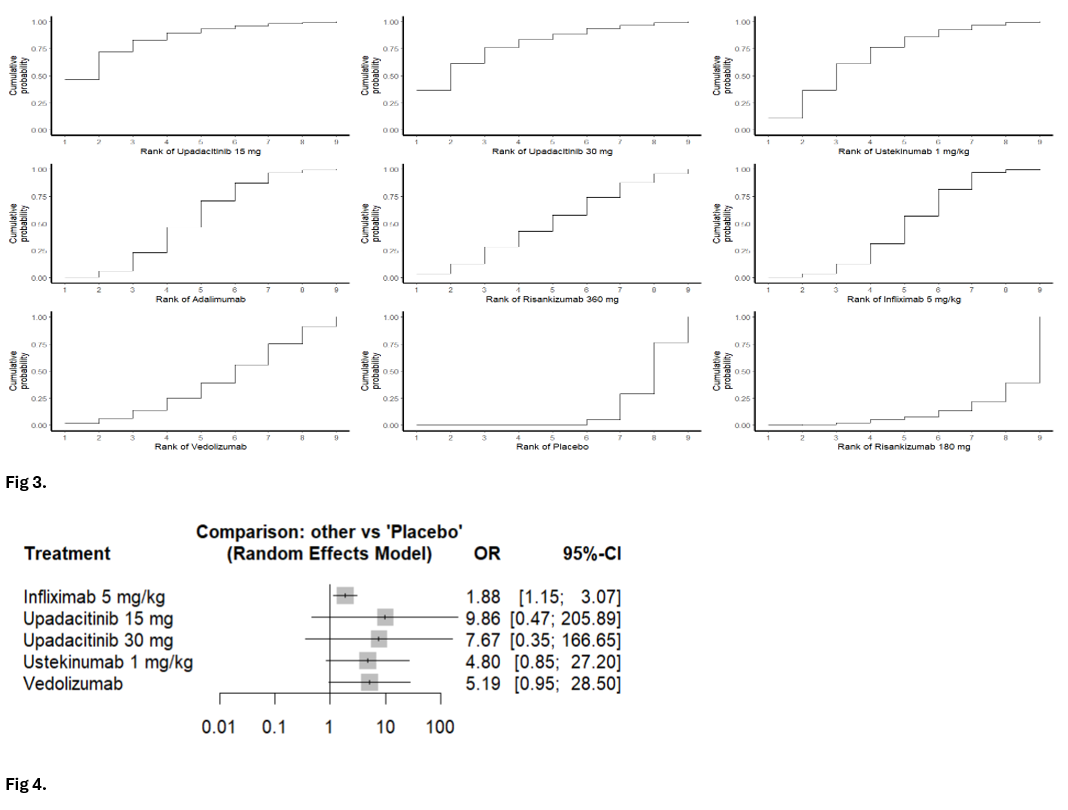
Figure: Fig 1. Forest plots of treatment comparisons for maintenance of fistula remission in fistulizing Crohn’s disease; Fig 2. Network geometry of included treatments for the maintenance of remission and response in fistulizing Crohn’s disease.
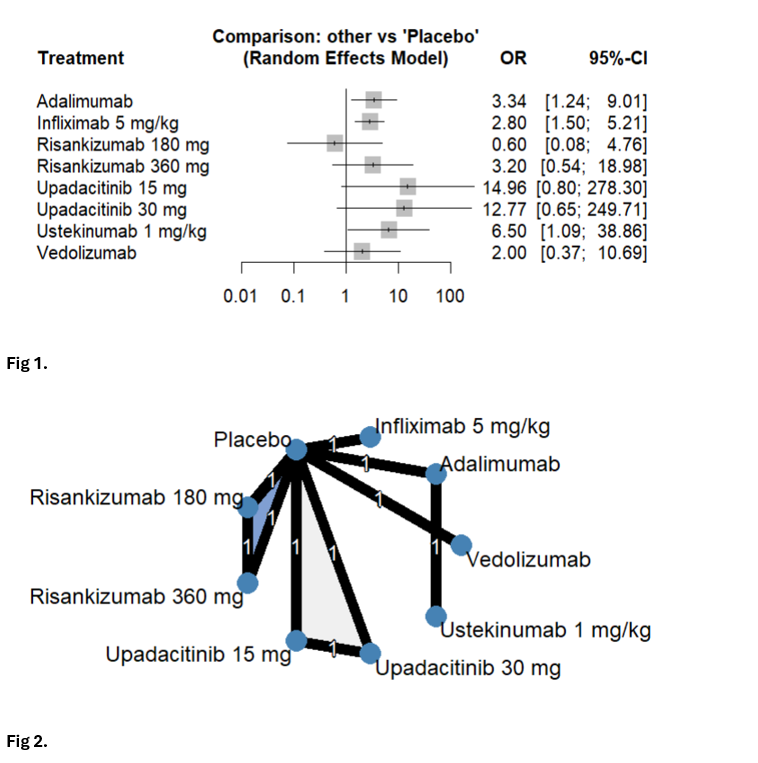
Figure: Fig 3. Treatment ranking based on P-scores for the maintenance of remission in fistulizing Crohn’s disease; Fig 4. Forest plots of treatment comparisons for maintenance of fistula response in fistulizing Crohn’s disease.
