Monday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P2994 - Performance of Novel AI Software for Colorectal Adenoma Detection in At-Risk Patient Population
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Nicholas Cumpian, MD (he/him/his)
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center
Torrance, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Nicholas Cumpian, MD, Fransia De Leon, MD, Fouzia Oza, MD, Idrees Suliman, MD, Michael Fleischman, MD, Viktor Eysselein, MD, FACG, Sofiya Reicher, MD, FACG
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA
Introduction: Though the field is rapidly developing, there is still a paucity of data on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in computer-aided detection of colorectal polyps among various patient populations. We aimed to evaluate the effect of the latest generation of AI software on colonoscopy quality metrics within a diverse, at-risk patient population.
Methods: AI software (GI Genius, Medtronic) was implemented at our institution in November 2022; the latest generation AI software (ColonPro, Medtronic) was integrated in February 2025. In our safety net healthcare system, colonoscopies are performed for positive stool-based screening tests or symptoms. Three time intervals were evaluated: pre-AI (8/1/22-10/31/22), AI GI Genius (3/1/23-4/30/23), and AI ColonPro (2/15/25-5/27/25). Data on patient demographics, procedure indication, bowel preparation, polyp size, location, and histology were collected. Polyp detection rates (PDR), adenoma detection rates (ADR), advanced ADR (AADR), and non-neoplastic PDR (NNPDR) were calculated. All colonoscopies were performed by or under the supervision of expert endoscopists ( >3,000 colonoscopies) with routine “second look” examination or retroflexion in right colon.
Results: We evaluated 1018 polyps/829 colonoscopies (278 pre-AI, 285 AI GI Genius, and 266 AI ColonPro). The mean age was 56.6; 63% were Hispanic/Latino. FIT positivity was the most common indication 237/829 (28.6%). Bowel preparation was excellent/good/fair in 780/829 (94.1%) and poor in 49/829 (5.9%). The most common polyp size was < 5 mm (643/1018, 63.1%), followed by 5-10mm (217/1018, 21.3%), > 10mm (129/1018, 12.7%), and unspecified size (29/1018, 2.8%). The PDRs of pre-AI, AI GI Genius, and AI ColonPro groups were 166/278 (59.7%), 161/285 (56.5%, p=0.44), and 119/266 (44.7%, p=0.16), respectively. The ADR of pre-AI cohort was 106/278 (38.1%), 114/285 (40.0%, p=0.65) in AI GI Genius, and 71/266 (26.7%, p=0.16) in AI ColonPro. AADR for pre-AI was 45/278 (16.2%), 43/285 (15.1%, p=0.72) for AI GI Genius, and 43/266 (16.2%, p=0.16) for AI ColonPro, with NNPDRs of 83/278 (30%), 77/285 (27%, p=0.46), and 72/266 (27%, p=0.16), respectively [Table].
Discussion: In our experience, the latest generation AI software did not significantly impact colonoscopy quality metrics. Our findings highlight a complex relationship between AI technology, endoscopist experience, and patient factors suggesting the effectiveness of AI may be limited in high-quality diagnostic colonoscopy.
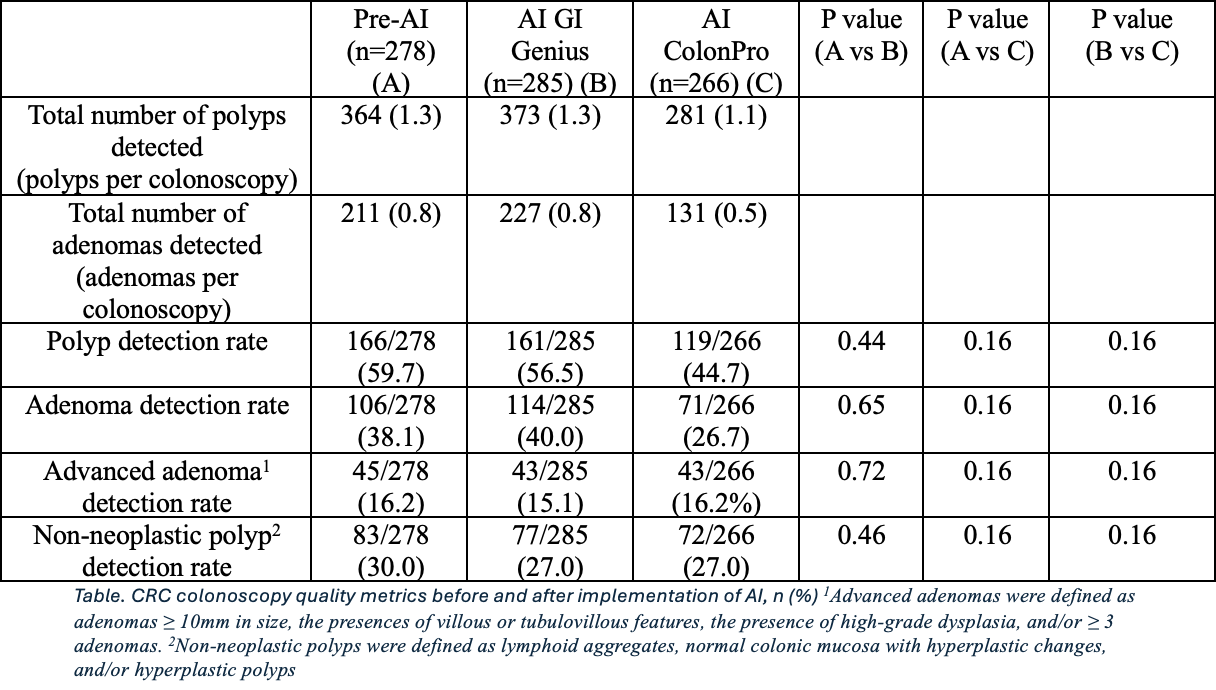
Figure: Table. CRC colonoscopy quality metrics before and after implementation of AI, n (%) 1Advanced adenomas were defined as adenomas ≥ 10mm in size, the presences of villous or tubulovillous features, the presence of high-grade dysplasia, and/or ≥ 3 adenomas. 2Non-neoplastic polyps were defined as lymphoid aggregates, normal colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes, and/or hyperplastic polyps
Disclosures:
Nicholas Cumpian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fransia De Leon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fouzia Oza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Idrees Suliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Fleischman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Viktor Eysselein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sofiya Reicher: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Nicholas Cumpian, MD, Fransia De Leon, MD, Fouzia Oza, MD, Idrees Suliman, MD, Michael Fleischman, MD, Viktor Eysselein, MD, FACG, Sofiya Reicher, MD, FACG. P2994 - Performance of Novel AI Software for Colorectal Adenoma Detection in At-Risk Patient Population, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA
Introduction: Though the field is rapidly developing, there is still a paucity of data on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in computer-aided detection of colorectal polyps among various patient populations. We aimed to evaluate the effect of the latest generation of AI software on colonoscopy quality metrics within a diverse, at-risk patient population.
Methods: AI software (GI Genius, Medtronic) was implemented at our institution in November 2022; the latest generation AI software (ColonPro, Medtronic) was integrated in February 2025. In our safety net healthcare system, colonoscopies are performed for positive stool-based screening tests or symptoms. Three time intervals were evaluated: pre-AI (8/1/22-10/31/22), AI GI Genius (3/1/23-4/30/23), and AI ColonPro (2/15/25-5/27/25). Data on patient demographics, procedure indication, bowel preparation, polyp size, location, and histology were collected. Polyp detection rates (PDR), adenoma detection rates (ADR), advanced ADR (AADR), and non-neoplastic PDR (NNPDR) were calculated. All colonoscopies were performed by or under the supervision of expert endoscopists ( >3,000 colonoscopies) with routine “second look” examination or retroflexion in right colon.
Results: We evaluated 1018 polyps/829 colonoscopies (278 pre-AI, 285 AI GI Genius, and 266 AI ColonPro). The mean age was 56.6; 63% were Hispanic/Latino. FIT positivity was the most common indication 237/829 (28.6%). Bowel preparation was excellent/good/fair in 780/829 (94.1%) and poor in 49/829 (5.9%). The most common polyp size was < 5 mm (643/1018, 63.1%), followed by 5-10mm (217/1018, 21.3%), > 10mm (129/1018, 12.7%), and unspecified size (29/1018, 2.8%). The PDRs of pre-AI, AI GI Genius, and AI ColonPro groups were 166/278 (59.7%), 161/285 (56.5%, p=0.44), and 119/266 (44.7%, p=0.16), respectively. The ADR of pre-AI cohort was 106/278 (38.1%), 114/285 (40.0%, p=0.65) in AI GI Genius, and 71/266 (26.7%, p=0.16) in AI ColonPro. AADR for pre-AI was 45/278 (16.2%), 43/285 (15.1%, p=0.72) for AI GI Genius, and 43/266 (16.2%, p=0.16) for AI ColonPro, with NNPDRs of 83/278 (30%), 77/285 (27%, p=0.46), and 72/266 (27%, p=0.16), respectively [Table].
Discussion: In our experience, the latest generation AI software did not significantly impact colonoscopy quality metrics. Our findings highlight a complex relationship between AI technology, endoscopist experience, and patient factors suggesting the effectiveness of AI may be limited in high-quality diagnostic colonoscopy.

Figure: Table. CRC colonoscopy quality metrics before and after implementation of AI, n (%) 1Advanced adenomas were defined as adenomas ≥ 10mm in size, the presences of villous or tubulovillous features, the presence of high-grade dysplasia, and/or ≥ 3 adenomas. 2Non-neoplastic polyps were defined as lymphoid aggregates, normal colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes, and/or hyperplastic polyps
Disclosures:
Nicholas Cumpian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fransia De Leon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fouzia Oza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Idrees Suliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Fleischman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Viktor Eysselein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sofiya Reicher: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Nicholas Cumpian, MD, Fransia De Leon, MD, Fouzia Oza, MD, Idrees Suliman, MD, Michael Fleischman, MD, Viktor Eysselein, MD, FACG, Sofiya Reicher, MD, FACG. P2994 - Performance of Novel AI Software for Colorectal Adenoma Detection in At-Risk Patient Population, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

