Monday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P2953 - Towards an Optimal Body Position and Device for Performing Balloon Expulsion Test
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Karlo P. Fidel, MD (he/him/his)
Augusta University Medical Center
Augusta, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Karlo Fidel, MD1, Neelima Reddy, MD2, Danielle Long, BS1, Delaram Asadi, MD1, Yun Yan, PA-C1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG1
1Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 2Ekam Operations, Baton Rouge, LA
Introduction:
Background: Assessment of defecation using a surrogate stool is an essential test for evaluation of anorectal disorders. However, body position and type of balloon device has been suggested to affect the results of balloon expulsion test (BET), but has not been systematically assessed.
Aim: To prospectively assess and compare results of BET in 2 different body positions, and by using 2 different balloon devices.
Methods:
Methods: In a randomized order, healthy subjects performed the BET by using 2 different devices (50cc water-filled balloon and 30cc Foley balloon), and in 2 different positions, either sitting on a commode or by squatting using a specially designed motorized toilet that raises the feet from a sitting to squatting position. For each device and position, subjects were asked to report if the device/position simulated their sensation of having a bowel movement and describe the straining effort and discomfort.
Results:
Results: Twenty healthy volunteers (11 females, 9 males; mean age= 44 ± 15 years) participated in the study. The mean BET of the 50cc water-filled balloon in both the sitting (29.8 secs, 95% CI [8.2–51.4]) and squatting positions (25.2 secs, 95% CI [0-55.1]) were significantly shorter (p=< .001, p=< .001) than the Foley balloon respectively (Figure 1). Five subjects (25%) could not expel the Foley balloon in both the sitting and squatting positions, but the squatting position had a significantly shorter expulsion time than sitting position (p=.037). The BET of 50cc balloon was similar between the sitting and squatting positions (p=.504). Subjects reported significantly more straining and discomfort with Foley catheter compared to the 50cc party balloon (p< .001). However, both devices induced a similar sensation to defecate.
Discussion:
Conclusion: The 50cc water-filled balloon should be used as the standard device for balloon expulsion test. Our data reaffirms the published normative values of less than 1 minute. On average, healthy subjects took 2 minutes to expel foley balloon and 25% failed and it caused more discomfort, suggesting that it is an inappropriate device for BET. Squatting position using a motorized toilet may be preferable to a standard commode as it promotes a more natural evacuation.
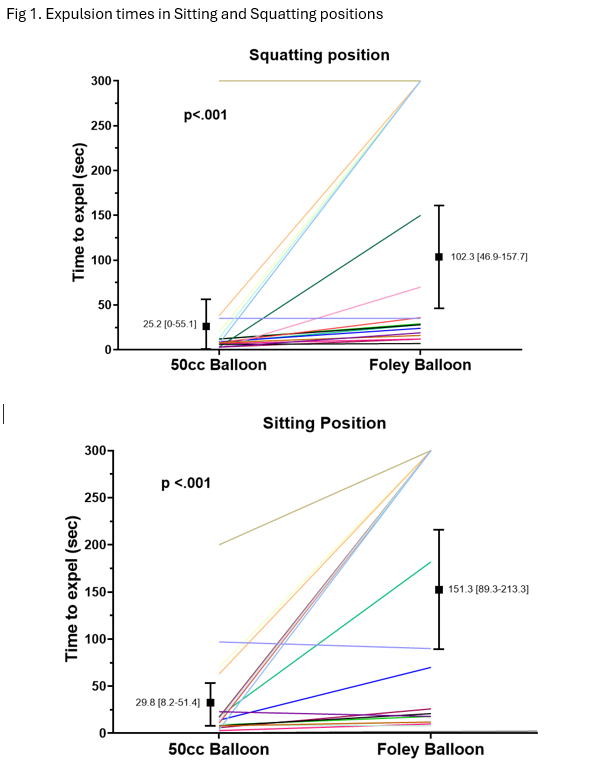
Figure: Figure 1. Expulsion Times in Sitting and Squatting Positions
Disclosures:
Karlo Fidel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neelima Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danielle Long indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Delaram Asadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yun Yan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Satish Rao: Laborie Medical Technologies – Grant/Research Support. Vibrant Ltd – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Karlo Fidel, MD1, Neelima Reddy, MD2, Danielle Long, BS1, Delaram Asadi, MD1, Yun Yan, PA-C1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG1. P2953 - Towards an Optimal Body Position and Device for Performing Balloon Expulsion Test, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 2Ekam Operations, Baton Rouge, LA
Introduction:
Background: Assessment of defecation using a surrogate stool is an essential test for evaluation of anorectal disorders. However, body position and type of balloon device has been suggested to affect the results of balloon expulsion test (BET), but has not been systematically assessed.
Aim: To prospectively assess and compare results of BET in 2 different body positions, and by using 2 different balloon devices.
Methods:
Methods: In a randomized order, healthy subjects performed the BET by using 2 different devices (50cc water-filled balloon and 30cc Foley balloon), and in 2 different positions, either sitting on a commode or by squatting using a specially designed motorized toilet that raises the feet from a sitting to squatting position. For each device and position, subjects were asked to report if the device/position simulated their sensation of having a bowel movement and describe the straining effort and discomfort.
Results:
Results: Twenty healthy volunteers (11 females, 9 males; mean age= 44 ± 15 years) participated in the study. The mean BET of the 50cc water-filled balloon in both the sitting (29.8 secs, 95% CI [8.2–51.4]) and squatting positions (25.2 secs, 95% CI [0-55.1]) were significantly shorter (p=< .001, p=< .001) than the Foley balloon respectively (Figure 1). Five subjects (25%) could not expel the Foley balloon in both the sitting and squatting positions, but the squatting position had a significantly shorter expulsion time than sitting position (p=.037). The BET of 50cc balloon was similar between the sitting and squatting positions (p=.504). Subjects reported significantly more straining and discomfort with Foley catheter compared to the 50cc party balloon (p< .001). However, both devices induced a similar sensation to defecate.
Discussion:
Conclusion: The 50cc water-filled balloon should be used as the standard device for balloon expulsion test. Our data reaffirms the published normative values of less than 1 minute. On average, healthy subjects took 2 minutes to expel foley balloon and 25% failed and it caused more discomfort, suggesting that it is an inappropriate device for BET. Squatting position using a motorized toilet may be preferable to a standard commode as it promotes a more natural evacuation.

Figure: Figure 1. Expulsion Times in Sitting and Squatting Positions
Disclosures:
Karlo Fidel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neelima Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danielle Long indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Delaram Asadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yun Yan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Satish Rao: Laborie Medical Technologies – Grant/Research Support. Vibrant Ltd – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Karlo Fidel, MD1, Neelima Reddy, MD2, Danielle Long, BS1, Delaram Asadi, MD1, Yun Yan, PA-C1, Satish SC. Rao, MD, PhD, FACG1. P2953 - Towards an Optimal Body Position and Device for Performing Balloon Expulsion Test, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