Disclosures:
Shahryar Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asad Ur Rahman: Abbvie Inc – Speakers Bureau.
Noor Ehsan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Nazari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manav Nayeni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azzah Muhammad Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sayed Tauseef Ahmad Jan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shadi Hamdeh: Abbvie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Shahryar Khan, MD1, Asad Ur Rahman, MD2, Noor Ehsan, MD3, Ryan Nazari, BS4, Manav Nayeni, BMSc4, Azzah Muhammad Hayat, MD5, Ahmad Khan, 5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Sayed Tauseef Ahmad Jan, MD7, Shadi Hamdeh, MD, FACG1. P3197 - Efficacy of Biologics and Small Molecules for Maintenance of Response and Remission in Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS; 2Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, FL; 3Gulab Devi Teaching Hospital, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Kansas City University, Kansas City, MO; 5Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 7University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics, Iowa City, IA
Introduction: Fistulizing Crohn’s disease (FCD) is a debilitating complication associated with high rates of recurrence and long-term morbidity. While the induction of fistula closure is essential, sustained maintenance of remission and response remains a key therapeutic challenge. Despite the availability of biologics and small molecules, the comparative efficacy of these agents in sustaining fistula healing over extended follow-up periods remains poorly defined. This network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed to evaluate and rank the efficacy of advanced therapies for maintaining clinical remission and response in patients with FCD.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and frequentist random-effects NMA of RCTs evaluating biologics and small molecules for maintenance therapy in FCD over a 12-month period. Fistula remission was defined as complete closure of all external draining fistulas, and response as a ≥50% reduction in the number of draining fistulas from baseline without new fistula formation. A frequentist random-effects NMA was performed using the netmeta package in R to estimate the odds ratios and P-scores for treatment ranking.
Results: Ten RCTs were included to evaluate the efficacy of nine advanced therapies for maintaining fistula remission and response with a mean follow-up duration of 13.5 months. Perianal FCD was the predominant phenotype observed in the study population. Adalimumab (OR 3.34; 95% CI 1.24-9.01), Infliximab 5 mg/kg (OR 2.80; 95% CI 1.50-5.21), and Ustekinumab (OR 6.50; 95% CI 1.09-38.8) significantly increased the odds of maintaining complete fistula remission compared to placebo (Fig 1, Fig 2). Only five studies reported maintenance of fistula response; infliximab 5 mg/kg showed significant improvement with fistula response (OR 1.88; 95% CI 1.15-3.07); however, Upadacitinib 15 mg (OR 9.86; 95% CI 0.47-206) and upadacitinib 30 mg (OR 7.67; 95% CI 0.35-166) demonstrated favorable trends, although the differences did not reach statistical significance (Fig 3, Fig 4). Vedolizumab did not demonstrate superiority over placebo in the maintenance of either fistula remission or response.
Discussion: This NMA supports the use of anti-TNF agents and Ustekinumab for maintaining fistula remission. These findings support the continued use of select biologics for long-term fistula management, though data on newer IL-23 inhibitors remain limited, highlighting the need for further studies to define their role in maintenance therapy.

Figure: Fig 1. Forest plots of treatment comparisons for maintenance of fistula remission in fistulizing Crohn’s disease; Fig 2. Network geometry of included treatments for the maintenance of remission and response in fistulizing Crohn’s disease.

Figure: Fig 3. Treatment ranking based on P-scores for the maintenance of remission in fistulizing Crohn’s disease; Fig 4. Forest plots of treatment comparisons for maintenance of fistula response in fistulizing Crohn’s disease.
Disclosures:
Shahryar Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asad Ur Rahman: Abbvie Inc – Speakers Bureau.
Noor Ehsan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Nazari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manav Nayeni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azzah Muhammad Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sayed Tauseef Ahmad Jan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shadi Hamdeh: Abbvie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Shahryar Khan, MD1, Asad Ur Rahman, MD2, Noor Ehsan, MD3, Ryan Nazari, BS4, Manav Nayeni, BMSc4, Azzah Muhammad Hayat, MD5, Ahmad Khan, 5, Fariha Hasan, MD6, Sayed Tauseef Ahmad Jan, MD7, Shadi Hamdeh, MD, FACG1. P3197 - Efficacy of Biologics and Small Molecules for Maintenance of Response and Remission in Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
